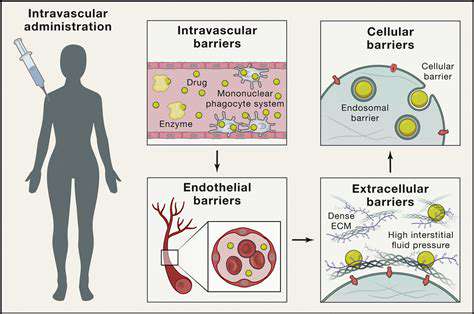
Optimizing core functionalities remains essential for achieving superior performance and responsiveness. This requires comprehensive evaluation and refinement of the underlying algorithms and operational processes. Through systematic identification and resolution of performance constraints, we can ensure optimal data processing efficiency.
Reproductive Technologies: Expanding Breeding Potential
Advancements in Artificial Insemination Techniques
The practice of artificial insemination (AI) has transformed animal husbandry by facilitating the controlled transfer of genetic material from superior males to females, substantially improving offspring quality. Modern innovations in sperm preservation and revival techniques have boosted fertility outcomes and sperm survival rates. These developments enable global access to premium genetics without the logistical complexities of live animal transport.
Contemporary AI protocols now integrate genetic screening to identify optimal sperm donors, guaranteeing the transmission of favorable characteristics. This approach also reduces disease transmission risks compared to traditional mating methods, establishing it as a safer alternative for breeding initiatives. Consequently, artificial insemination continues to drive rapid genetic enhancement across livestock species, supporting sustainable farming and global food production.
Role of Embryo Transfer in Enhancing Breeding Programs
Embryo transfer (ET) technology multiplies valuable genetic resources by implanting fertilized embryos from genetically superior donors into recipient females. This process exponentially increases the reproductive output of elite animals, yielding multiple offspring from a single exceptional female. Breakthroughs in cryopreservation have further enhanced ET flexibility, enabling long-term genetic storage and international genetic exchange.
ET also facilitates genetic diversity and disease prevention through pre-transfer embryo screening. The integration of in vitro fertilization (IVF) and advanced embryo culture methods has significantly improved procedure success rates. As a result, embryo transfer serves as a fundamental technology for accelerating genetic progress in animal populations.
Genetic Editing and Its Impact on Reproductive Technologies
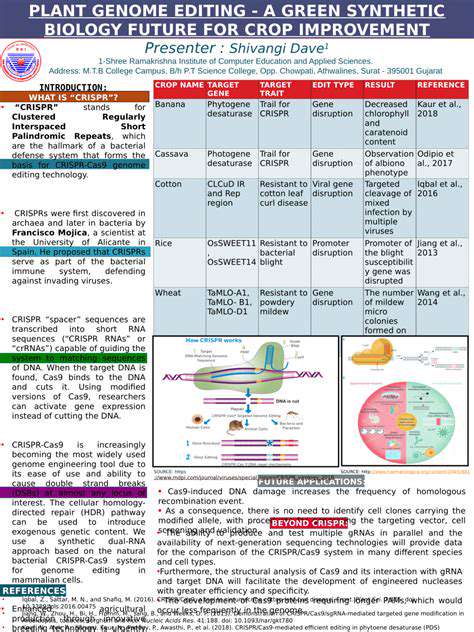
Innovations like CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing have revolutionized animal biotechnology by enabling precise genomic modifications. This breakthrough allows direct incorporation of beneficial traits such as enhanced disease resistance or productivity into breeding stock. When combined with reproductive technologies, genetic editing can rapidly disseminate advantageous characteristics throughout herds, compressing traditional breeding timelines.
While ethical considerations and regulatory standards continue to evolve, the potential for creating healthier, more efficient livestock through genetic modification remains enormous. Ongoing research promises to broaden the applications of reproductive technologies powered by genetic engineering, further expanding breeding possibilities worldwide.
Synchronization and Superovulation in Breeding Programs
Hormonal synchronization and superovulation protocols represent critical tools for maximizing reproductive output. Through targeted hormonal treatments, breeders can coordinate estrous cycles across multiple females, enabling precisely timed insemination or embryo collection. Superovulation stimulates increased follicle production, yielding greater numbers of viable embryos for transfer or preservation.
These techniques optimize reproductive efficiency, particularly in high-value breeding animals, while reducing generational intervals. Improvements in hormonal formulations and administration methods have enhanced procedure success rates, making these technologies more practical for commercial operations. Collectively, these methods significantly expand the reproductive capacity of livestock populations.
Cloning and Its Role in Preserving Elite Genetics
Cloning technology provides an unprecedented method for replicating animals with exceptional genetic merit, ensuring the preservation and propagation of valuable traits. Using somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT), researchers can create genetic duplicates of superior animals for breeding or genetic conservation purposes. This technology has proven successful across multiple species, including cattle and swine.
Beyond commercial applications, cloning offers solutions for preserving endangered breeds and preventing genetic diversity loss. While cost and ethical concerns persist, ongoing technological refinements aim to improve efficiency and accessibility. As such, cloning is increasingly viewed as a complementary approach to conventional breeding, pushing the boundaries of reproductive possibilities in animal science.