Identifying Patients Most Likely to Benefit
Identifying Key Factors for Personalized Treatment
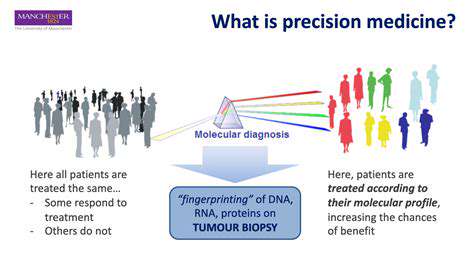
Personalized medicine's cornerstone lies in discerning which patients will respond best to specific therapies. This demands a nuanced grasp of each individual's unique traits, spanning genetic predispositions, daily habits, and clinical background. By accurately mapping these critical elements, healthcare providers can customize interventions, boosting effectiveness while reducing unwanted reactions. Spotting these tendencies early often proves decisive for treatment success and patient comfort.
Moreover, appreciating how different elements interact remains vital. Genetic differences, for instance, can alter how drugs are processed, affecting both their potency and safety profile. Daily choices like nutrition and physical activity similarly mold a person's therapeutic response. Pinpointing these variables creates a blueprint for individualized care plans, elevating results and patient satisfaction.
The Role of Biomarkers in Prediction
Biomarkers—quantifiable biological signals—serve as crucial compasses for predicting treatment suitability. These indicators, ranging from DNA alterations to protein concentrations, offer windows into a patient's condition and probable therapy response. Through biomarker analysis, clinicians gain foresight about treatment potential and risks, empowering smarter therapeutic selections.
Biomarker applications are undergoing rapid transformation. Ongoing research continuously uncovers novel, more precise markers, enabling sharper predictions about intervention outcomes. Such progress directly translates to safer, more effective patient care.
Analyzing Patient Medical History and Lifestyle
A thorough review of medical records forms the bedrock of treatment suitability assessment. This includes scrutinizing past diagnoses, surgical interventions, and prior therapy responses. When combined with lifestyle examination—diet patterns, exercise regimens, tobacco use—this creates a multidimensional health portrait that predicts treatment compatibility.
Lifestyle factors frequently intersect with genetic tendencies and disease trajectories. Weaving this information into diagnostics fosters comprehensive understanding of patient needs and probable treatment reactions, becoming indispensable for therapy customization.
Utilizing Advanced Diagnostic Tools
Cutting-edge diagnostic technologies like next-generation sequencing and protein mapping are reshaping patient selection paradigms. These tools decode disease mechanisms at molecular levels, revealing unique patient characteristics. Such granular understanding facilitates development of precisely targeted treatments aligned with individual biological profiles.
Sophisticated data analysis from these instruments enables accurate prediction of treatment responses and complication risks, markedly improving intervention safety. Early detection and interpretation of these factors proves pivotal for optimal patient results.
Developing Predictive Models for Personalized Treatment
Sophisticated predictive frameworks incorporating biomarkers, clinical history, and lifestyle factors are emerging to identify ideal treatment candidates. These models employ complex algorithms to process multifaceted datasets, yielding actionable insights about individual patients. Their evolution through continuous data integration ensures sustained accuracy in matching patients with optimal therapies.
Ongoing refinement of these analytical tools enhances healthcare efficiency while elevating patient outcomes through increasingly precise treatment pairing.
The Future of Biomarker-Guided Therapy
Harnessing the Power of Molecular Signatures
Biomarker-driven treatment marks a healthcare revolution, replacing blanket approaches with precision medicine. By detecting unique molecular patterns in patients' biological samples, clinicians can calibrate interventions for maximum impact with minimal harm. This proves especially transformative in oncology, where tumors with similar appearances may behave radically differently at cellular levels.
Identifying these molecular distinctions enables selection of therapies targeting specific tumor weaknesses, improving outcomes while avoiding ineffective or damaging treatments. Such customization promises better patient results alongside healthcare savings.
Unveiling the Potential of Liquid Biopsies
Liquid biopsy technology—analyzing tumor DNA fragments in blood—represents a diagnostic breakthrough. These non-invasive tests provide real-time disease monitoring, treatment assessment, and early recurrence detection. Their ability to map tumor genetics without invasive procedures makes them invaluable, particularly for patients unsuitable for traditional biopsies.
Continuous ctDNA tracking allows dynamic treatment modifications, while early residual disease detection enables preemptive interventions before progression occurs.
Personalized Cancer Treatment Strategies
Biomarker analysis underpins customized cancer care. By identifying genetic mutations or protein markers, clinicians can select precision therapies that target malignant cells while sparing healthy tissue. This approach enhances effectiveness, reduces resistance risks, and minimizes side effects.
Treatment personalization based on individual profiles optimizes outcomes and life quality for cancer patients. Predictive capability regarding treatment response and resistance patterns facilitates proactive care adjustments.
Improving Drug Development and Discovery
Biomarker research accelerates pharmaceutical innovation. Identifying markers linked to disease progression or treatment response enables development of targeted drugs. This streamlined approach reduces clinical trial timelines and resource requirements while improving success rates through precise patient selection.
Integrating Biomarkers into Routine Clinical Practice
Mainstreaming biomarker analysis requires substantial infrastructure investment—advanced lab equipment and specialized personnel—to ensure reliable, timely testing. Standardized protocols must be established to guarantee consistent, high-quality implementation.
Wider adoption hinges on increasing test accessibility and affordability. Researcher-clinician-industry collaboration is essential to translate innovations into everyday practice.
Addressing Ethical and Societal Implications
Biomarker implementation raises important ethical questions. Ensuring equitable access and mitigating analytical biases are crucial to prevent healthcare disparities. Genetic data protection requires robust security frameworks. Transparent stakeholder dialogue must guide responsible, fair application of these advancements.
Future Directions and Research Priorities
Continued biomarker research remains imperative. Discovering novel markers, refining existing techniques, and improving analytical cost-efficiency will drive wider adoption. Exploration of preventive applications and early disease detection will dominate future investigations.
Innovative diagnostic and therapeutic development based on biomarker profiles will revolutionize healthcare delivery. Sustained collaboration across research, clinical, and industry sectors remains vital to realizing biomarker medicine's full potential.