The Future of Bioinformatics: Challenges and Opportunities
Data Integration and Management
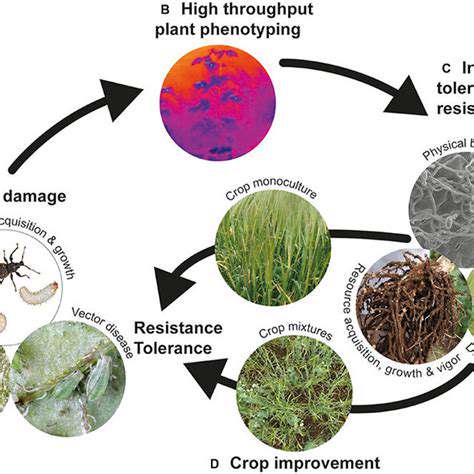
A critical challenge in bioinformatics is the ability to effectively integrate and manage the vast amounts of data generated by high-throughput technologies. This includes not only genomic data, but also proteomic, transcriptomic, and metabolomic data, all of which need to be stored, processed, and analyzed in a coherent manner. Efficient data management systems are essential for extracting meaningful insights from this complex data landscape, enabling researchers to identify patterns and correlations that could otherwise be missed.
Developing standardized data formats and interoperable databases is crucial. This will allow researchers to seamlessly share and combine data from different sources, fostering collaboration and accelerating the pace of discovery. Furthermore, robust data security and privacy measures are paramount to protect sensitive biological information.
Advanced Computational Tools and Algorithms
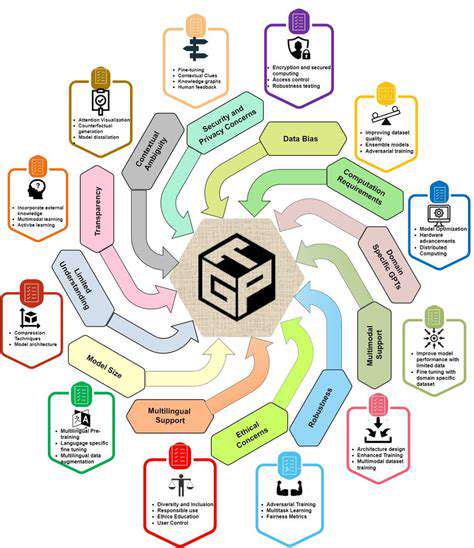
The ever-increasing complexity of biological data necessitates the development of sophisticated computational tools and algorithms. These tools need to be capable of handling large datasets, performing complex analyses, and identifying subtle patterns. Machine learning, artificial intelligence, and deep learning approaches are proving increasingly valuable in this regard, allowing for the identification of intricate relationships and the prediction of biological phenomena.
The development of user-friendly interfaces and intuitive visualization tools is also essential. These tools will empower researchers with diverse backgrounds to utilize these sophisticated computational resources effectively, democratizing access to bioinformatics tools and accelerating the process of scientific discovery.
Addressing Ethical Considerations
As bioinformatics techniques advance, it's crucial to carefully consider the ethical implications of their application. These considerations encompass issues such as data privacy, informed consent, and the responsible use of genomic information. Ensuring equitable access to these technologies and preventing potential misuse are paramount.
Open discussions and collaborations between researchers, ethicists, policymakers, and the public are essential to navigate these complex ethical challenges and develop responsible guidelines for the future of bioinformatics. This includes proactively addressing concerns about the potential for discrimination, bias, and the misuse of genomic data.
Personalized Medicine and Healthcare
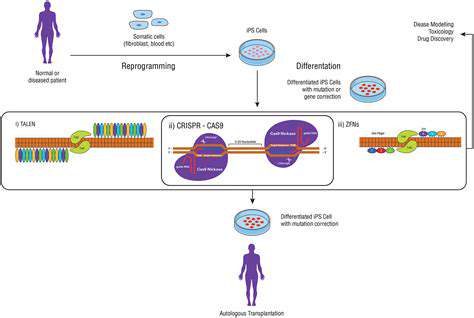
The intersection of bioinformatics and personalized medicine holds immense promise for revolutionizing healthcare. By analyzing individual genetic data, researchers and clinicians can tailor treatments to specific patients, leading to more effective and targeted therapies. This approach can lead to improved patient outcomes and reduced side effects.
Furthermore, bioinformatics can help predict an individual's risk of developing certain diseases, enabling proactive interventions and preventative measures. This proactive approach to healthcare has the potential to transform the way we approach disease prevention and treatment, leading to a healthier and more sustainable future.
Novel Applications in Drug Discovery and Development
Bioinformatics has the potential to dramatically accelerate the drug discovery and development process. By analyzing vast genomic and proteomic datasets, researchers can identify potential drug targets, predict drug efficacy and toxicity, and optimize drug design. This computational approach can significantly reduce the time and cost associated with traditional drug development methods.
Integration with Other Disciplines
The field of bioinformatics is not isolated; it thrives on interdisciplinary collaborations. Integrating bioinformatics with other fields, such as genomics, proteomics, and systems biology, can lead to a more holistic understanding of biological systems. Collaboration across disciplines can lead to innovative solutions for complex biological problems, accelerating scientific progress and ultimately improving human health.
By fostering cross-disciplinary collaborations, bioinformatics can leverage the expertise of diverse fields to address complex biological challenges and unlock new opportunities for discovery and innovation. This interdisciplinary approach enhances the depth and breadth of bioinformatics research, leading to more comprehensive and impactful results.