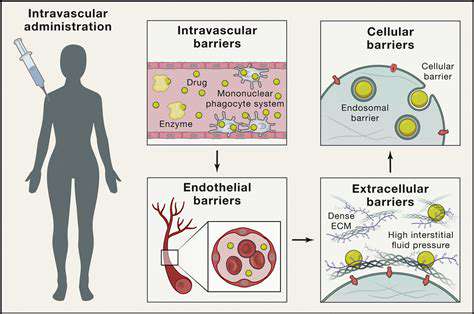
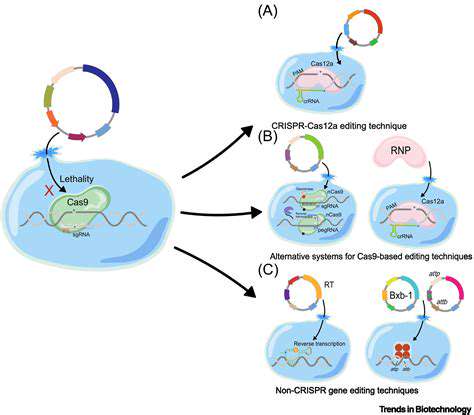
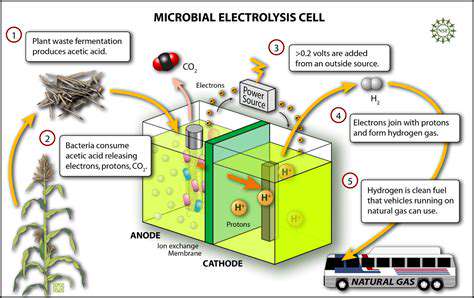
Synthetic biology, this rapidly evolving discipline, is fundamentally transforming biotechnology's landscape. Rather than merely observing nature, scientists now actively redesign biological components - genes, proteins, and metabolic pathways - to create novel functionalities. This paradigm shift enables solutions for pressing global challenges, from sustainable energy to breakthrough medicines.
What makes this field unique is its interdisciplinary nature, blending engineering precision with biological complexity. Researchers don't just study life; they reprogram it, creating biological systems that perform customized tasks with remarkable precision.
The Engineering of Biological Systems
At synthetic biology's core lies a revolutionary approach: treating biological components as programmable modules. Imagine constructing with molecular Legos where each piece serves a specific function. By combining these building blocks in novel configurations, scientists create organisms with precisely tailored behaviors - whether producing therapeutic compounds or detecting environmental pollutants.
This engineering mindset represents a fundamental departure from traditional biotechnology. Where conventional methods might modify existing systems, synthetic biology builds entirely new biological circuits from the ground up.
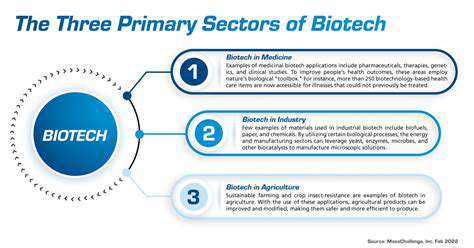
Commercial Applications: From Pharmaceuticals to Agriculture
The business potential of this technology spans multiple industries. In drug development, engineered microorganisms now produce complex molecules that were previously inaccessible or prohibitively expensive. This innovation could dramatically reduce medication costs while increasing production scalability - a potential game-changer for global healthcare access.
Agricultural applications show equal promise. Scientists are developing crops with built-in drought resistance and enhanced nutritional profiles. These advances couldn't come at a more critical time, as climate change threatens traditional farming yields worldwide.
Addressing Global Challenges with Biological Solutions
Beyond healthcare and agriculture, synthetic biology offers solutions for environmental crises. Engineered organisms can convert agricultural waste into clean biofuels, potentially reducing fossil fuel dependence. Perhaps more impressively, custom-designed microbes are being deployed to break down persistent environmental pollutants, offering new hope for contaminated ecosystems.
These applications demonstrate synthetic biology's unique strength: creating sustainable solutions that work with nature rather than against it.
Ethical Considerations and Regulatory Frameworks
With such powerful technology comes significant responsibility. The ability to redesign life raises profound ethical questions that demand thoughtful discussion. Establishing appropriate safeguards without stifling innovation represents one of our greatest challenges as this field matures.
Effective governance will require ongoing dialogue between scientists, policymakers, and the public. Only through transparent collaboration can we ensure these technologies develop responsibly while reaching their full potential.

Developing Robust Business Models for Synthetic Biology
Defining the Core Business
A successful venture begins with razor-sharp focus. Companies must articulate exactly which problem they solve and for whom. This clarity becomes the North Star guiding all subsequent decisions, from product development to marketing strategies. Without it, even the most innovative technology risks becoming a solution in search of a problem.
Thorough market analysis separates viable opportunities from scientific curiosities. Understanding competitors' strengths and weaknesses allows businesses to position themselves strategically in the marketplace.
Understanding the Target Market
Truly knowing your customers requires moving beyond demographics. Successful companies uncover not just who buys their products, but why they need them - the emotional drivers behind purchasing decisions. This depth of understanding informs everything from product features to marketing messages.
Market segmentation proves particularly valuable in synthetic biology, where applications span multiple industries with vastly different needs and regulations.
