Harnessing Natural Structures for Enhanced Properties
Bio-inspired nanotechnology leverages the intricate and often remarkable structures found in nature to create novel materials and devices with enhanced properties. Mimicking the hierarchical organization of bone, for example, allows us to develop stronger and more lightweight biomaterials for use in prosthetics and implants. The inherent strength and resilience of spider silk, derived from its nanoscale fiber architecture, inspires the creation of high-performance fabrics and protective gear. This approach offers a powerful strategy for developing materials that surpass current synthetic counterparts in terms of both performance and sustainability.
Nature's designs often incorporate features that optimize functionality and efficiency. From the light-gathering properties of butterfly wings to the self-healing capabilities of certain plants, nature has evolved ingenious solutions to complex problems over millions of years. By studying and replicating these designs at the nanoscale, we can develop innovative solutions in various fields, including medicine, electronics, and energy production, ultimately leading to a more sustainable and efficient future.
Creating Novel Nanomaterials with Superior Performance
Bio-inspired nanotechnology facilitates the creation of novel nanomaterials with exceptional properties that traditional methods cannot achieve. By replicating the molecular structure of natural materials, scientists can design materials with unique functionalities, such as enhanced catalytic activity, improved biocompatibility, or superior strength and flexibility. This approach allows for tailoring nanomaterials to specific applications, leading to more efficient and effective technologies.
For instance, the intricate hierarchical structures of some marine organisms, such as diatoms, inspire the design of new materials with enhanced optical properties. These materials can be used in applications ranging from solar cells to optical sensors, offering potential improvements in efficiency and sensitivity compared to existing technologies. This biomimetic approach is revolutionizing the way we design and fabricate nanomaterials.
Addressing Challenges in Nanotechnology through Biomimicry
Bio-inspired nanotechnology offers a powerful approach to address some of the significant challenges in conventional nanotechnology, such as toxicity and scalability. Nature's designs often incorporate mechanisms for self-assembly, biocompatibility, and efficient resource utilization. By mimicking these natural processes, researchers can create nanomaterials that are both safe and sustainable, reducing the environmental impact of nanotechnology applications. This approach also aims to overcome the scalability issues inherent in some nanotechnological processes, enabling the production of nanomaterials on a larger scale for broader applications.
Expanding Applications Across Diverse Fields
The principles of bio-inspired nanotechnology extend to a wide range of applications, from medicine and electronics to energy production and environmental remediation. In medicine, biomimetic nanomaterials can be used to deliver drugs more effectively, targeting specific cells and tissues, leading to improved treatment outcomes and reduced side effects. In electronics, bio-inspired designs can enhance the performance and efficiency of electronic devices, potentially leading to more energy-efficient and robust technologies. Moreover, bio-inspired nanomaterials can be employed in renewable energy solutions, such as more efficient solar cells and improved battery technologies, paving the way for a greener future.
Revolutionizing Healthcare through the Fusion of Biotech and Nanotech

Improving Patient Outcomes
Revolutionizing healthcare means focusing on improving patient outcomes, moving beyond simply treating symptoms to proactively addressing underlying health issues. This proactive approach leads to better health management, reduced hospital readmissions, and a greater sense of well-being for patients. By understanding the root causes of health problems, we can develop personalized strategies for disease prevention and management, ultimately leading to healthier and more fulfilling lives for individuals.
A key aspect of improving patient outcomes is enhancing the patient experience. This includes providing readily accessible and understandable information, fostering open communication between patients and healthcare providers, and ensuring that patients feel empowered and actively involved in their care.
Enhancing Access and Affordability
Healthcare should be a right, not a privilege. Making healthcare more accessible and affordable is a critical component of revolutionizing the system. This includes expanding access to quality care in underserved communities, reducing financial barriers to treatment, and promoting preventative measures that can help lower overall healthcare costs.
Innovative solutions, such as telehealth platforms and affordable prescription drug programs, are essential to bridging the gap and ensuring that all individuals have access to the care they need, regardless of their socioeconomic status.
Streamlining Healthcare Delivery
Modernizing healthcare delivery systems is crucial for efficiency and effectiveness. This involves implementing integrated electronic health records, streamlining administrative processes, and fostering collaboration among different healthcare providers. Such improvements can reduce wait times, minimize errors, and ensure that patients receive seamless care across various settings.
By optimizing workflows and communication channels, we can create a more efficient and patient-centered healthcare system.
