Genetic Engineering in Animal Breeding: A Revolution in Agriculture
Genetic engineering has become a transformative force in the field of animal breeding. By manipulating an animal's genetic material, scientists can enhance desirable traits, paving the way for more efficient and sustainable agricultural practices. This technology offers immense potential for improving animal health, productivity, and resilience to environmental challenges.
The ability to precisely target specific genes has unlocked exciting opportunities for animal breeders. This precision enables the development of animals with improved traits, such as increased milk production, leaner meat, or enhanced disease resistance, without the unintended consequences often seen in traditional breeding methods.
Improving Animal Health through Genetic Engineering
One of the most significant applications of genetic engineering in animal breeding is the enhancement of animal health. By modifying genes associated with disease susceptibility, researchers can create animals that are more resistant to common illnesses. This reduces the reliance on antibiotics and other medications, promoting healthier animals and a safer food supply.
Reducing antibiotic use in livestock is a critical goal in modern agriculture. Genetic engineering provides a promising pathway to achieve this, potentially contributing to a healthier ecosystem and combating the rise of antibiotic resistance.
Enhancing Productivity and Efficiency
Genetic engineering also holds the potential to significantly improve the productivity and efficiency of animal agriculture. By altering genes related to growth rate, feed conversion, or milk production, scientists can develop animals that produce more meat, milk, or eggs with less feed, ultimately reducing the environmental footprint of animal agriculture.
Increased livestock productivity translates to greater economic benefits for farmers and a more efficient food production system. This efficiency is essential for meeting the growing global demand for animal products while minimizing resource consumption.
Addressing Environmental Challenges
Animal agriculture has a substantial environmental impact. Genetic engineering could play a role in mitigating some of these effects. For example, modifying genes that regulate an animal's metabolism could help reduce greenhouse gas emissions from livestock. This area of research holds promise for a more sustainable future.
Ethical Considerations and Public Perception
Despite its potential benefits, genetic engineering in animal breeding raises important ethical questions. Public perception and acceptance of these technologies are crucial for their successful implementation. Open dialogue and transparent communication are essential for addressing concerns and building trust in the scientific process.
Public understanding and engagement are vital for navigating the ethical complexities of genetic engineering in animal breeding. Addressing public concerns and fostering transparency are critical steps toward gaining support for these transformative technologies.
Regulatory Frameworks and Safety Protocols
Effective regulatory frameworks and stringent safety protocols are necessary to ensure the responsible development and application of genetic engineering in animal breeding. These measures must address potential risks to animal health, the environment, and human health, ensuring that these technologies are implemented safely and ethically.
The Future of Animal Breeding
The future of animal breeding is closely tied to genetic engineering. This technology offers a powerful tool to address global challenges in food security, animal health, and environmental sustainability. Continued research and development, coupled with robust regulatory frameworks, will be essential for unlocking the full potential of this technology.
The future of animal agriculture is likely to be shaped by genetic engineering. By embracing innovation and responsible implementation, we can build a more sustainable and productive agricultural system.
A plant-powered pantry requires a thorough understanding of your nutritional needs. This includes considering your age, activity level, and any specific dietary restrictions or health conditions. A balanced plant-based diet should provide adequate protein, healthy fats, complex carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals. Understanding these needs will guide your shopping choices and ensure you’re meeting your body’s requirements.

Future Trends and Challenges: Shaping the Future of Animal Health
Gene Editing for Disease Resistance
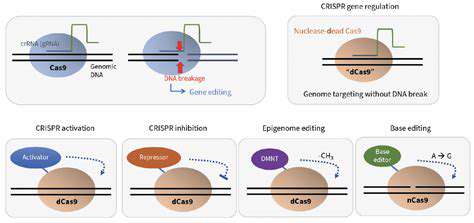
Gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR-Cas9, have immense potential for revolutionizing animal health. By precisely modifying genes responsible for disease susceptibility, we can create livestock breeds inherently resistant to common ailments. This approach promises a significant reduction in antibiotic use and other pharmaceutical interventions, leading to healthier animals and a safer food supply. The potential for personalized medicine in livestock, tailoring interventions to specific genetic predispositions, is also a promising application of this technology.
Ethical considerations surrounding gene editing, such as potential unintended consequences and long-term effects on animal welfare, need careful consideration. Regulatory frameworks must be developed to ensure responsible and equitable deployment of these powerful tools.
Precision Livestock Farming
The integration of technology, including sensors, data analytics, and artificial intelligence, is transforming livestock farming. Precision livestock farming allows for real-time monitoring of animal health parameters, such as body temperature, heart rate, and feed intake. This data-driven approach enables early disease detection and targeted interventions, optimizing animal well-being and resource utilization. Remote monitoring systems can also reduce labor costs and enhance farm efficiency.
Data security and privacy concerns are paramount in the implementation of these systems. Robust data management protocols and ethical guidelines are crucial to ensure the responsible use of sensitive animal health information.
Nanotechnology in Veterinary Medicine
Nanotechnology offers exciting possibilities for targeted drug delivery and improved diagnostics in veterinary medicine. Nanocarriers can deliver drugs directly to affected tissues, minimizing side effects and maximizing treatment efficacy. Moreover, nanoscale sensors can detect disease biomarkers at early stages, enabling rapid and accurate diagnosis. This technology can significantly enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of veterinary treatments.
The cost-effectiveness and scalability of nanotechnology-based solutions need further investigation to ensure wide accessibility for both large-scale farming operations and smaller, independent practitioners. Addressing potential environmental impacts of nanomaterials is also a critical consideration.
Sustainable Animal Feed and Nutrition
Developing sustainable and nutritious feed sources is crucial to enhancing animal health and promoting environmentally responsible farming practices. Alternative feed ingredients, such as algae and insect protein, can reduce reliance on traditional feed sources and minimize environmental impact. Precision nutrition strategies, tailored to specific animal needs, can further optimize feed utilization and reduce waste.
Ensuring the nutritional adequacy and safety of alternative feed sources is paramount. Rigorous research and testing are required to validate their effectiveness and potential impact on animal health and welfare.
Antimicrobial Resistance: A Growing Threat
The increasing prevalence of antimicrobial resistance poses a significant challenge to animal health. The overuse of antibiotics in animal agriculture contributes to the emergence of resistant strains, which can also affect human health. Strategies to reduce antibiotic reliance, such as vaccination programs, improved hygiene practices, and the development of alternative therapies, are essential to mitigate this threat. Collaboration between veterinary professionals, researchers, and policymakers is crucial for developing effective solutions.
Zoonotic Diseases: Preventing Cross-Species Transmission
The emergence of zoonotic diseases, those that can be transmitted between animals and humans, necessitates a proactive approach to prevent cross-species transmission. Enhanced surveillance systems, improved biosecurity measures in animal facilities, and public health education campaigns are crucial for mitigating the risk of zoonotic disease outbreaks. International cooperation and information sharing are vital for preventing global pandemics.