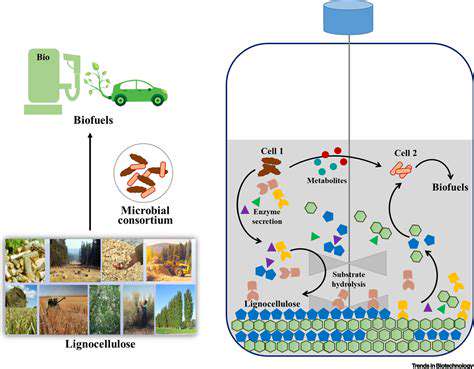
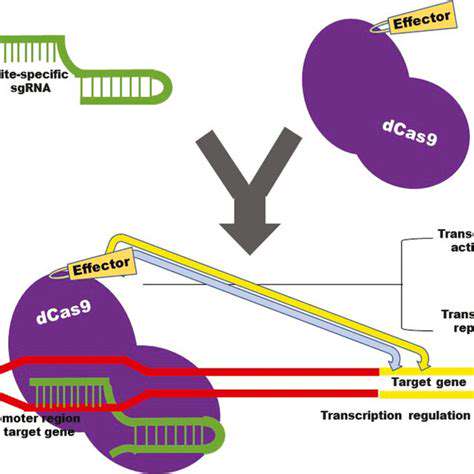
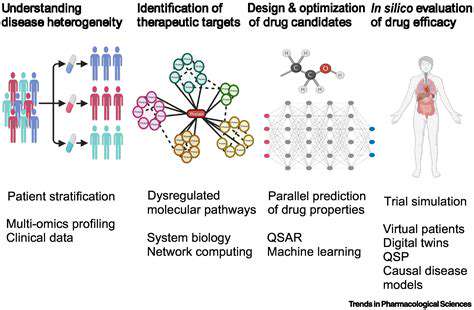
The Bioeconomy's Core Principles
The bioeconomy, in its essence, is a paradigm shift in how we view and utilize biological resources. It's not just about harvesting biological materials, but about understanding, harnessing, and optimizing biological processes for economic gain. This encompasses a broad spectrum of activities, from cultivating crops for biofuels to developing novel pharmaceuticals derived from microorganisms. A key principle is sustainability; aiming to minimize environmental impact and maximize resource efficiency. This fundamental shift from fossil fuel-based industries to bio-based systems is crucial for a more sustainable future.
This approach emphasizes the circular economy, where waste becomes a resource. The bioeconomy aims to create closed-loop systems, reducing reliance on finite resources and lowering waste generation, ultimately leading to a more environmentally responsible and economically viable model.
Driving Forces Behind the Bioeconomy's Growth
Several factors are propelling the bioeconomy's rapid expansion. Technological advancements, particularly in biotechnology, are crucial. New genetic engineering techniques and sophisticated analytical tools allow for more efficient extraction of valuable compounds from biological sources and the creation of novel biomaterials. Increased consumer demand for sustainable products is also a significant driver. Consumers are increasingly seeking eco-friendly alternatives, driving demand for products made from renewable resources.
Biotechnology's Role in the Bioeconomy
Biotechnology is the engine driving the bioeconomy. It's the application of biological systems and organisms to develop or make useful products or processes. From genetic engineering to fermentation technology, biotechnology's tools are essential for creating biofuels, producing bioplastics, and creating sustainable agricultural practices. This crucial role in developing and implementing bio-based solutions makes biotechnology a vital component of the bioeconomy's success.
Challenges and Opportunities in Scaling Up
Despite the immense potential, the bioeconomy faces various challenges in scaling up. One significant hurdle is the high initial investment required for research and development, infrastructure, and scaling production facilities. Another challenge lies in regulatory hurdles; navigating complex regulations surrounding bio-based products and processes can hinder swift deployment. However, these challenges are also opportunities. The bioeconomy presents an excellent avenue for innovation and job creation, particularly in research and development, manufacturing, and related sectors.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
The bioeconomy's sustainability hinges on minimizing its environmental footprint. Careful consideration of land use, water consumption, and waste management is critical. Sustainable practices throughout the entire lifecycle of bio-based products, from raw material sourcing to manufacturing and disposal, are crucial. This includes promoting responsible farming practices and prioritizing resource efficiency in production. A thorough understanding and careful management of environmental impacts are vital for the bioeconomy's long-term viability.
