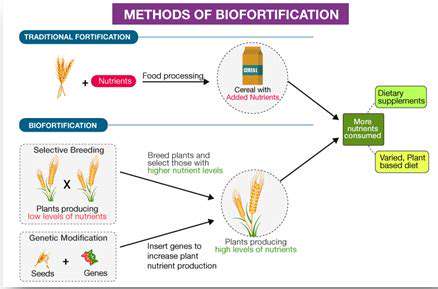
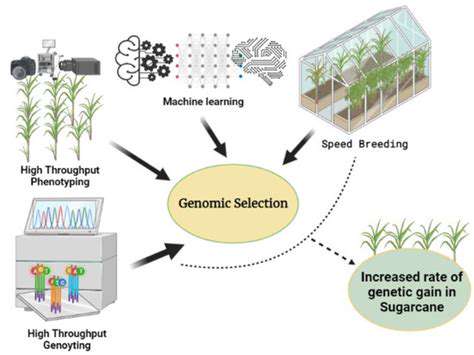
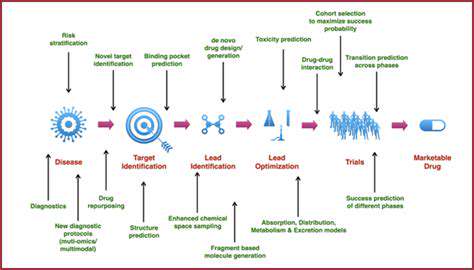
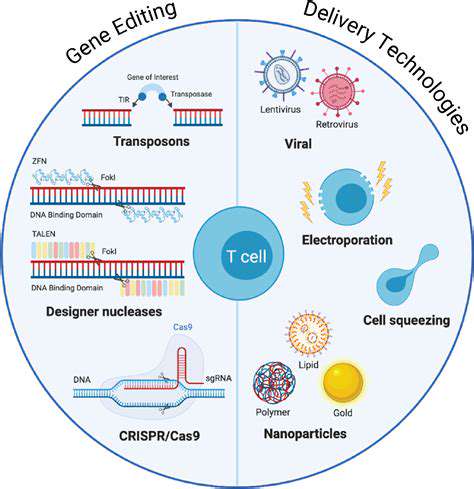
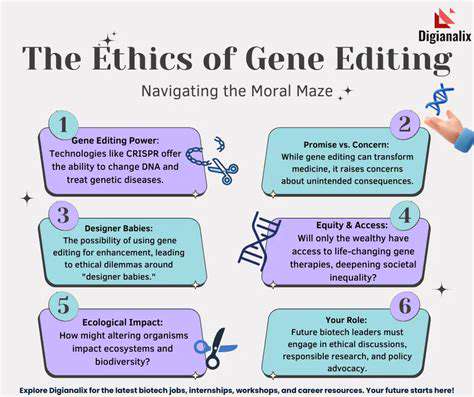
Ethical Considerations in Gene Editing
Informed Consent and Patient Autonomy
Ensuring informed consent is paramount in gene editing procedures. Patients undergoing gene editing treatments must fully understand the potential benefits, risks, and alternatives. This includes a comprehensive explanation of the technology, its efficacy, possible side effects, and the long-term implications. Informed consent should be a truly voluntary process, free from coercion or undue influence. Patients must have the autonomy to make decisions about their own bodies and health, and this includes the right to refuse treatment.
Furthermore, the potential for unintended consequences and long-term effects must be carefully considered and communicated to the patient. Transparent communication and ongoing dialogue between the patient and the medical team are critical components of ethical gene editing practices.
Equity and Access to Gene Editing Technologies
Gene editing technologies have the potential to revolutionize medicine, but equitable access to these advancements is crucial. The high cost of gene editing treatments could lead to significant disparities in healthcare, with only the wealthy having access to these life-changing interventions. Robust policies and regulations are needed to ensure that these technologies are accessible to all individuals, regardless of socioeconomic status or geographic location.
Potential for Germline Editing and its Societal Impact
Germline editing, which alters genes in reproductive cells, raises significant ethical concerns. This type of editing could potentially have unforeseen consequences on future generations, and the long-term impacts on human evolution are difficult to predict. The potential for unintended genetic changes and their impact on future generations demands careful consideration and stringent oversight.
Public discussion and engagement are crucial to navigate the complex ethical and social implications of germline editing. The potential for altering the human gene pool necessitates a thorough exploration of the societal implications. International collaborations and consensus-building processes are essential to ensure responsible and ethical development and implementation.
Potential for Enhancement and its Impact on Human Values
Gene editing technologies could be used to enhance human traits beyond treating diseases. This raises concerns about the potential for creating a genetically stratified society and exacerbating existing societal inequalities. Careful consideration must be given to the potential impact on human values and the inherent worth of all individuals. The use of gene editing for enhancement purposes must be approached with extreme caution and ethical prudence.
