Targeting Specific Inflammatory Pathways
Precision Approaches in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases
Chronic inflammatory conditions pose a substantial challenge to global healthcare systems, affecting multiple bodily systems. The medical community recognizes that unraveling the complex mechanisms behind these diseases is fundamental to crafting impactful treatment protocols. Modern therapeutic development emphasizes pathway-specific intervention over broad immunosuppression, allowing for more nuanced control of inflammatory responses while reducing collateral damage to the immune system.
By concentrating on discrete inflammatory pathways, scientists can better understand the sophisticated interactions between molecular and cellular components driving disease pathology. This focused methodology frequently reveals promising new drug candidates that may offer greater specificity and effectiveness. For instance, selectively modulating particular cytokines or signaling molecules could potentially mitigate inflammatory damage without compromising essential immune defenses against pathogens.
Key Players in Chronic Inflammation
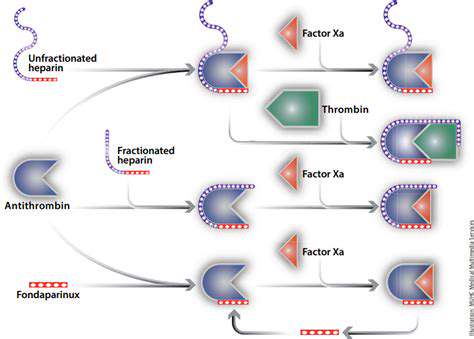
Crucial inflammatory mediators including TNF-α, IL-1β, chemokines, and adhesion molecules serve as primary drivers in establishing and maintaining chronic inflammatory states. Contemporary treatment strategies increasingly focus on neutralizing these molecular actors through various mechanisms. Interrupting their production, activity, or downstream effects can significantly dampen inflammatory processes and improve clinical outcomes.
Pharmaceutical approaches employing monoclonal antibodies, small molecule inhibitors, or other targeted therapies show particular promise in intercepting these mediators. However, the intricate nature of inflammatory cascades demands careful therapeutic calibration to avoid disrupting beneficial immune functions while achieving desired anti-inflammatory effects.
Innovative Treatment Paradigms
Beyond singular molecular targets, researchers are investigating broader strategies to regulate entire inflammatory networks. This includes identifying master regulators like transcription factors and upstream signaling molecules that coordinate inflammatory mediator production. Such approaches may yield more comprehensive solutions for persistent inflammatory conditions.
Alternative strategies focus on modifying the behavior of inflammatory cell populations such as macrophages and T lymphocytes. Adjusting their activation thresholds, functional profiles, or tissue recruitment patterns could provide significant clinical benefits while preserving protective immunity. These sophisticated interventions require detailed knowledge of immune cell dynamics in chronic inflammation.
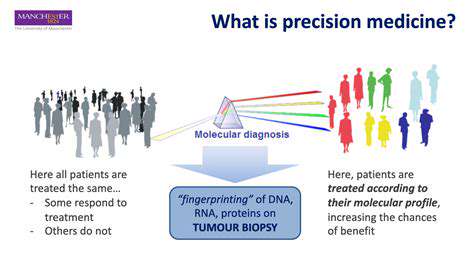
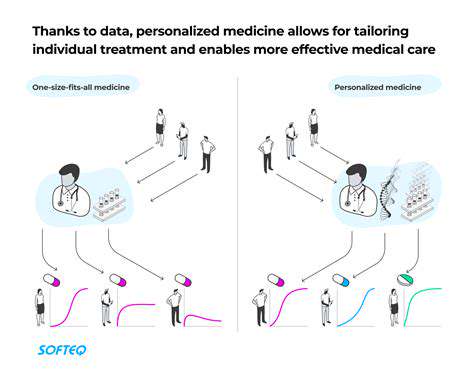
Emerging research into genetic predispositions and environmental triggers offers possibilities for personalized medicine approaches. Customizing treatments based on individual patient profiles could dramatically improve therapeutic precision and outcomes for chronic inflammatory disorders.
The continued advancement of targeted inflammatory pathway interventions represents a vital frontier in improving care for patients with chronic inflammatory diseases. Ongoing innovation in this field remains essential for developing safer, more effective treatment options.
Developing Combination Therapies for Enhanced Efficacy
Synergy in Multi-Agent Treatments
Multi-drug regimens offer significant potential for improving outcomes in chronic disease management. By simultaneously addressing multiple disease mechanisms, these approaches frequently surpass single-agent therapies in clinical effectiveness and disease control. Successful combination strategies depend on identifying complementary drug interactions where combined effects exceed individual drug performance.
Comprehensive evaluation of potential drug-drug interactions is essential to prevent adverse events or therapeutic interference. Detailed pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic analyses help optimize dosing schedules and administration protocols to maximize benefits while minimizing risks.
Multi-Pathway Intervention Strategies
Complex chronic diseases typically involve multiple interacting biological pathways. Strategic combinations of monoclonal antibodies, kinase inhibitors, and other novel agents can create comprehensive treatment approaches that disrupt disease networks more effectively. This multi-target strategy may produce more durable and complete therapeutic responses, though it requires thorough understanding of disease pathophysiology.
Combining agents that target different disease phases may provide comprehensive clinical benefits. For example, pairing early disease-modifying agents with treatments for advanced complications could yield superior long-term outcomes.
Advanced Drug Delivery Considerations
Therapeutic success in combination approaches depends heavily on delivery system design. Innovative technologies including targeted nanocarriers and controlled-release platforms can enhance drug bioavailability, improve tissue specificity, and extend therapeutic windows. These engineering solutions are crucial for ensuring reliable drug delivery to intended targets.
Overcoming Treatment Limitations
Chronic disease management often faces challenges of treatment resistance. Combination therapies can bypass resistance mechanisms by attacking diseases through multiple angles. Additionally, carefully selected drug pairings may help balance toxicity profiles, reducing adverse effects compared to single-agent regimens.
Clinical Development Challenges
Rigorous clinical evaluation is paramount for combination therapy development. Trial designs must account for complex drug interactions while ensuring reliable assessment of safety and efficacy. Appropriate patient stratification, standardized endpoints, and robust statistical methods are essential for generating meaningful clinical data.
Healthcare Economic Factors
The economic viability of combination therapies requires careful analysis. While potentially offering superior outcomes, the increased costs of multi-drug regimens must be justified by measurable improvements in disease control, quality of life, and potential reductions in long-term healthcare utilization. Comprehensive cost-benefit analyses are essential for healthcare decision-making.