Introduction to Synthetic Biology in Agriculture

What is Synthetic Biology?
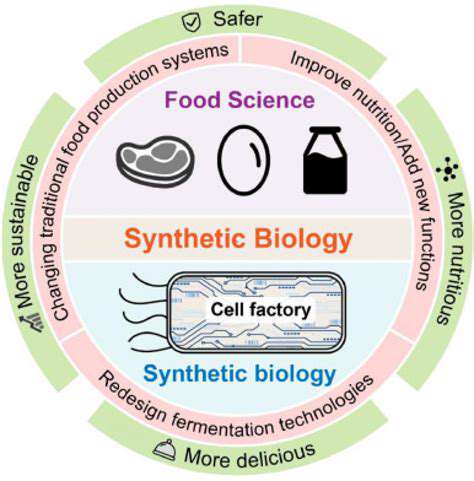
Synthetic biology represents a groundbreaking convergence between biological sciences and engineering disciplines. Researchers actively design novel biological components while refining existing systems to serve specific functions. This cutting-edge methodology enables cellular reprogramming, yielding breakthroughs across diverse sectors including pharmaceuticals and renewable energy.
The fundamental objective revolves around deciphering biological mechanisms and strategically altering them to accomplish targeted outcomes. This sophisticated fusion of biological understanding and engineering innovation propels unconventional solutions to worldwide issues.
Key Concepts in Synthetic Biology
Modular design principles and standardized protocols constitute the foundation of synthetic biology. Biological elements like genetic sequences and protein structures can be systematically assembled and reconfigured with predictable results, analogous to electronic circuit construction. Standardization protocols guarantee interoperability and support the development of sophisticated biological networks.
Applications of Synthetic Biology
Synthetic biology demonstrates remarkable versatility with far-reaching implications. Medical applications include engineered cellular therapies for disease treatment. Agricultural implementations focus on developing crops with superior nutritional profiles and natural pest resistance. Environmental applications showcase particular promise for bioremediation of contaminated ecosystems.
These selected examples merely illustrate the expansive potential of this revolutionary discipline, with novel applications continually surfacing.
Tools and Technologies Used
Specialized instrumentation drives synthetic biology investigations. Precision DNA synthesis and sequencing platforms facilitate meticulous genetic blueprint creation and analysis. Advanced genome editing systems, including CRISPR-Cas9 technology, provide unprecedented control over genetic modifications. These sophisticated instruments empower researchers to construct and evaluate biological systems with exceptional fidelity.
Ethical Considerations in Synthetic Biology
Transformative technologies invariably raise important ethical questions. Paramount concerns include potential ecological impacts and the necessity for comprehensive safety measures. The scientific community and regulatory bodies must carefully evaluate long-term consequences while establishing responsible implementation frameworks.
Intellectual property distribution and universal access to synthetic biology resources demand thoughtful management to ensure equitable benefit sharing across global communities.
The Future of Synthetic Biology
Synthetic biology stands poised to confront critical global issues through innovative solutions. Ongoing technological refinement and intensified interdisciplinary collaboration will catalyze groundbreaking developments. This discipline promises to transform multiple industries, from medical science to ecological conservation.
Emerging research domains including sustainable biofuel generation and advanced agricultural systems anticipate substantial progress in forthcoming years.
Optimizing Metabolic Pathways for Enhanced Nutrient Uptake and Utilization
Understanding Metabolic Pathways
Metabolic processes constitute elaborate biochemical networks that convert nutritional inputs into cellular energy and structural components. These fundamental systems influence all biological functions from organismal development to pathological vulnerabilities. Comprehensive pathway analysis reveals critical insights into nutritional energy conversion mechanisms.
Metabolic networks exhibit extensive interconnectivity, with each biochemical transformation influencing multiple parallel processes through sophisticated regulatory feedback. This complex integration enables dynamic resource management and environmental adaptation.
Nutrient Uptake Mechanisms
Effective nutrient absorption serves as the foundation for metabolic efficiency. Cellular membranes employ specialized transport systems including ATP-dependent active transport for uphill concentration gradients and facilitated diffusion for downhill movement. Uptake efficiency depends on multiple variables including nutrient concentration gradients, transporter protein availability, and membrane integrity.
Compromised absorption mechanisms frequently lead to nutritional deficiencies and metabolic dysfunction.
Enzymatic Regulation of Pathways
Metabolic flow is precisely controlled through enzymatic modulation. These biological catalysts accelerate specific reactions while responding to allosteric effectors, signaling molecules, and post-translational modifications. Such dynamic regulation permits rapid cellular adaptation to fluctuating nutritional availability and metabolic demands.
During nutrient abundance, utilization pathways activate while non-essential routes experience suppression, demonstrating the system's remarkable efficiency.
Impact of Genetic Variations on Metabolism
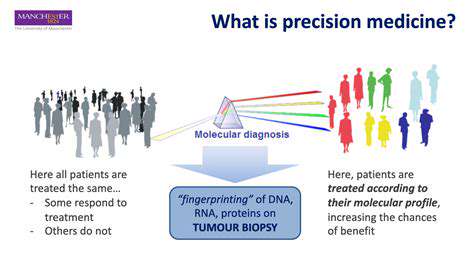
Genetic polymorphisms substantially influence metabolic performance through altered enzyme kinetics, affecting nutrient processing at multiple levels. This genetic variability contributes to differential disease susceptibility and nutritional response patterns.
Personalized medical approaches increasingly incorporate metabolic genetic profiling to optimize therapeutic interventions and dietary recommendations.
Dietary Strategies for Optimizing Metabolic Function
Nutritional intake significantly shapes metabolic regulation. Balanced diets supplying essential micronutrients and macronutrients support optimal biochemical pathway operation. Certain dietary patterns demonstrate protective metabolic effects, as evidenced by epidemiological studies of traditional Mediterranean eating habits.
Strategic nutrient timing further enhances metabolic outcomes, with pre-exercise protein consumption exemplifying targeted pathway activation for muscular anabolism.
Metabolic Engineering for Enhanced Nutrient Utilization
Directed metabolic pathway modification represents a powerful tool for agricultural and industrial applications. Microbial pathway engineering enhances substrate utilization efficiency and valuable compound biosynthesis. This approach involves strategic manipulation of genetic and enzymatic network components to achieve desired metabolic outcomes.
Clinical Implications and Therapeutic Applications
Metabolic dysregulation underlies numerous pathological conditions including metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disorders. Pathway analysis informs targeted therapeutic development, particularly in precision medicine applications. Current research focuses on identifying critical regulatory nodes for therapeutic modulation, aiming to restore physiological metabolic homeostasis.