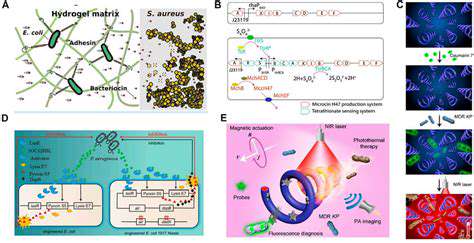
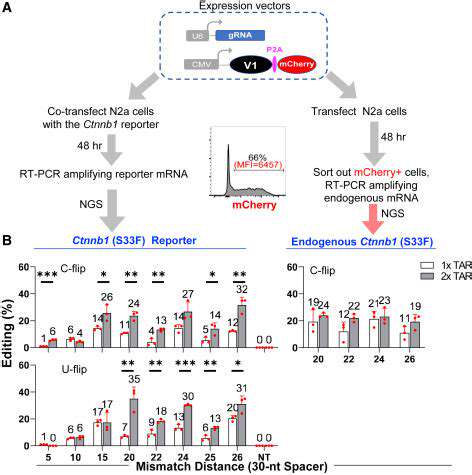
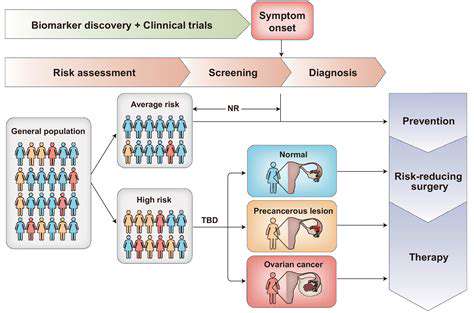
The field of personalized medicine is reshaping modern healthcare, shifting from standardized treatments to customized solutions. This paradigm acknowledges that genetic makeup, environmental influences, and lifestyle choices all play critical roles in how patients respond to medical interventions. The result? More precise therapies with fewer side effects and better overall results.
Customizing treatments based on individual genetic blueprints represents a quantum leap in therapeutic effectiveness. Matching patients with their ideal treatment protocols not only boosts success rates but also eliminates the frustration and expense of trial-and-error approaches, dramatically improving patients' daily lives.
Genetic Testing and Diagnostics
Cutting-edge genetic testing methods now empower physicians to detect subtle DNA variations that predict disease susceptibility or medication responses. These breakthroughs enable proactive prevention measures and data-driven treatment choices, fundamentally changing how we approach patient care.
Pharmacogenomics: Tailoring Medications
This specialized field examines how personal genetics influence drug interactions. By mapping genetic markers related to drug processing, doctors can prescribe medications with pinpoint accuracy, reducing harmful reactions while optimizing treatment results. Such precision transforms medication from a guessing game into a science.
Decoding the genetic factors in drug metabolism allows clinicians to exclude potentially dangerous or ineffective medications upfront, ensuring patients receive only the most promising treatments from day one.
Precision Oncology: Targeted Cancer Therapies
Cancer treatment has entered a new era through personalized approaches. Tumor DNA analysis now reveals the specific genetic defects fueling cancer growth, enabling therapies that precisely target these vulnerabilities. This paradigm shift means fewer side effects and better outcomes for countless patients.
These targeted strategies have already improved survival statistics across multiple cancer types. By focusing on unique tumor characteristics, doctors can design attack plans that maximize effectiveness while minimizing collateral damage to healthy tissue.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its potential, personalized medicine faces hurdles. Cost barriers, data infrastructure demands, and genetic privacy concerns must be resolved to ensure fair access and ethical practice. Continued innovation will be essential to overcome these obstacles and unlock the field's full potential.
Personalized medicine stands poised to redefine healthcare through customized treatment solutions. As research progresses and practical challenges are addressed, we move closer to a future where every patient receives care tailored to their biological uniqueness.
Ethical Considerations and Future Directions

Ethical Implications of AI in Healthcare
The healthcare landscape is undergoing radical transformation through artificial intelligence, but these technological leaps come with profound ethical questions. AI systems trained on historical data risk amplifying existing healthcare disparities, potentially disadvantaging certain patient groups. This necessitates sophisticated bias detection systems and corrective measures.
Patient data security presents another critical concern. With AI processing sensitive health information, robust cybersecurity protocols become non-negotiable. Comprehensive regulations must govern data handling to prevent breaches and maintain public trust in these emerging technologies.
Transparency and Explainability in AI Systems
The opaque nature of many AI decision-making processes creates accountability challenges. When algorithms can't explain their diagnostic conclusions or treatment suggestions, verifying their accuracy becomes problematic.
Developing interpretable AI systems isn't optional - it's fundamental to establishing clinical trust. Clear explanations of algorithmic decisions enable proper oversight, informed patient consent, and continuous system improvement.
Bias Detection and Mitigation Strategies
Since AI reflects the data it's trained on, historical healthcare biases can resurface in algorithmic decisions. Left unchecked, this could lead to uneven care quality across demographic groups.
Researchers are combating this through techniques like synthetic data generation and adversarial testing. Ongoing algorithmic audits remain essential to identify and correct bias creep in live healthcare applications.
Data Security and Privacy in AI Systems
Healthcare AI's hunger for patient data creates significant privacy challenges. Maintaining ironclad data protection measures is crucial for ethical operation. Advanced encryption, strict access controls, and thorough anonymization protocols form the foundation of trustworthy systems.
Clear patient communication about data usage policies helps build the transparency needed for meaningful consent in this data-driven healthcare era.
Potential Impact on Healthcare Professionals
AI integration will inevitably transform medical practice. Clinicians must develop new competencies to effectively partner with intelligent systems. The goal isn't replacement but enhancement - using AI to augment human expertise rather than supplant it.
Proactive retraining initiatives will help smooth the transition for healthcare workers. By preparing the workforce for technological change, we can ensure that AI serves as a tool for medical professionals rather than a threat to their roles.
Future of AI in Healthcare
AI's healthcare potential spans from diagnostic assistance to drug discovery breakthroughs. These technologies promise to solve longstanding challenges in patient care and medical research. However, ethical safeguards must evolve alongside technical capabilities.
Sustained dialogue between technologists, clinicians, and policymakers will determine whether AI fulfills its potential to improve global health. Only through collaborative governance can we harness these powerful tools responsibly.