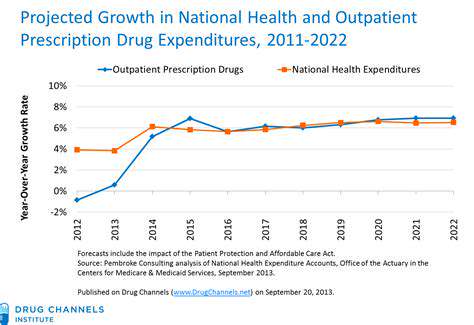
Human clinical trials represent one of the most expensive phases in drug development. These carefully controlled studies involve multiple stages of testing with human volunteers to assess safety and efficacy. The process requires meticulous planning, ethical oversight, and rigorous data collection, all of which drive up costs. Patient recruitment, medical supervision, and regulatory compliance add layers of complexity and expense. Large-scale trials involving thousands of participants across multiple locations can cost hundreds of millions of dollars.
Regulatory Approvals: Navigating Complex Requirements
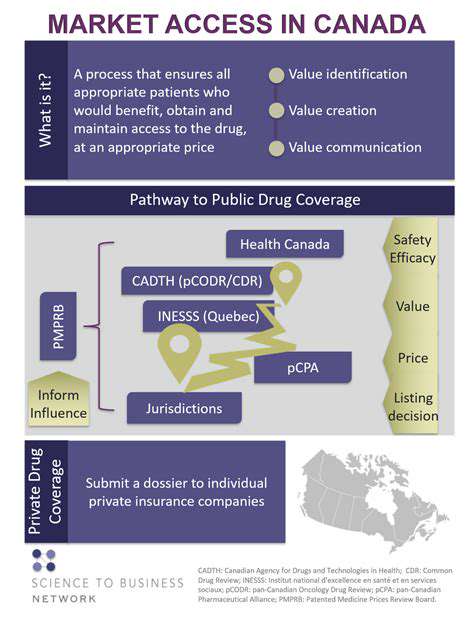
Obtaining approval from regulatory agencies like the FDA involves an exhaustive review process. Pharmaceutical companies must prepare extensive documentation demonstrating a drug's safety and effectiveness. This process often requires teams of regulatory specialists and legal experts, adding to the financial burden. The potential for delays or requests for additional data can significantly increase costs and extend development timelines.
Manufacturing and Distribution: Scaling Up Production
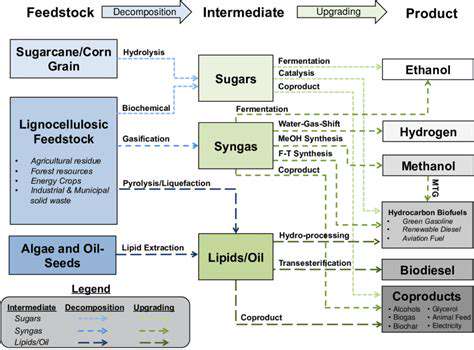
After approval, companies face the challenge of commercial-scale manufacturing. Building specialized production facilities and implementing quality control systems require substantial capital investments. The costs of raw materials, equipment validation, and personnel training contribute significantly to the total expenditure. Establishing reliable distribution networks, especially for global markets, adds another layer of complexity and expense.
Marketing and Sales: Connecting with Healthcare Providers
Successful market introduction requires significant investment in promotional activities and medical education. Pharmaceutical companies must demonstrate the value of new treatments to healthcare professionals and payers. Negotiating reimbursement with insurance providers and government health programs adds another dimension to the financial challenges. These activities are essential for ensuring patient access but represent a major cost component.
The Role of Intellectual Property and Licensing
Intellectual Property Rights in Drug Development
Intellectual property protection serves as the foundation for pharmaceutical innovation. Patents provide temporary exclusivity that allows companies to recover their substantial research investments. Different forms of IP protection apply to various aspects of drug development, from chemical compounds to manufacturing processes. Effective IP management is crucial for maintaining competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Licensing Agreements and Strategic Partnerships
Collaborative arrangements through licensing enable companies to share risks and resources. These agreements can provide critical funding for smaller biotech firms while giving larger companies access to innovative technologies. Well-structured licensing deals can accelerate development timelines and improve market penetration, benefiting all parties involved. The negotiation process requires careful consideration of market potential and development risks.
