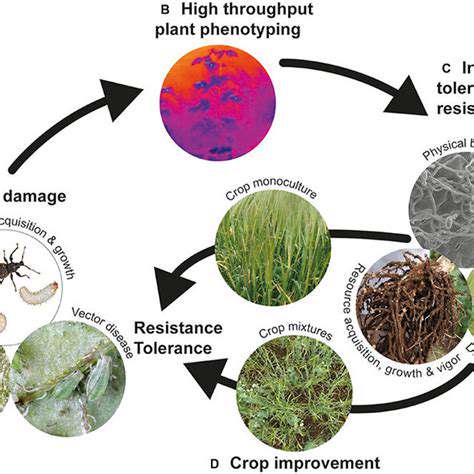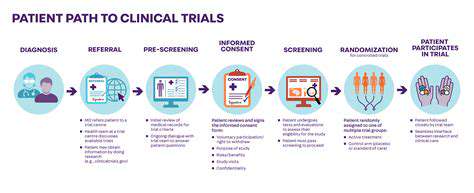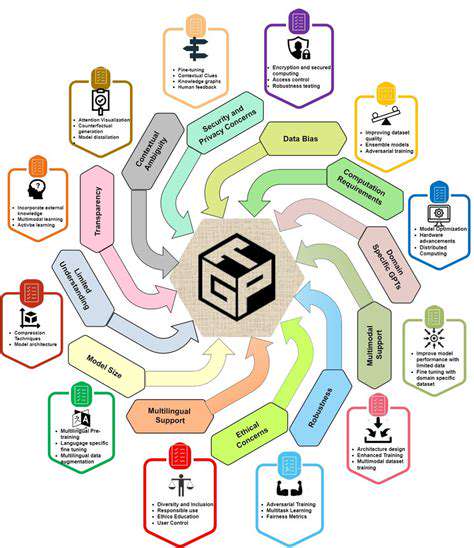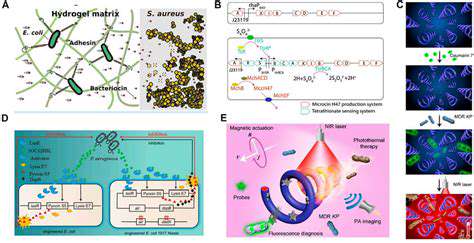
Targeting Cancer Cell Metabolism:
Understanding and manipulating the unique metabolic pathways of cancer cells is a promising avenue for developing novel therapies. Targeting enzymes crucial for these pathways can disrupt the cancer cell's ability to proliferate and survive, potentially leading to more effective and less toxic treatments. This approach holds significant promise for developing therapies that are more precisely tailored to individual patients' needs, maximizing efficacy while minimizing side effects.
Cancer cells often exhibit altered metabolic activity compared to normal cells. This metabolic rewiring is a key driver of cancer growth and survival. By identifying and targeting these metabolic vulnerabilities, researchers can potentially develop more effective and targeted therapies.
Inhibiting Angiogenesis:
Angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, is essential for tumor growth and metastasis. Blocking this process can starve the tumor of nutrients and oxygen, leading to its shrinkage or destruction. Developing novel inhibitors of angiogenesis promises a significant advancement in cancer treatment, particularly for aggressive and metastatic cancers. These inhibitors could be combined with other therapies to create more potent and effective treatments.
Modulating Immune Response:
The immune system plays a critical role in recognizing and eliminating cancer cells. Developing therapies that enhance the body's natural immune response against cancer cells is a major focus in cancer research. This approach can lead to more durable and potentially curative treatments, as it aims to harness the body's own defenses. Immunotherapies hold great promise for treating a wide range of cancers, from those that are difficult to treat to those that have metastasized.
Harnessing the power of the immune system to fight cancer is a rapidly evolving field. Researchers are exploring various strategies, including checkpoint inhibitors and adoptive cell therapies, to bolster the immune response and enhance its ability to target and destroy cancer cells effectively.
Developing Novel Delivery Systems:
Effective drug delivery is critical for maximizing the therapeutic efficacy of novel drugs. Creating targeted delivery systems that can deliver drugs directly to cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissues is a significant challenge in drug development. This is paramount in improving patient outcomes and reducing the potential side effects associated with conventional chemotherapy. Innovative approaches, such as nanoparticles and liposomes, hold great promise in this area.
Targeting Specific Genetic Mutations:
Many cancers are driven by specific genetic mutations that disrupt cellular processes. Targeting these mutations with therapies designed to specifically correct or inhibit their effects is a promising strategy. This approach offers the potential for highly effective and personalized treatments. Targeting these genetic vulnerabilities can lead to more precise and effective therapies for patients with specific genetic profiles. The development of targeted therapies has revolutionized cancer treatment, offering hope for patients with previously untreatable cancers.
