Sustainable Dyeing and Finishing Processes

Sustainable Dyeing Practices
Sustainable dyeing methods are crucial for minimizing the environmental impact of textile production. These methods focus on reducing the use of harmful chemicals, conserving water resources, and minimizing waste generation throughout the entire dyeing process. Implementing sustainable dyeing practices is essential for a more environmentally conscious textile industry.
One key aspect is the exploration of natural dyes derived from plants, fruits, or insects. These natural sources offer a wide array of colors and often have lower environmental footprints compared to synthetic dyes. Sustainable dyeing processes also prioritize the reduction of water usage by employing more efficient techniques and utilizing closed-loop systems.
Chemical Reduction in Dyeing
Minimizing the use of harmful chemicals in the dyeing process is paramount for both worker safety and environmental protection. These chemicals often have detrimental effects on aquatic ecosystems and contribute to water pollution. Many conventional dyeing techniques rely heavily on synthetic dyes and harsh chemicals for colorfastness and brightness.
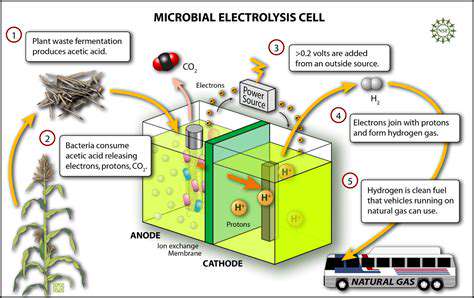
Exploring alternative chemical formulations and processes is critical. This includes the development of bio-based dyes and the use of environmentally friendly auxiliaries in the dyeing process. These advancements have the potential to significantly reduce the environmental footprint of the textile industry.
Water Conservation in Dyeing Processes
Water conservation is a critical aspect of sustainable dyeing and finishing. Textile dyeing often consumes significant amounts of water, leading to water pollution and strain on water resources. Implementing water-saving technologies and optimizing dyeing procedures can dramatically reduce the environmental impact.
Techniques such as pre-treatment and dyeing in smaller batches, combined with the implementation of closed-loop systems, can significantly reduce water consumption. These methods reduce water waste and promote the responsible use of water resources. This also helps reduce the overall cost of the process.
Waste Minimization and Management
Waste generated during dyeing and finishing processes can pose a significant environmental challenge. Effective waste management strategies are essential for reducing pollution and promoting a circular economy in the textile industry. The focus should be on minimizing waste generation through process optimization and the use of recycled materials.
Advanced treatment methods for wastewater and the recycling of byproducts can minimize the environmental impact of textile dyeing and finishing operations. These measures are critical for responsible resource management and reducing the impact of textile production on the environment.
Eco-Friendly Finishing Techniques
Sustainable finishing techniques are essential for enhancing the quality and longevity of textiles while minimizing environmental impact. These techniques often include the use of eco-friendly softeners, anti-wrinkle agents, and other finishing agents that are derived from natural sources. These eco-friendly alternatives to conventional finishing agents are vital for a sustainable textile industry.
The Role of Certifications and Standards
Implementing certifications and standards for sustainable dyeing and finishing practices is critical for ensuring accountability and transparency. These certifications provide consumers and stakeholders with assurance that products meet specific environmental and social criteria. Standards and certifications play a crucial role in driving innovation and promoting responsible production practices. The adoption of these standards also encourages a shift towards a more sustainable textile industry, fostering trust and accountability.