Ensuring Safety and Preventing Off-Target Effects
The safety and efficacy of gene editing technologies are critical concerns. Gene editing tools have the potential to introduce unintended genetic modifications, known as off-target effects, which could have harmful consequences. Rigorous testing and validation procedures are essential to minimize these risks and ensure the safety of patients. Thorough pre-clinical and clinical trials are necessary to assess the long-term safety and efficacy of gene editing treatments.
Public Engagement and Societal Dialogue
Open and honest public engagement is essential to address the ethical considerations surrounding gene editing. This requires transparent communication about the risks and benefits of these technologies. Public dialogue and participation are vital in shaping policies and regulations that ensure responsible development and use. The public's concerns and perspectives must be taken into account to foster societal acceptance and trust in gene editing technologies.
Regulatory Frameworks and Oversight
Robust regulatory frameworks are needed to ensure the responsible development and application of gene editing technologies. Clear guidelines and regulations are necessary to govern the research, clinical trials, and commercialization of gene editing therapies. International collaboration and harmonization of regulations are crucial to address the global implications of gene editing. Independent oversight bodies are needed to monitor the ethical and safety aspects of gene editing procedures.
The Future of Gene Edited Therapies: A Glimpse Beyond
Precision Editing: Revolutionizing Treatment Strategies
Gene editing technologies, particularly CRISPR-Cas9, are poised to transform the landscape of medical treatments. Their ability to precisely target and modify specific DNA sequences opens doors to therapies previously unimaginable. This precision allows for the correction of disease-causing mutations, potentially eliminating the root cause of conditions rather than simply managing their symptoms. The potential extends far beyond single-gene disorders, as researchers explore ways to tackle complex diseases like cancer and autoimmune disorders.
Beyond Single-Gene Disorders: Addressing Complex Diseases
While initial applications of gene editing focused on single-gene disorders, the field is rapidly expanding to encompass more complex conditions. Researchers are investigating strategies to target multiple genes involved in the development and progression of diseases like cancer. This includes modifying immune cells to enhance their anti-tumor activity and developing therapies for neurological disorders where genetic factors play a significant role. The future holds the promise of a more comprehensive approach to treatment, going beyond the limitations of traditional methods.
Ethical Considerations and Public Dialogue
The rapid advancement of gene editing technologies necessitates a robust ethical framework. Discussions around safety, accessibility, and potential unintended consequences are crucial. Open public dialogue, involving scientists, ethicists, policymakers, and the public, is vital to ensure responsible development and implementation of these powerful tools. Careful consideration of potential societal impacts and equitable access to these treatments is paramount.
Delivery Systems and Challenges in Implementation
Delivering gene editing tools effectively to target cells and tissues is a significant challenge. Scientists are exploring various delivery methods, such as viral vectors and non-viral nanoparticles, to improve the efficiency and safety of gene therapies. Optimization of delivery mechanisms is crucial to maximize the therapeutic potential of gene editing and ensure its successful translation to clinical practice. The development of safe and efficient delivery methods remains a critical area of research.
Safety and Long-Term Effects: Ensuring Efficacy and Patient Well-being
The safety and long-term effects of gene editing therapies are paramount. Thorough pre-clinical testing and rigorous clinical trials are essential to evaluate the potential risks and benefits. Monitoring patients for long-term side effects and potential off-target effects is crucial to ensure the safety and efficacy of these interventions. Longitudinal studies and comprehensive safety assessments are vital components of responsible gene editing research.
Regulatory Frameworks and Clinical Trials: Navigating the Path to Approval
Establishing robust regulatory frameworks for gene editing therapies is critical. Clear guidelines and protocols are needed to ensure the safety and efficacy of these treatments before they are approved for widespread use. Careful design and execution of clinical trials are essential to gather the necessary data to support regulatory approval. This process demands a collaborative effort between researchers, regulatory bodies, and healthcare professionals.
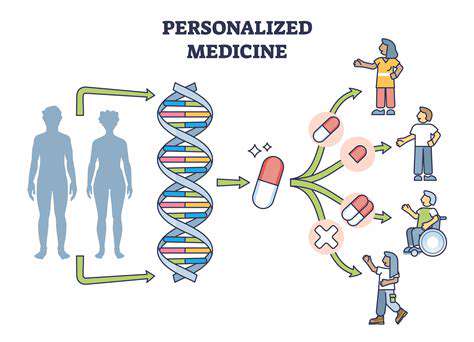
Personalized Medicine: Tailoring Therapies for Individual Needs
The future of gene editing holds the promise of personalized medicine. By analyzing an individual's genetic makeup, gene editing therapies can be tailored to address specific genetic predispositions and vulnerabilities. This approach allows for more effective treatments and minimizes potential side effects. The ability to personalize gene therapies will significantly enhance the efficacy and safety of these powerful interventions, paving the way for a more precise and individualized approach to healthcare.