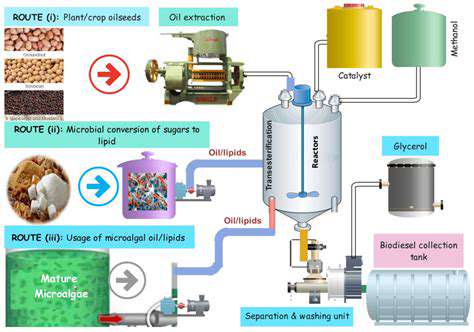
Biofuel Production: Environmental Considerations
The production of biofuels, while touted as a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, presents several environmental challenges. A crucial aspect is the land use required for cultivating feedstocks. Expanding dedicated farmland for biofuel crops can lead to deforestation and habitat loss, impacting biodiversity and potentially contributing to climate change through the release of stored carbon. Careful land-use planning and sustainable agricultural practices are essential to mitigate these negative impacts.
Furthermore, the production process itself can have significant environmental consequences. Large-scale biofuel production often demands substantial water resources, potentially straining local water supplies in already water-stressed regions. The use of fertilizers and pesticides in biofuel crop cultivation can also lead to water pollution, harming aquatic ecosystems and impacting human health. Implementing environmentally friendly production methods and minimizing the use of harmful chemicals are critical to achieving true sustainability.
Economic Viability and Societal Impact
The economic viability of biofuel production is a complex issue, influenced by factors such as feedstock costs, processing technologies, and market demand. The fluctuating prices of raw materials and competition from other energy sources can significantly affect the profitability of biofuel projects. Governments often incentivize biofuel production through subsidies, which can impact their competitiveness in the energy market. It's crucial to analyze the long-term economic sustainability of these initiatives beyond short-term subsidies.
The societal impact of biofuel production extends beyond economic considerations. Job creation and rural development are potential benefits, but these must be balanced against potential negative impacts on local communities, such as displacement or loss of traditional livelihoods. A thorough assessment of the social implications alongside the environmental and economic aspects is essential for responsible biofuel development.
Technological Advancements and Future Prospects
Ongoing research and development in biofuel technology are constantly striving to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Innovative techniques in feedstock processing and conversion are being explored to optimize yields and minimize waste. Utilizing alternative feedstocks, such as algae or agricultural residues, is one avenue of research, offering potential solutions to the land-use challenges faced by traditional biofuel crops. Furthermore, advances in biofuel refining and distribution infrastructure are crucial to ensure efficient and sustainable delivery to consumers.
The future of biofuels hinges on the continued development of sustainable technologies and practices. Integrating biofuels into existing energy systems in a responsible manner, considering environmental and socioeconomic factors, will be essential to their success. This will require collaborative efforts between researchers, policymakers, and industry stakeholders to achieve a truly sustainable energy future.
Future Prospects and Challenges

Emerging Opportunities in the Field
The future of the field presents exciting prospects, driven by advancements in technology and evolving societal needs. Innovative solutions are constantly being developed to address complex problems, creating numerous opportunities for growth and advancement. These opportunities span various sectors, from healthcare and energy to environmental sustainability and communication technologies. This dynamic environment will undoubtedly shape the future trajectory of the field, demanding adaptability and a willingness to embrace new challenges.
The integration of emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning is poised to revolutionize numerous aspects of the field. This integration promises to enhance efficiency, improve decision-making, and unlock previously unimaginable possibilities. The ability to leverage these technologies effectively will be crucial for success in the future landscape.
Technological Advancements and their Impact
Technological advancements are fundamentally reshaping the field, driving innovation and creating a more interconnected and dynamic environment. These advancements are not just limited to specific applications; they are impacting the very core principles and methodologies that underpin the field. This evolution demands a continuous learning process for professionals within the field, requiring them to adapt and acquire new skills to remain relevant.
The increasing accessibility of powerful computing resources and sophisticated algorithms is transforming how we approach complex problems. This makes it possible to analyze vast datasets, identify subtle patterns, and develop more accurate and effective solutions. The ability to leverage these computational tools will be critical in unlocking new discoveries and advancements in the field.
Addressing the Challenges of Scalability and Sustainability
One of the key challenges facing the field is the need to ensure scalability and sustainability in its solutions. As the field expands, it becomes crucial to develop solutions that can be deployed and maintained effectively across diverse contexts and populations. This requires careful consideration of resource allocation, infrastructure development, and long-term implications for the environment. It is imperative that solutions developed are not only effective but also environmentally responsible, ensuring their impact on future generations is positive.
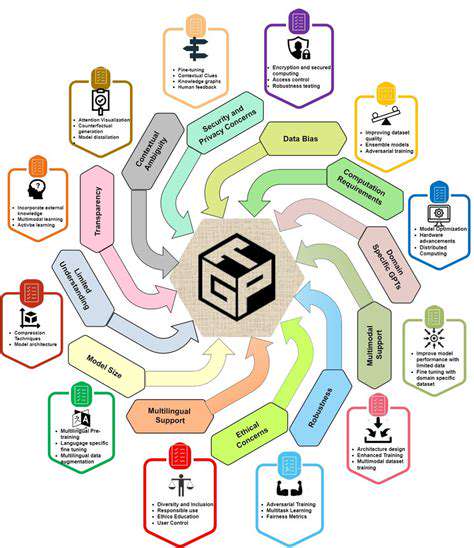
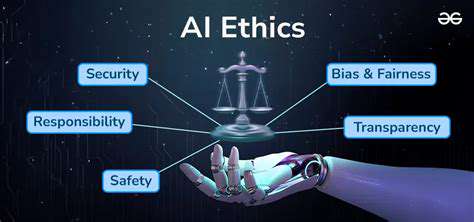
Another crucial challenge relates to the ethical considerations of advanced technologies. As the field relies more heavily on automation and artificial intelligence, it is important to carefully consider the ethical implications of these advancements. Addressing these concerns proactively is essential to ensure that the field maintains its integrity and benefits all stakeholders. This includes establishing guidelines, protocols, and ethical frameworks to navigate the complexities of technological advancement.
Adapting to a Changing Workforce
The evolving nature of the workforce within the field requires adaptation and proactive measures to ensure that professionals possess the necessary skills for success. Continuous learning and upskilling are paramount for professionals in this field to remain competitive and impactful. The ability to embrace new technologies and methodologies is crucial for navigating the dynamic and rapidly evolving landscape.
The changing demands of the job market necessitate the development of a skilled and adaptable workforce. This includes fostering innovation, encouraging collaboration, and investing in educational opportunities. This focus on workforce development is essential for ensuring that the field continues to thrive and address the challenges of today and the future.