Economic Impacts and Job Creation
The bioeconomy is poised to create significant economic opportunities and jobs. From developing and producing biofuels to creating novel biomaterials, the bioeconomy is projected to generate a wealth of employment in various sectors. This includes opportunities for researchers, engineers, technicians, and skilled laborers. The bioeconomy's economic impact extends beyond job creation, encompassing investments, innovation, and the development of new industries. This creates a ripple effect, stimulating related sectors and driving overall economic growth.
The Future of the Bioeconomy: Emerging Trends
The bioeconomy is constantly evolving, with emerging trends shaping its future. Synthetic biology is rapidly advancing, offering exciting possibilities for creating novel biological systems and products. The integration of technology and data analytics is revolutionizing the bioeconomy, allowing for more efficient and sustainable processes. Furthermore, the focus on personalized medicine and precision agriculture is expected to significantly influence the bioeconomy's future trajectory. This exciting future promises to be filled with innovative solutions to global challenges.

Challenges and Future Directions
Challenges in Scaling Biotechnology Innovation
One significant hurdle in the biotechnology sector is the transition from laboratory breakthroughs to large-scale commercial applications. Developing robust, cost-effective manufacturing processes for biopharmaceuticals, biofuels, and other biotechnological products is crucial, but often presents substantial technical and financial challenges. Overcoming these barriers requires significant investment in research and development, as well as collaboration between academia, industry, and government.
Furthermore, regulatory hurdles can impede the swift adoption of new technologies. Complex regulatory frameworks for safety and efficacy assessments can delay the approval process for novel biotechnological products, potentially hindering their widespread adoption and economic impact.
Addressing Ethical Concerns in Biotechnology
As biotechnology advances, ethical considerations become increasingly paramount. Issues surrounding gene editing, synthetic biology, and the potential for misuse of these technologies demand careful examination and public discourse. Establishing transparent and responsible guidelines for research and development is essential to ensure that these powerful tools are used ethically and for the benefit of humanity.
Public perception and trust play a critical role in the responsible development and implementation of biotechnology. Open communication and education are vital to fostering public understanding and allaying concerns about potential risks and benefits.
Financial Sustainability of Biotech Startups
Securing sufficient funding to support research and development, product development, and commercialization is a persistent challenge for many biotechnology startups. Attracting venture capital and securing grants often requires demonstrating a compelling business model and a high probability of success, which can be difficult in a high-risk, high-reward environment.
Intellectual Property Protection and Licensing
Protecting intellectual property rights is crucial for incentivizing innovation in biotechnology. Developing robust strategies for patenting and licensing inventions can encourage investment and collaboration, fostering the growth of the bioeconomy. However, navigating the complexities of intellectual property law and ensuring equitable access to technologies are important considerations.
Training and Workforce Development
A skilled workforce is essential for driving innovation and growth in the biotechnology sector. Developing educational programs and training initiatives that equip individuals with the necessary expertise in biotechnology, bioinformatics, and related fields is crucial for meeting the demands of an expanding bioeconomy. Addressing the need for specialized talent across various levels of the industry will be critical for future success.
Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing
Effective collaboration between researchers, industry partners, and regulatory bodies is essential for accelerating the development and implementation of biotechnological solutions. Facilitating knowledge sharing and information exchange through platforms and networks can foster innovation and accelerate the progress of the bioeconomy. Cross-sectoral collaborations will be critical to overcome silos and unlock the full potential of this field.
Sustainable Production and Resource Management
The environmental impact of biotechnology processes needs careful consideration. Sustainable production practices, minimizing waste, and responsible resource management are crucial for ensuring the long-term viability of the bioeconomy. Developing bio-based materials and processes that reduce reliance on fossil fuels and minimize environmental footprint is paramount to the future of this field.