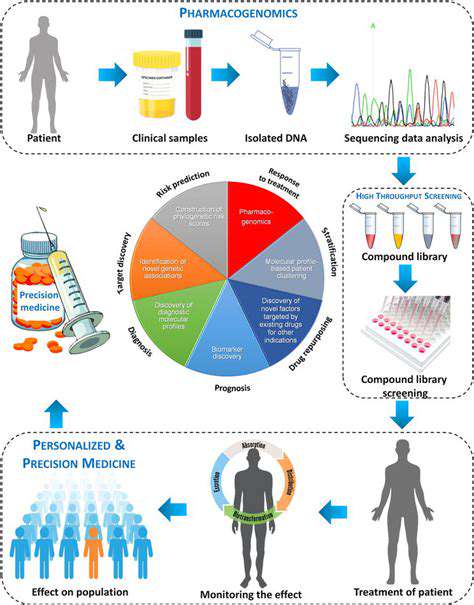
The Economic Benefits of Sustainability
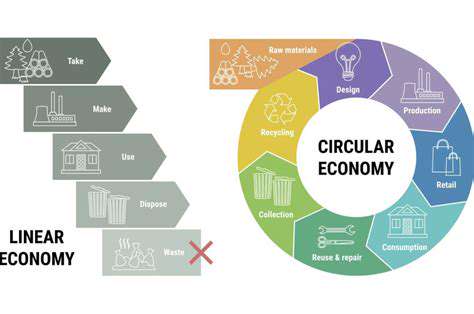
Transitioning to a sustainable economy presents significant economic opportunities. Investing in renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and green technologies can create new jobs, boost innovation, and foster economic growth in the long run. This shift also reduces reliance on finite resources, decreasing vulnerability to price volatility and supply chain disruptions.
Companies embracing sustainable practices often see improvements in brand reputation, attracting environmentally conscious consumers and investors. This demonstrates that sustainability is not just a social responsibility, but a smart business strategy.
Protecting Biodiversity and Ecosystems
Healthy ecosystems are essential for human well-being, providing clean air and water, regulating climate, and supporting biodiversity. Protecting and restoring these vital systems is crucial to ensuring a healthy planet for future generations. The loss of biodiversity threatens the delicate balance of nature and can have cascading effects on entire ecosystems.
Protecting endangered species and their habitats is paramount. This includes conserving forests, oceans, and wetlands, which are vital for maintaining biodiversity and supporting numerous species.
The Role of Government Policies
Government policies play a critical role in driving environmental progress. Implementing carbon pricing mechanisms, investing in renewable energy infrastructure, and enacting regulations to reduce pollution are key steps in achieving sustainability goals. Stronger environmental regulations can incentivize businesses to adopt sustainable practices and encourage innovation in green technologies.
International cooperation is also essential to address global environmental challenges. Sharing best practices, coordinating policies, and supporting developing nations in their transition to sustainability are crucial components of a global effort.
Individual Actions for a Greener Future
Individual actions can significantly contribute to environmental protection. Making conscious choices about consumption, reducing waste, and supporting sustainable products and businesses can all make a difference. Adopting energy-efficient practices in our homes, using public transportation, and reducing our carbon footprint through mindful choices are all essential steps.
Raising awareness about environmental issues and engaging in discussions with others are critical to fostering a culture of sustainability. Educating ourselves and others about the importance of environmental protection can lead to positive change.
Technological Advancements for a Sustainable World
Technological advancements offer promising solutions for environmental challenges. Innovations in renewable energy, waste management, and sustainable agriculture can dramatically reduce our environmental impact. New technologies offer the potential to revolutionize our approach to resource use and waste disposal.
Developing and implementing these technologies effectively requires ongoing research and development. Continued investment in green technologies will be vital to driving a sustainable future.
The Interconnectedness of Environmental Issues
Environmental issues are deeply interconnected. Climate change, deforestation, pollution, and biodiversity loss are all linked, and addressing one often impacts the others. A holistic approach that considers these interconnectedness is essential for developing effective solutions. Recognizing the interdependence of environmental problems allows for a more comprehensive and effective approach to sustainability.
Addressing the complexity of environmental challenges requires collaboration between scientists, policymakers, businesses, and individuals. This collaborative approach is critical to developing and implementing sustainable solutions.
