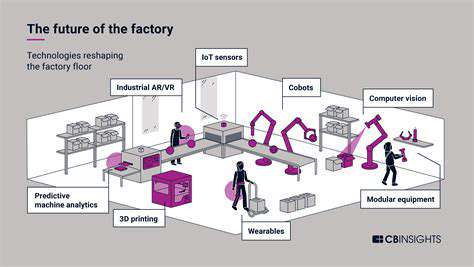
Automation and the Future of Work
Industries worldwide are undergoing a profound transformation due to the integration of automation and robotics, affecting sectors ranging from manufacturing to healthcare. This shift creates both remarkable opportunities and formidable challenges for the workforce of tomorrow. As machines assume responsibility for repetitive tasks, human workers must increasingly focus on roles demanding creativity and complexity. This evolution underscores the importance of reskilling and upskilling initiatives to prepare employees for the emerging economic paradigm.
While the potential for enhanced productivity is undeniable, the societal implications of widespread automation demand careful scrutiny. Proactive measures are needed to address concerns regarding job displacement, the strengthening of social safety nets, and the ethical dimensions of increasingly sophisticated artificial intelligence.
Robotics in Manufacturing
Modern manufacturing has become dependent on robotics, which enable unprecedented precision, higher output volumes, and reduced operational costs. Automated systems function continuously without fatigue, optimizing operational uptime and productivity. From assembly processes to quality assurance, robotic technologies are revolutionizing production methodologies, resulting in faster and more accurate manufacturing across diverse product categories.
The implementation of robotic solutions has also stimulated innovation in material handling, creating more responsive and adaptable production systems. This flexibility proves essential for meeting the dynamic requirements of contemporary markets. Industry experts anticipate continued advancement, with next-generation robots capable of executing increasingly sophisticated operations.
Automation in Customer Service
Customer service operations are being reshaped by automation, resulting in quicker response times, round-the-clock availability, and enhanced operational efficiency. Intelligent virtual assistants and AI-driven platforms now manage routine customer inquiries, allowing human representatives to concentrate on more nuanced cases. This optimized approach can dramatically decrease customer wait periods while elevating overall service quality.
While automation improves service efficiency, the intrinsic value of human interaction remains paramount. Finding the optimal equilibrium between automated solutions and personalized human engagement will prove critical for sustaining customer satisfaction and brand loyalty.
Ethical Considerations of Automation
The accelerating development of automation technologies presents numerous ethical dilemmas. Issues including workforce displacement, algorithmic bias, and the deployment of robots in potentially hazardous applications require urgent attention. The creation and implementation of these technologies must be governed by ethical frameworks and societal priorities.
Prioritizing fairness and equality in automation adoption is essential. Comprehensive strategies for workforce retraining, combined with measures to prevent widening economic inequality, should form integral components of any automation implementation plan.
The Role of Humans in an Automated Future
Despite automation's growing prevalence, human workers maintain irreplaceable value. People excel in areas requiring innovation, analytical reasoning, complex decision-making, and emotional awareness. In the automated workplaces of tomorrow, human oversight and management of technological systems will become increasingly vital.
The workforce must cultivate skills that complement automation, including advanced problem-solving capabilities, leadership competencies, and creative thinking. Such development will ensure continued relevance in an ever-changing technological environment.
Automation and Economic Growth
Automation possesses the capacity to stimulate substantial economic expansion through productivity gains across multiple sectors. This enhanced output can translate to reduced consumer costs, increased corporate profitability, and ultimately, improved living standards. However, realizing these benefits requires careful management to ensure equitable distribution across society.
Successful automation integration demands strategic planning and investment in infrastructure, educational programs, and workforce development initiatives. Such proactive measures can help minimize potential negative consequences while maximizing the long-term economic advantages of technological progress.
The Impact on Different Industries
Nearly every industry faces disruption from automation, though the specific effects vary by sector. Manufacturing positions prove particularly vulnerable to automation, while roles requiring sophisticated interpersonal skills and complex problem-solving demonstrate greater resilience.
