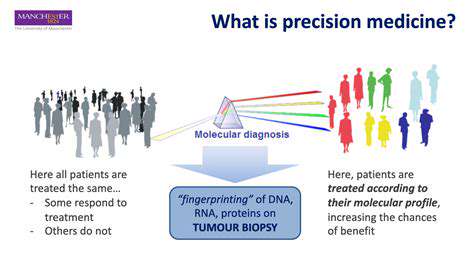
Modern medicine is experiencing a radical transformation, shifting from generic treatments to highly customized solutions. This revolution stems from breakthroughs in genomics, proteomics, and related technologies, enabling therapies to be adapted to each patient's genetic profile, lifestyle, and environmental influences. Such precision medicine aims to enhance treatment success rates, minimize side effects, and create a more streamlined healthcare framework.
Personalized therapeutics extend beyond medication adjustments; they involve bespoke diagnostic tools, targeted treatments, and even biological solutions designed for individual patients. This demands an in-depth grasp of personal biology to predict treatment responses and prevent complications.
The Role of Synthetic Biology
Synthetic biology serves as a cornerstone for personalized medicine. By designing and constructing biological components, it enables therapies tailored to genetic profiles. This technology facilitates targeted drug delivery, personalized vaccines, and engineered cellular treatments.
Customizing Drug Delivery Systems
A key application of synthetic biology is developing personalized drug delivery mechanisms. Engineered carriers can direct medications to affected cells, sparing healthy tissue. This precision boosts treatment effectiveness while reducing dosage and side effects.
These systems can be programmed to release drugs at specific rates and locations, offering unprecedented control. Such customization represents a major leap forward in medical treatment.
Creating Personalized Vaccines
Synthetic biology enables vaccine customization based on individual immune responses and genetic data. This approach proves particularly valuable against rapidly evolving pathogens, allowing swift development of targeted immunizations.
Engineering Cellular Therapies
The field shows remarkable potential for creating patient-specific immune cells to combat diseases. Tailored T-cell therapies could revolutionize cancer treatment by precisely targeting malignant cells while preserving healthy tissue.
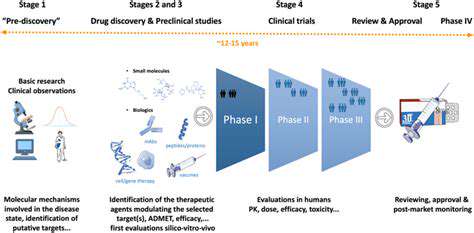
Accelerating Drug Discovery
Beyond treatment customization, synthetic biology speeds up drug development through rapid testing platforms. This acceleration is crucial for addressing emerging health threats promptly.
Ethical Considerations
While promising, synthetic biology raises important ethical questions regarding data privacy, equitable access, and potential risks. Responsible implementation requires ongoing dialogue among scientists, ethicists, and policymakers to ensure benefits outweigh potential drawbacks.
Customizing Immunotherapy with Synthetic Biology
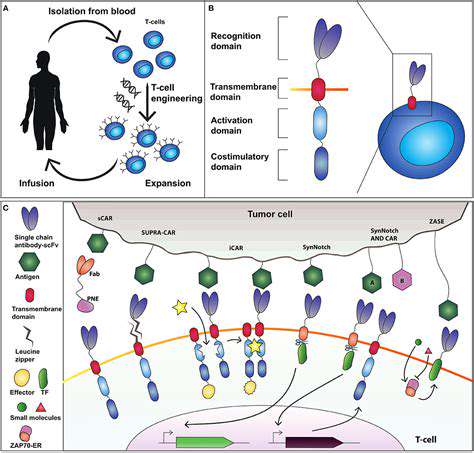
Harnessing the Power of Synthetic Biology
Synthetic biology transforms immunotherapy by enabling customized biological systems. Through genetic circuit manipulation, researchers enhance existing treatments and develop novel approaches with improved precision. This innovation promises better outcomes with reduced side effects.
Tailoring Immunotherapy for Specific Cancers
The technology allows therapies to target unique cancer markers. This specificity increases effectiveness while decreasing collateral damage to healthy cells.
Enhancing Immune Cell Functionality
Genetic modifications can boost immune cell performance. Enhanced T-cells and NK cells demonstrate greater cancer-fighting capabilities, potentially improving treatment success rates.
Developing Targeted Delivery Systems
Precision delivery mechanisms direct immune cells specifically to tumors, maximizing therapeutic impact.
Improving Immune Response Durability
Engineered memory cells may provide longer-lasting protection against cancer recurrence. Such sustained responses could significantly improve patient prognosis.
Addressing Immunotherapy Resistance
Synthetic approaches may overcome cancer's defense mechanisms. This breakthrough could solve one of immunotherapy's greatest challenges.
Challenges and Future Directions
Data Integration Complexities
Combining diverse data types requires standardized formats and rigorous quality control. Effective governance ensures reliable, actionable information.
Data Security Imperatives
Protecting sensitive information demands comprehensive safeguards. Security awareness must permeate organizational culture.
Storage Optimization
Choosing appropriate storage solutions balances performance with cost. Strategic planning prevents infrastructure limitations.
Visualization Tools
Intuitive interfaces transform complex data into understandable formats. Effective visualization drives informed decision-making.
Quality Assurance
Rigorous validation processes maintain data integrity. Accurate information forms the foundation for sound conclusions.
Collaborative Ecosystems
Breaking down data silos enhances organizational effectiveness. Shared access multiplies data's potential value.
Emerging Technologies
AI and machine learning open new analytical possibilities. Staying current with innovations maintains competitive advantage.