Personalized Cancer Treatment Through Gene Editing
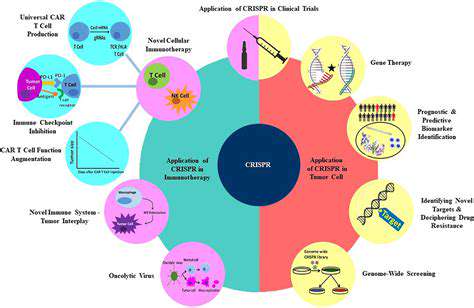
Personalized Medicine in Cancer Treatment
Tailored cancer therapy marks a revolutionary change in oncology, shifting from generalized treatments to customized approaches based on each patient's unique tumor characteristics. This perspective acknowledges that cancers are diverse diseases with varied origins and behaviors. Understanding these individual traits is fundamental for creating effective precision therapies.
By examining a tumor's genetic profile—including mutations and gene activity patterns—doctors can pinpoint specific weaknesses in cancer cells. This information enables selection of therapies that work better and cause fewer side effects, ultimately improving outcomes and reducing treatment toxicity. This methodology also permits earlier intervention and more precise risk assessment, allowing proactive cancer management.
Targeted Therapies and Immunotherapy
Personalized medicine facilitates the use of targeted treatments that specifically attack cancer's molecular drivers. Unlike conventional chemotherapy, these therapies focus on particular genetic abnormalities or pathways active in malignant cells, minimizing harm to healthy tissue.
Immunotherapy, another cornerstone of personalized oncology, harnesses the body's natural defenses against cancer. By identifying and attacking specific tumor markers, immunotherapy can trigger an immune response that destroys cancerous cells. This approach proves especially effective for cancers with distinct immune characteristics and often works best when combined with targeted treatments.
The emergence of targeted therapies and immunotherapies is radically transforming cancer care. These innovations are producing more effective, less toxic treatments that improve patients' lives and boost survival rates.
Genetic Testing and Diagnostic Tools
Progress in genetic testing is revolutionizing cancer diagnosis. These advanced tests provide comprehensive analysis of a tumor's genetic composition, including mutations, gene combinations, and epigenetic changes—critical information for treatment planning. These diagnostics play a vital role in identifying the precise genetic causes of cancer, helping clinicians choose the most appropriate therapy.
High-quality genetic testing is indispensable for accurate diagnosis and treatment selection in personalized oncology. Test results guide the choice of targeted and immunotherapies, leading to more effective, less harmful treatments. The availability of these sophisticated diagnostic tools represents a major leap forward in cancer care.
Ongoing research continues to refine these tools, achieving even greater precision in identifying genetic drivers of tumor growth. This constant improvement is essential for optimizing personalized cancer treatment approaches.
Challenges and Future Directions
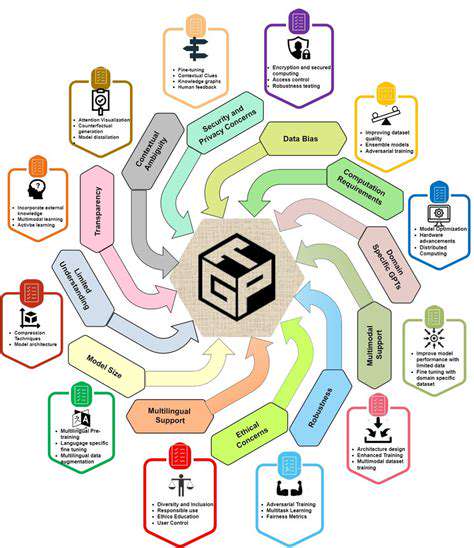
Navigating the Complexities of Data Integration
Combining data from multiple sources presents significant hurdles in modern applications. Challenges include managing diverse data formats and ensuring system compatibility. Maintaining data accuracy and consistency across different platforms is crucial for reliable analysis and decision-making. Overcoming these obstacles requires thorough planning, careful execution, and deep data expertise.
The changing nature of data formats demands continuous adaptation of integration methods. Keeping strategies flexible is necessary to accommodate future data sources and structures—a critical factor for long-term success.
Addressing Scalability Concerns in Large-Scale Systems
As systems expand, scalability becomes increasingly important. Solutions must manage growing data volumes and user demands without performance loss. Creating scalable architectures and implementing efficient processing methods is essential for maintaining system performance. This involves selecting appropriate technologies and strategies for horizontal expansion.
Distributed computing systems can help address scaling challenges. Properly utilizing these frameworks enables handling massive datasets and high-volume operations.
The Importance of Data Security and Privacy
With growing reliance on data analytics, security and privacy concerns have intensified. Implementing strong protective measures for sensitive information is vital for maintaining trust and regulatory compliance. Safeguarding data against unauthorized access and misuse is a fundamental responsibility. This requires encryption, access controls, and regular security assessments.
Privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA mandate strict data handling practices. Organizations must follow guidelines for data collection, storage, and usage to avoid penalties. Compliance with these regulations is essential for protecting brand reputation and avoiding legal issues.
Evolving Data Storage Technologies
Rapid advancements in data storage present both opportunities and challenges. Cloud-based solutions and distributed databases offer improved scalability, availability, and cost efficiency. These technologies support massive datasets and complex analytical tasks.
However, adopting new storage solutions requires careful planning regarding compatibility and migration. Understanding each technology's specifics is necessary to maximize benefits. Proactive planning is crucial for successful implementation.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Data Management
AI is transforming multiple aspects of data handling, including analysis, prediction, and automation. AI tools can automate data cleaning and transformation tasks, allowing humans to focus on strategic work.
AI algorithms can detect data patterns and anomalies that traditional methods might miss, leading to better predictions and decisions. Effective AI implementation can dramatically enhance data management efficiency and effectiveness.
Advancements in Data Visualization Techniques
Effective data presentation is crucial for communicating insights and supporting decisions. Modern visualization tools create interactive, engaging dashboards that clearly represent complex information. These resources make data more accessible to broader audiences.
Improved visualization methods enable more sophisticated data representation, revealing hidden relationships and trends. This leads to better understanding and more informed choices.
The Human Factor in Data-Driven Decision Making
Despite technological progress, human judgment remains essential in data-based decision processes. Analysts must interpret data insights and convert them into practical strategies. Clear communication and collaboration bridge the gap between technical expertise and business requirements. Strong relationships between data teams and business leaders are crucial for success.
Data literacy training ensures responsible data use and prevents misinterpretation. Equipping people with data skills maximizes the impact of data-driven initiatives.