Beyond CRISPR: Exploring Alternative Gene Editing Approaches
Beyond the Gene Editing Revolution: Exploring Alternative Approaches
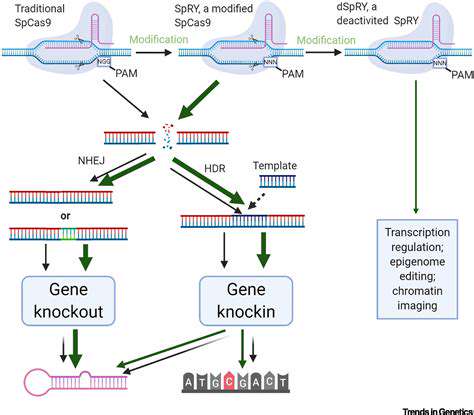
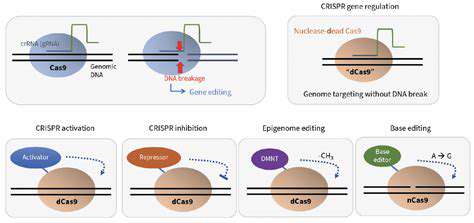
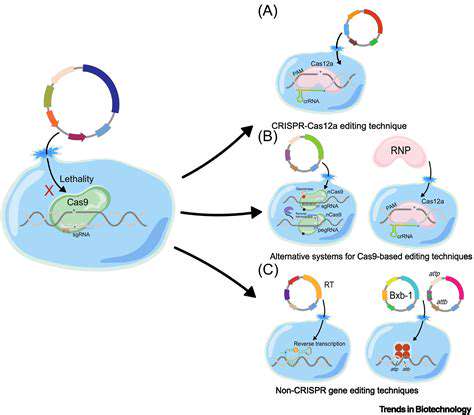
CRISPR-Cas9 has undeniably revolutionized gene editing, offering unprecedented precision and accessibility. However, its potential applications, while vast, are not without limitations. The search for alternative gene editing tools is therefore crucial for broadening the scope of genetic manipulation and addressing the inherent challenges of CRISPR. This exploration goes beyond simply finding faster or cheaper methods; it delves into entirely different mechanisms of gene regulation and modification.
Harnessing the Power of Transcription Factors
Transcription factors are proteins that control the expression of genes. Their precise binding to specific DNA sequences can initiate or repress gene activity. Manipulating these factors offers an avenue for targeted gene regulation, potentially sidestepping the need for direct DNA modifications entirely. This approach holds tremendous promise for therapeutic interventions and agricultural applications.
By developing methods to precisely control transcription factor activity, scientists can create new ways to modulate gene expression without altering the DNA sequence itself. This opens up possibilities for treating genetic disorders and enhancing desirable traits in organisms.
Exploring RNA-Based Gene Regulation
RNA interference (RNAi) and other RNA-based mechanisms offer a powerful arsenal for gene silencing and regulation. These techniques can effectively reduce or eliminate the expression of specific genes without permanently altering the DNA sequence, providing a less invasive alternative to gene editing. Researchers are actively exploring novel RNA-based approaches to control gene expression with greater precision and control.
Further research into RNA interference and similar methods could unlock new possibilities for treating a wide array of diseases, from cancer to viral infections. The versatility of RNA-based strategies makes them a compelling alternative to CRISPR in many scenarios.
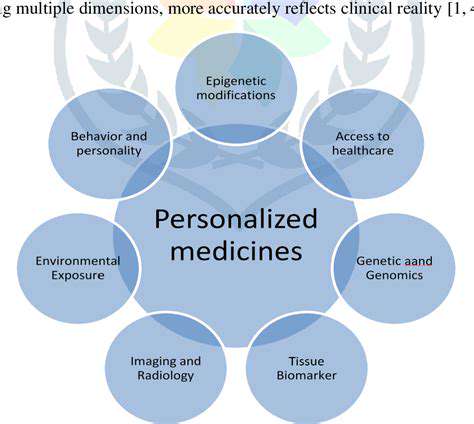
Utilizing Epigenetic Modifications
Epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation and histone modifications, alter gene expression without changing the underlying DNA sequence. These modifications play a critical role in development and disease, and their manipulation presents a promising avenue for treating genetic disorders and potentially even preventing disease progression. Epigenetic therapies have the potential to be less invasive and more targeted than traditional gene therapies.
