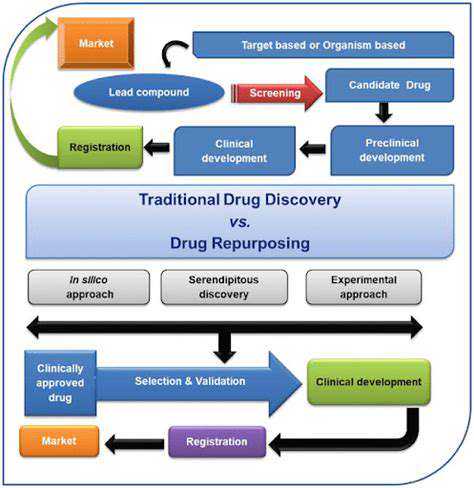
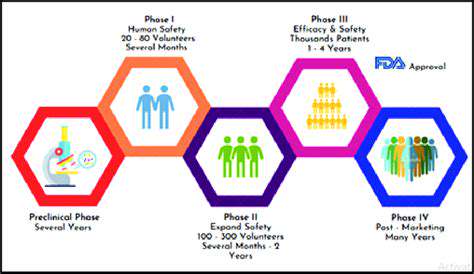
Clinical Trials and the Road Ahead
Early-Stage Trials and Promising Results
Initial clinical trials for gene editing therapies in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) are yielding encouraging results, demonstrating the potential of these innovative approaches. These early-stage studies are crucial for assessing safety and efficacy, providing a foundation for larger, more comprehensive trials. Researchers are carefully monitoring patient responses to identify optimal treatment strategies and potential side effects, a process that requires meticulous attention to detail and long-term follow-up.
While the initial findings are promising, it's vital to acknowledge the limitations of early-stage trials. Sample sizes are often small, and the duration of follow-up may not be sufficient to fully evaluate long-term outcomes. These trials, however, are pivotal in informing future research directions and laying the groundwork for more definitive conclusions.
Targeting Specific Genes for ALS
ALS is a complex neurodegenerative disease with a range of genetic causes. Gene editing therapies aim to address these underlying genetic defects, potentially halting or reversing disease progression. Researchers are focusing on specific genes implicated in ALS pathogenesis, such as those involved in motor neuron function and survival. The goal is to develop therapies that specifically target these genes to minimize off-target effects and maximize therapeutic benefit.
Identifying the most relevant genes for targeted intervention is a critical aspect of this research. The complexity of the disease necessitates a nuanced approach, considering the multitude of factors that contribute to ALS development and progression.
Delivery Methods and Challenges
One of the key challenges in gene editing therapies is delivering the gene-editing tools to the correct cells within the nervous system. Researchers are exploring various delivery methods, including viral vectors, which can carry the gene-editing machinery into specific cells. These methods must be safe and effective, minimizing potential side effects and maximizing the therapeutic impact.
Ethical Considerations and Public Perception
Gene editing technologies raise significant ethical concerns, prompting careful consideration of their potential impact on society. The potential for unintended consequences and the equitable access to these therapies are important aspects to address. Public dialogue and engagement are essential for navigating these ethical questions and building public trust in the development and application of gene editing therapies for ALS.
Open and honest communication about the potential benefits and risks of gene editing, coupled with transparent research practices, is crucial for fostering public understanding and acceptance of these potentially transformative treatments.
Long-Term Outcomes and Future Directions
The long-term outcomes of gene editing therapies for ALS are still largely unknown. Extensive long-term studies are needed to assess the sustained effectiveness and safety of these interventions. Researchers are committed to designing trials that follow patients for many years to monitor for any long-term effects and assess the durability of any treatment gains.
Future research directions include developing more precise and efficient gene editing tools, optimizing delivery methods, and exploring combination therapies that combine gene editing with other treatments to achieve even greater therapeutic impact and address the complex nature of ALS.
Collaboration and Funding
The development of gene editing therapies for ALS requires significant collaboration among researchers, clinicians, and regulatory bodies. International collaboration facilitates the sharing of knowledge and resources, accelerating the pace of research and development. Robust funding mechanisms are essential to support these efforts and ensure continued progress in this critical area of medical research.
Attracting funding for long-term research projects is essential for maintaining momentum and exploring the many avenues for advancement in gene editing technology. Innovative funding models that support long-term research are necessary for achieving the ultimate goal of effective treatments and potentially a cure for ALS.