Exploring Cellular Signaling Pathways:
Cellular signaling pathways are complex networks that regulate various cellular processes, including cell growth, proliferation, and differentiation. Disruptions in these pathways can contribute to cancer development. Identifying and targeting key components of these pathways offers the potential for developing novel therapies that can effectively disrupt the cancer cell's ability to function. This strategy can lead to more effective and targeted treatments, potentially improving patient outcomes.
Combating Drug Resistance:
Drug resistance is a significant challenge in cancer treatment. Tumors can develop resistance to existing therapies, rendering them ineffective. Overcoming drug resistance is crucial for improving patient outcomes. Developing strategies to circumvent or overcome these mechanisms of resistance is a critical area of research. Developing novel strategies to circumvent drug resistance is a priority in the pursuit of more effective and durable cancer treatments. This includes identifying new drug targets and exploring ways to enhance drug delivery and efficacy.
When selecting medicinal herbs, thorough research is crucial to ensure you're using the correct plant and avoiding potential harm. Knowing the specific herb you need and its intended use is paramount to a successful and safe treatment. Consult reputable sources, such as botanical texts, experienced herbalists, and qualified healthcare professionals, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the herb's properties and potential interactions.

Combining Therapies for Enhanced Efficacy and Safety
Synergistic Effects of Combined Therapies
Combining different therapies for diabetes treatment can often yield synergistic effects, meaning the combined effect is greater than the sum of the individual effects. This approach can lead to better glycemic control, reduced risk of complications, and improved patient outcomes. Careful consideration of the potential interactions and side effects of the combined therapies is crucial to ensure patient safety and maximize effectiveness.
For example, a combination of metformin and a GLP-1 receptor agonist might achieve better blood sugar control than either therapy alone, while minimizing the risk of hypoglycemia. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic interactions need to be evaluated to optimize the efficacy of the combined regimen.
Personalized Treatment Strategies
Diabetes is a complex disease with diverse presentations. A one-size-fits-all approach to treatment is often inadequate. Personalized treatment strategies, tailored to individual patient needs and characteristics, are essential for optimal outcomes. These strategies should consider factors like age, lifestyle, comorbidities, and individual responses to different medications.
Genetic predisposition, specific metabolic profiles, and the patient's overall health status are all crucial factors to consider when designing a personalized treatment plan. This individualized approach can lead to better adherence to treatment plans and improved long-term outcomes.
Addressing Cardiovascular Risk Factors
Diabetes significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular disease. Combined therapies that address both glycemic control and cardiovascular risk factors are increasingly important in diabetes management. Certain medications, like specific SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists, have demonstrated cardiovascular benefits beyond their glucose-lowering effects, making them valuable components of combined therapies.
Careful assessment of cardiovascular risk factors, including blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and lipid profiles, is critical when selecting combined therapies. The use of therapies with proven cardiovascular safety profiles is paramount.
Minimizing Adverse Drug Reactions
The use of multiple medications can increase the potential for adverse drug reactions (ADRs). Careful monitoring and proactive management of potential ADRs are essential when combining therapies. This includes regular assessments of blood glucose levels, kidney function, and liver function, as well as proactive identification and mitigation of any reported side effects.
Pharmacokinetic interactions between medications need to be meticulously evaluated to prevent drug-drug interactions and ensure that the combined therapies do not negatively impact the safety profile. A comprehensive understanding of the potential side effects of each medication and their interactions is essential.
Improving Patient Adherence
Patient adherence to complex treatment regimens is often a significant challenge. Well-designed combined therapies can enhance patient adherence by simplifying medication regimens and improving patient outcomes. Minimizing the number of pills patients need to take and ensuring that the medication schedule aligns with their daily routine can significantly improve adherence rates.
Educating patients about the importance of their treatment regimen and providing support and resources to help them manage their condition effectively are crucial elements of improving patient adherence to combined therapies. Strategies that promote patient engagement and empower them to actively participate in their care are essential.
Enhancing Treatment Efficacy through Combination
Combining different classes of antidiabetic drugs can often enhance treatment efficacy by targeting multiple pathophysiological mechanisms underlying diabetes. This approach can lead to more comprehensive glucose control and potentially reduce the risk of long-term complications. For instance, combining a drug that improves insulin sensitivity with one that increases insulin secretion can achieve a more robust effect than either drug alone.
Evaluating Cost-Effectiveness of Combined Therapies
The cost-effectiveness of combined therapies needs careful consideration. While combined therapies may offer significant benefits in terms of enhanced efficacy and reduced complications, the associated costs of multiple medications must be weighed against the potential long-term savings from improved health outcomes. Cost-benefit analyses should be performed to evaluate the overall economic impact of different treatment strategies.
Careful consideration should be given to the comparative costs of individual medications, the potential for reduced healthcare utilization associated with improved patient outcomes, and the long-term implications of potential complications from poorly controlled diabetes. Comprehensive cost-effectiveness analyses are essential to ensure that the most beneficial and affordable treatment strategies are adopted.