Sector-specific strategies must be developed to navigate this transformation successfully. This includes fostering innovation ecosystems, supporting employee retraining programs, and implementing policies that promote equal access to opportunities in the automated economy.
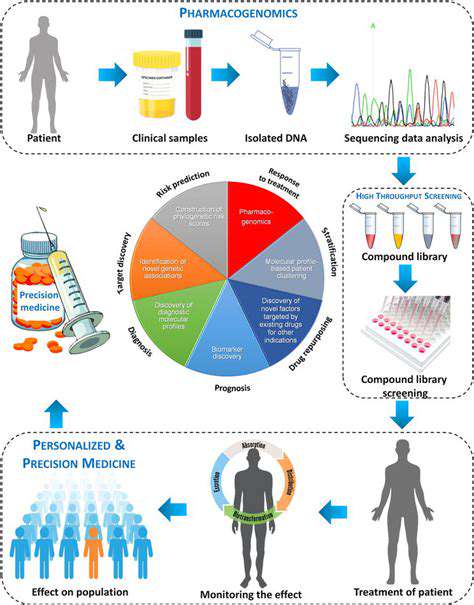
High-Throughput Screening in Specific Therapeutic Areas
High-Throughput Screening in Oncology
High-throughput screening (HTS) serves as a cornerstone of modern oncology research by rapidly assessing extensive compound libraries against cancer cell models. This methodology enables researchers to pinpoint potential anticancer compounds with specific biological activities, from tumor suppression to programmed cell death induction. HTS dramatically accelerates lead compound identification, facilitating the development of innovative cancer treatments.
Automated screening processes reduce human error while maximizing testing capacity. This proves especially valuable in oncology, where cancer's molecular complexity demands comprehensive testing approaches. The capability to evaluate thousands of compounds efficiently helps identify potential solutions for drug-resistant cancers and targeted therapies.
High-Throughput Screening in Infectious Diseases
Addressing global infectious disease challenges, HTS plays a pivotal role in discovering new antimicrobial compounds. Rapid evaluation against diverse pathogens is critical for combating antimicrobial resistance. HTS can reveal compounds that disrupt essential microbial processes, potentially leading to novel treatments and resistance mitigation strategies.
HTS offers distinct advantages in infectious disease research by enabling simultaneous screening against multiple pathogens. This facilitates discovery of either broad-spectrum antimicrobials or compounds targeting specific pathogen vulnerabilities, dramatically accelerating therapeutic development timelines.
High-Throughput Screening in Neurological Disorders
Neurological conditions including Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases present significant therapeutic challenges. HTS provides a powerful tool for identifying potential treatments by screening compounds against relevant disease models. The technology's scalability allows exploration of extensive chemical libraries, increasing the probability of discovering neuroactive compounds that could alleviate symptoms or modify disease progression.
High-Throughput Screening in Cardiovascular Diseases
As leading causes of global mortality, cardiovascular diseases benefit significantly from HTS applications. This approach efficiently identifies potential therapeutic compounds by screening against cardiovascular disease models. Researchers can discover agents capable of improving heart function, reducing vascular inflammation, or inhibiting atherosclerotic development, accelerating the path to clinical trials.
High-Throughput Screening in Metabolic Disorders
Metabolic conditions like diabetes and obesity represent major public health concerns worldwide. HTS enables identification of compounds that modulate metabolic pathways, potentially yielding new treatment options. Screening against metabolic disease models can reveal compounds that enhance insulin response, regulate fat metabolism, or support weight control, paving the way for innovative therapeutic approaches.
High-Throughput Screening in Cancer Drug Resistance
Therapeutic resistance remains a critical challenge in oncology. HTS offers a valuable strategy for identifying compounds that overcome resistance mechanisms. By screening against drug-resistant cancer models, researchers can pinpoint compounds capable of restoring treatment sensitivity, potentially improving patient outcomes. HTS's rapid screening capacity proves particularly valuable in this challenging research area.