Crafting a Sustainable Revenue Model
Diversification separates thriving businesses from vulnerable ones. The most resilient companies develop multiple income streams - perhaps combining product sales with licensing fees and service contracts. This financial flexibility becomes especially crucial in emerging fields where market conditions can shift rapidly.
Managing Costs Effectively
Financial discipline enables innovation. By identifying and eliminating inefficiencies, companies free up resources for strategic investments. Smart cost management isn't about cutting corners - it's about maximizing the impact of every dollar spent.
Emerging technologies particularly benefit from lean operations, allowing more runway to achieve technological and commercial milestones.
Building a Scalable Infrastructure
Growth potential depends on foundational strength. Systems designed for today's needs often buckle under tomorrow's demands. Forward-thinking companies invest in adaptable infrastructure that grows with their ambitions, whether in manufacturing capacity or computational resources.
Maintaining a Strong Competitive Advantage
In fast-moving fields, standing still means falling behind. The most successful companies institutionalize innovation, creating cultures that continuously seek better solutions. They monitor industry trends while anticipating customer needs before customers themselves recognize them.
Protecting intellectual property while fostering collaboration represents a delicate but necessary balance in synthetic biology's collaborative ecosystem.
Exploring Key Sectors for Commercial Application
Synthetic Materials in Construction
The construction industry increasingly adopts advanced materials that combine strength with sustainability. New polymer composites enable lighter, more durable structures while reducing environmental impact. These innovations address two critical needs simultaneously: improved performance and reduced carbon footprint.
From self-healing concrete to insulation materials with unprecedented thermal properties, synthetic materials are redefining what's possible in building design and construction.
Synthetic Textiles in Apparel and Fashion
Modern fabrics blend performance with aesthetics like never before. Technical textiles now regulate temperature, resist stains, and even monitor vital signs - all while maintaining fashion-forward designs. This convergence of function and style drives innovation across the apparel industry.
Athleisure wear exemplifies this trend, where clothing must perform during workouts while remaining stylish enough for social settings.
Synthetic Polymers in Packaging and Logistics
The packaging revolution balances protection with sustainability. New biodegradable materials maintain product safety while addressing environmental concerns. Smart packaging goes further, incorporating sensors that monitor freshness or tampering - adding unprecedented value to supply chains.
These advances respond to growing consumer demand for sustainable options without compromising product quality or safety.
Synthetic Rubber in Automotive and Transportation
Tire technology illustrates synthetic materials' transformative potential. Modern compounds improve fuel efficiency while enhancing safety in all weather conditions. These innovations contribute significantly to reducing transportation's environmental impact while improving performance.
Beyond tires, synthetic rubber enables numerous automotive components that withstand extreme conditions while reducing vehicle weight.
Synthetic Leather in the Furniture and Interior Design Industry
Today's synthetic leathers challenge perceptions. Advanced materials replicate natural leather's look and feel while offering superior durability and easier maintenance. This combination of aesthetics and practicality drives widespread adoption across residential and commercial spaces.
Ethical consumers particularly appreciate cruelty-free alternatives that don't sacrifice quality or style.
Synthetic Fibers in the Aerospace Industry
Aviation's relentless pursuit of lighter, stronger materials finds perfect partners in advanced synthetics. Composite materials enable aircraft to fly further using less fuel while maintaining structural integrity. These weight savings translate directly into reduced emissions and operating costs.
As air travel demand grows, such innovations become increasingly critical for sustainable industry growth.
Synthetic Biomaterials in Healthcare
Medical technology advances through materials science. From biodegradable stents to antimicrobial wound dressings, synthetic biomaterials improve patient outcomes while reducing complications. Perhaps most exciting are materials that actively promote healing while gradually dissolving, eliminating the need for removal surgeries.
These innovations demonstrate synthetic biology's potential to revolutionize patient care across numerous medical specialties.
The Role of Collaboration and Infrastructure in the Ecosystem
Collaboration in a Thriving Ecosystem
True innovation thrives on connection. The most significant breakthroughs often emerge from interdisciplinary collaborations that combine diverse perspectives. Shared knowledge accelerates progress more effectively than isolated efforts ever could.
In synthetic biology, these partnerships prove particularly valuable, as challenges often require expertise spanning biology, engineering, and business disciplines.
Infrastructure as the Foundation
Physical and digital infrastructure forms the backbone of innovation. Advanced research facilities enable experimentation at scales previously unimaginable, while cloud computing allows global collaboration in real-time. This infrastructure democratizes access to cutting-edge tools, allowing smaller organizations to compete with established players.
Investment in infrastructure yields compounding returns, as each improvement enables further advancements across the entire field.
Navigating Regulatory Landscapes
Clear, science-based regulations provide essential guardrails for responsible innovation. The most effective frameworks balance safety with flexibility, adapting to new discoveries while maintaining consistent standards.
Engaging regulators early in development helps align new technologies with existing frameworks, smoothing the path to commercialization.
Cultivating a Supportive Environment
Innovation ecosystems require nurturing. Access to capital, mentorship, and professional networks all contribute to entrepreneurial success. Perhaps most importantly, a culture that embraces calculated risk-taking enables bold ideas to flourish.
Educational institutions play a crucial role in this ecosystem, preparing the next generation of scientists and entrepreneurs to advance the field responsibly.