Understanding and manipulating epigenetic mechanisms is a complex but potentially rewarding endeavor. The ability to precisely control these modifications could lead to revolutionary treatments for diseases that were previously considered intractable.
Developing Novel Gene Delivery Systems
Efficient and targeted delivery of gene-editing tools or other genetic materials is a critical hurdle in gene therapy. Developing novel vectors and delivery methods that can efficiently transport these materials to the desired cells remains a key area of research. Improved delivery systems are crucial for maximizing the efficacy and minimizing the off-target effects of both gene editing and alternative gene regulation strategies.
The development of more precise and efficient delivery systems will be essential for advancing the use of alternative gene manipulation techniques and CRISPR itself. This area of research holds the key to unlocking the full therapeutic potential of these powerful technologies.
Challenges and Future Directions
Overcoming Existing Barriers
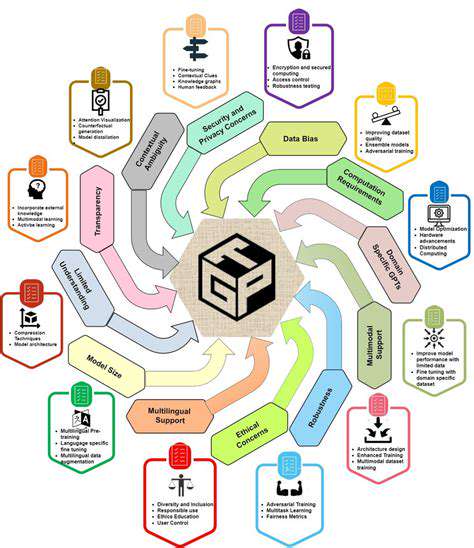
The current landscape presents several obstacles to widespread adoption of innovative technologies. Significant financial investment is often required to implement new systems and processes, and this can be a major hurdle for smaller organizations. Furthermore, the lack of skilled personnel with the necessary expertise to manage and maintain these complex systems can impede progress. This creates a bottleneck in the development and deployment pipeline.
Another key challenge is the compatibility of different systems and platforms. Integrating disparate technologies into a cohesive whole can be extremely complex and time-consuming, requiring significant resources and expertise. This interoperability issue poses a significant roadblock to building truly integrated and seamless solutions.
Addressing Data Security Concerns
Data security and privacy are paramount in today's digital age. As we move towards more interconnected systems, the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access increases exponentially. Robust security measures are crucial to safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining public trust.
Implementing robust encryption protocols and access controls is essential. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are necessary to identify and mitigate potential risks. Establishing clear data governance policies and procedures is critical for ensuring compliance with regulations and maintaining data integrity.
Enhancing User Experience
Creating intuitive and user-friendly interfaces is essential for maximizing the adoption rate of new technologies. A poor user experience can lead to frustration and ultimately discourage users from utilizing the system. User-centered design principles should be prioritized throughout the development process to ensure that the technology meets the needs and expectations of its target audience.
Accessibility considerations are also crucial. The technology should be usable by individuals with diverse abilities and needs. This includes providing alternative text for images, keyboard navigation options, and support for screen readers. Prioritizing accessibility from the outset will ensure inclusivity and broaden the potential user base.
Exploring Emerging Technologies
The field of technology is constantly evolving, presenting exciting opportunities for innovation. Exploring cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain can significantly enhance existing solutions and open up new possibilities. These advancements have the potential to revolutionize various sectors and drive significant progress.
Integrating AI into decision-making processes, for instance, can lead to more efficient and effective outcomes. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast datasets to identify patterns and trends, allowing businesses to make data-driven decisions. Blockchain technology can enhance security and transparency in various applications, particularly in supply chain management and financial transactions.
Promoting Collaboration and Innovation
Collaboration and knowledge sharing are vital for driving innovation and accelerating progress. Encouraging collaboration between researchers, developers, and industry professionals can foster the exchange of ideas and accelerate the development of new solutions.
Establishing open-source platforms and communities can facilitate collaboration and knowledge sharing. Providing funding opportunities and support for startups and innovators can fuel the development of new technologies and foster a vibrant ecosystem. Supporting interdisciplinary research and development can lead to breakthroughs in many fields.