Advancing Technological Innovations
Technological advancements are transforming healthcare in profound ways. From AI-powered diagnostics to robotic surgery, technology is enabling more precise diagnoses, less invasive procedures, and better overall patient care.
The integration of artificial intelligence in medical imaging and diagnostics holds enormous potential for early disease detection and improved treatment outcomes. Further, telemedicine platforms are expanding access to specialists and care providers, especially in rural and underserved areas.
Promoting Preventive Care
Shifting the focus from reactive to proactive care is vital for long-term health. Preventive care strategies, such as regular checkups, vaccinations, and healthy lifestyle choices, can significantly reduce the risk of chronic diseases and improve overall well-being.
Promoting healthy habits and educating individuals about disease prevention through accessible resources can empower them to take control of their health and contribute to a healthier population.
Empowering Patients
Empowering patients to actively participate in their healthcare journey is paramount. This involves providing patients with comprehensive information about their conditions, treatment options, and potential risks.
Giving patients the knowledge and tools to make informed decisions about their health empowers them to take ownership of their well-being and work collaboratively with healthcare providers to achieve optimal outcomes. Providing patients with access to their health records and encouraging open communication between patients and providers are crucial steps in this process.
Environmental Applications: Cleaning Up the Planet with Biotech and Nanotech
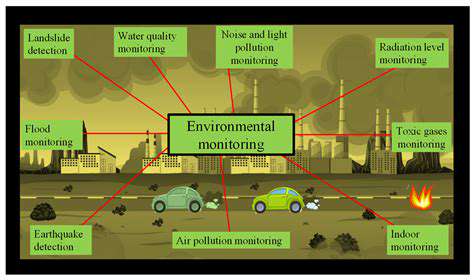
Environmental Remediation
Environmental remediation is a crucial aspect of environmental applications, focusing on the cleanup and restoration of contaminated sites. This process involves identifying the source of contamination, assessing its extent, and implementing appropriate methods to remove or neutralize the pollutants. This often requires a multi-faceted approach that considers the specific nature of the contaminant, the surrounding environment, and potential human health risks. These efforts are critical in protecting ecosystems and human well-being.
Wastewater Treatment
Wastewater treatment plays a vital role in environmental protection by removing pollutants and contaminants from wastewater before it's discharged back into the environment. Effective wastewater treatment significantly reduces the negative impact of human activities on water bodies. The techniques used vary depending on the type and concentration of pollutants present, but the overarching goal is always to ensure that the treated water meets the required standards for safe discharge.
This process often involves several stages, from physical separation to biological degradation and chemical treatment. Each stage is carefully designed to target specific pollutants, leading to a cleaner and safer final product.
Air Quality Improvement
Improving air quality is essential for public health and environmental sustainability. Strategies for air quality improvement include the development and implementation of stricter emission standards for industries and vehicles, promoting the use of cleaner energy sources, and encouraging sustainable transportation options. These measures are crucial in reducing harmful pollutants in the air, thus mitigating their impact on human health and the environment. These initiatives also contribute to a healthier planet.
Sustainable Agriculture Practices
Sustainable agricultural practices are vital for minimizing the environmental impact of food production. These practices focus on minimizing the use of harmful pesticides and fertilizers, promoting soil health, and optimizing water usage. Adopting such practices can lead to improved soil quality, reduced water pollution, and enhanced biodiversity. Ultimately, sustainable agriculture helps ensure the long-term viability of food production while safeguarding the environment.
Pollution Monitoring and Control
Monitoring and controlling pollution levels are fundamental to environmental protection. Regular monitoring allows for the identification of pollution sources and the assessment of their impact. This data is crucial for developing targeted interventions and implementing effective control measures. The information gathered also informs the creation of effective policies and regulations, which are essential for mitigating the negative consequences of pollution.
Conservation and Restoration
Conservation and restoration efforts are vital for preserving biodiversity and maintaining the health of ecosystems. These efforts aim to protect endangered species and habitats, and to restore degraded ecosystems to a healthier state. These efforts often involve the careful management of natural resources, the implementation of protected areas, and the promotion of sustainable practices.
Green Building Design
Green building design is a critical strategy to reduce the environmental impact of buildings. By incorporating sustainable materials, energy-efficient technologies, and water conservation measures, green buildings contribute to a healthier environment. This approach results in lower energy consumption, reduced waste generation, and a more sustainable built environment. It is a critical aspect of creating environmentally responsible structures.