Sustainable Manufacturing Practices for Pharmaceuticals
Minimizing Environmental Impact
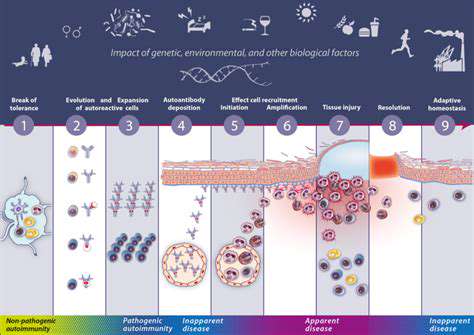
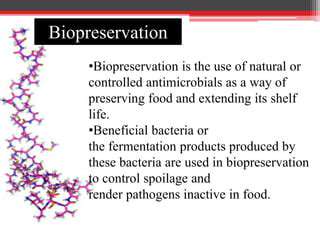
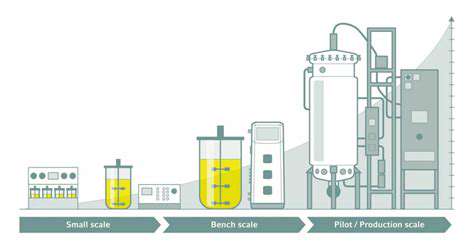
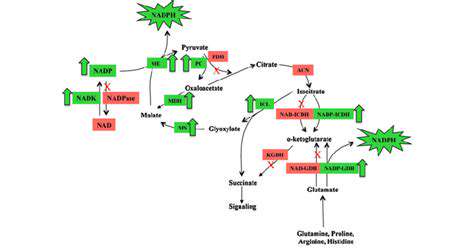
Sustainable manufacturing practices in the pharmaceutical industry prioritize minimizing the environmental footprint of drug production. This involves reducing waste generation, conserving water and energy resources, and employing eco-friendly materials. Minimizing chemical waste and utilizing recycled materials are crucial steps in achieving this goal. Careful consideration must be given to the entire lifecycle of the product, from raw material sourcing to final disposal, to identify and mitigate environmental risks.
Implementing closed-loop systems, where byproducts are reused as inputs, is a key strategy. This reduces the demand for virgin materials and minimizes the environmental burden associated with their extraction and processing. Furthermore, optimizing energy consumption through the adoption of renewable energy sources and energy-efficient technologies can significantly reduce carbon emissions and promote sustainability.
Resource Efficiency
Pharmaceutical manufacturing often involves substantial consumption of water, energy, and raw materials. Sustainable practices focus on optimizing resource utilization to reduce waste and consumption. This includes implementing water-efficient technologies, such as advanced filtration systems, and energy-efficient equipment to minimize energy consumption across the entire production process. Careful process optimization and lean manufacturing principles can reduce material waste and improve overall efficiency.
Waste Reduction and Management
Minimizing waste generation is paramount in sustainable manufacturing. This involves implementing strategies to reduce the amount of waste produced at each stage of the manufacturing process, from raw material procurement to final product packaging. Proper waste segregation, recycling, and composting programs are essential components of an effective waste management system. Pharmaceutical companies must also adhere to stringent regulations regarding hazardous waste disposal to protect human health and the environment.
Green Chemistry Principles
Green chemistry principles guide the design of chemical processes and products to minimize or eliminate the use and generation of hazardous substances. This approach emphasizes the use of safer solvents, catalysts, and reagents, promoting atom efficiency to reduce waste, and designing safer products. Implementing these principles throughout the entire drug development lifecycle, from research and development to manufacturing, can significantly reduce environmental impact.
Supply Chain Sustainability
Sustainable manufacturing extends beyond the factory walls to encompass the entire supply chain. Companies need to collaborate with suppliers who adhere to ethical and environmental standards, ensuring the responsible sourcing of raw materials. This includes evaluating the environmental impact of the entire supply chain and working with suppliers who share a commitment to sustainability. Transparency and traceability throughout the supply chain are crucial for identifying and addressing potential environmental risks.
Employee Training and Awareness
Empowering employees with the knowledge and skills necessary to implement sustainable practices is vital. Comprehensive training programs should be established to educate employees about the principles of sustainable manufacturing and their role in achieving sustainability goals. Raising awareness about the environmental impact of their work and encouraging participation in sustainability initiatives are crucial for fostering a culture of sustainability within the organization. This includes training on waste reduction techniques, energy conservation measures, and proper hazardous material handling.
Regulatory Compliance and Certifications
Pharmaceutical companies must adhere to strict regulatory requirements and industry standards for sustainable practices. Obtaining relevant certifications and adhering to regulatory guidelines is essential for maintaining credibility and demonstrating commitment to sustainability. These certifications can help companies demonstrate their adherence to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles. This includes compliance with environmental regulations, reporting requirements, and product safety standards.