Financial Considerations in Licensing
Licensing arrangements create important revenue streams through upfront payments and royalties. These financial models help distribute the substantial costs of drug development across multiple organizations. For licensees, such agreements provide access to valuable technology without bearing the full burden of development costs. The financial terms must reflect the stage of development and market potential of the therapeutic product.
Emerging Licensing Models
The pharmaceutical industry has developed various licensing approaches to meet different strategic needs. Co-development agreements allow for shared risk and reward between partners. Regional licensing can optimize market penetration in specific geographic areas. These flexible models help companies tailor their approaches to specific products and market conditions.
The Future of Drug Development Finance
Artificial Intelligence in Drug Discovery
Advanced computational methods are transforming how new medicines are discovered. Machine learning algorithms can analyze complex biological data to identify promising drug candidates more efficiently. These technologies have the potential to reduce both the time and cost of bringing new treatments to market, particularly for diseases with significant unmet medical needs.
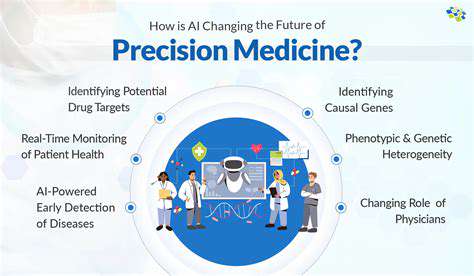
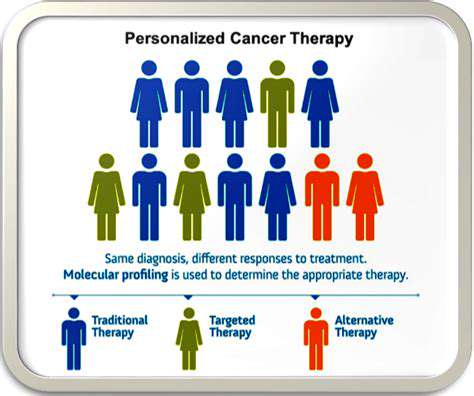
Personalized Medicine Approaches
The shift toward targeted therapies based on individual patient characteristics represents a major advancement. Understanding genetic factors that influence drug response enables more precise treatment strategies. This approach can improve clinical outcomes while reducing adverse effects, creating value for both patients and healthcare systems.
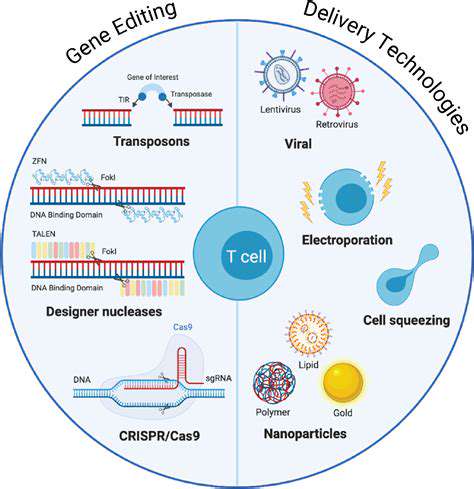
Innovative Drug Delivery Technologies
New methods for delivering medications directly to affected tissues show great promise. These technologies aim to enhance therapeutic effectiveness while minimizing side effects. Advances in nanotechnology and controlled-release formulations could revolutionize treatment paradigms across multiple therapeutic areas.
Biomarker Development
The identification of reliable biological indicators is improving diagnostic and treatment approaches. These tools enable earlier disease detection and more accurate monitoring of treatment response. Such advancements contribute to more efficient clinical development programs and better patient care.
Regenerative Medicine Advances
Cutting-edge cellular therapies offer potential solutions for previously untreatable conditions. These approaches harness the body's natural healing mechanisms to repair damaged tissues. The field holds particular promise for chronic degenerative diseases and traumatic injuries.
Data-Driven Development
The integration of large-scale data analysis is enhancing every stage of drug development. Sophisticated modeling techniques allow researchers to predict drug behavior and optimize clinical trial designs. This approach leads to more informed decision-making throughout the development process.