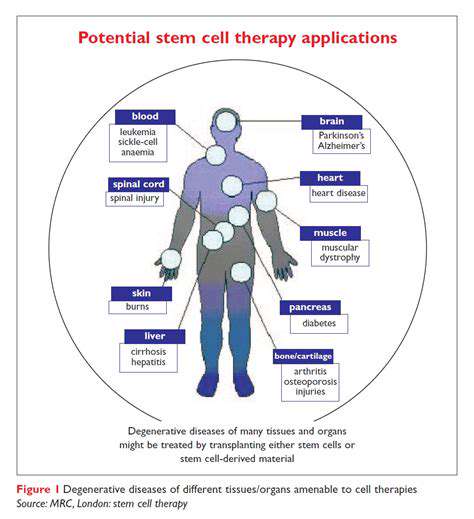
Harnessing Synthetic Biology for Enhanced Crop Traits
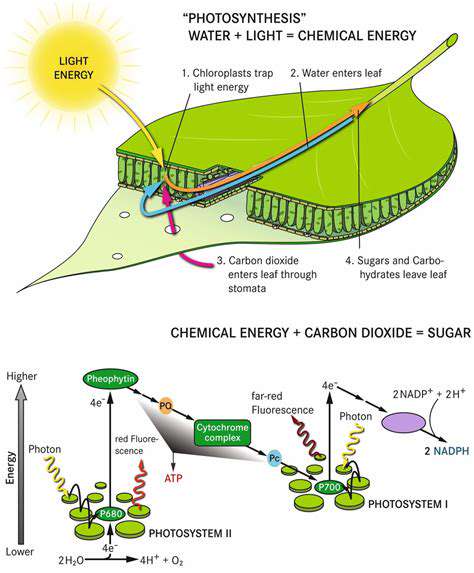
Synthetic biology, a revolutionary field, offers unprecedented opportunities to engineer crops with enhanced traits. By meticulously designing and assembling genetic components, researchers can precisely manipulate plant characteristics, leading to crops that are more resilient to environmental stresses like drought and salinity. This approach allows for the targeted introduction of desirable traits without the need for traditional breeding methods, significantly accelerating the development of improved crop varieties.
Precision Agriculture and Data-Driven Decision Making
The integration of synthetic biology with data analytics promises a new era of precision agriculture. By equipping crops with sensors and biosensors, we can monitor their health and environmental conditions in real-time. This data-driven approach allows for the optimization of resource utilization, reducing input costs and environmental impact while maximizing yield. Predictive models can further anticipate potential threats and trigger appropriate interventions, revolutionizing agricultural practices.
Addressing Nutritional Deficiencies Through Genetic Engineering
Malnutrition remains a significant global challenge, and synthetic biology presents a powerful tool to address this issue. Researchers are exploring ways to engineer crops with enhanced nutritional profiles, fortifying them with essential vitamins and minerals. This targeted approach can contribute significantly to improving public health, particularly in regions where malnutrition is prevalent. The development of crops with higher levels of essential nutrients holds immense potential for improving dietary intake and reducing health disparities.
Improving Pest and Disease Resistance
Crop losses due to pests and diseases represent a substantial economic burden worldwide. Synthetic biology offers a promising avenue to develop crops with inherent resistance to these threats. By introducing genes that confer resistance or by engineering plants to produce natural pesticides, we can safeguard agricultural yields and minimize the need for chemical interventions. This approach can reduce environmental pollution and promote sustainable agricultural practices.
Sustainable Agriculture Through Enhanced Stress Tolerance
Climate change poses significant challenges to global agriculture, leading to increased frequency and severity of droughts, floods, and extreme temperatures. Synthetic biology enables the development of crops with enhanced stress tolerance, allowing them to thrive in challenging environments. By incorporating genes that promote drought resistance, salinity tolerance, or heat tolerance, we can foster more resilient agricultural systems, ensuring food security in the face of environmental uncertainties. This approach has the potential to dramatically improve agriculture's ability to adapt to the changing climate.
Developing Bio-Based Pesticides and Fertilizers
Synthetic biology can be harnessed to create bio-based pesticides and fertilizers, reducing reliance on harmful chemical inputs. By engineering microorganisms to produce natural compounds with pest-control properties, we can develop environmentally friendly alternatives to conventional pesticides. Similarly, synthetic biology can enhance the effectiveness of biofertilizers, promoting plant growth and nutrient uptake. These innovations contribute to sustainable agricultural practices by minimizing environmental impact and promoting ecological harmony.
Targeted Trait Enhancement: From Pest Resistance to Nutrient Uptake
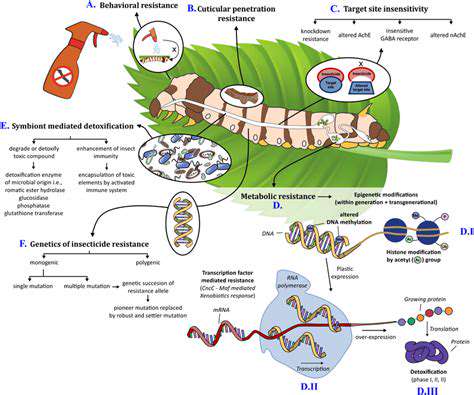
Targeted Trait Enhancement: A New Frontier in Human Potential
Targeted trait enhancement, a field rapidly gaining momentum, focuses on improving specific human characteristics through various methods. This encompasses a broad spectrum of approaches, from lifestyle interventions and nutritional strategies to emerging technologies like gene editing and personalized medicine. The ethical considerations surrounding these advancements are significant and require careful and multifaceted discussion. The potential benefits are substantial, offering the possibility of mitigating genetic predispositions to disease, enhancing cognitive function, and even increasing athletic performance.
One of the primary drivers behind this pursuit is the desire to improve human well-being and resilience. By addressing vulnerabilities and enhancing strengths, we could potentially create a healthier and more productive population. This is not merely about superficial enhancements but about tackling fundamental issues related to health, longevity, and overall quality of life. The field is brimming with possibilities, promising a future where human potential is not constrained by limitations but rather empowered by tailored interventions.
Methodologies and Techniques
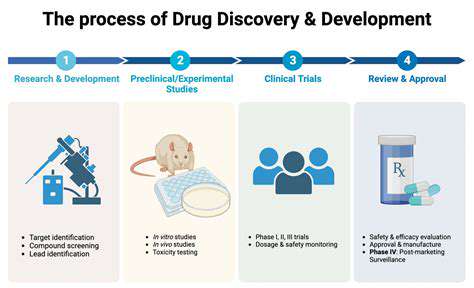
A range of methodologies are being employed in the pursuit of targeted trait enhancement. These span from established practices like structured exercise programs and balanced diets to more innovative approaches such as personalized nutritional plans based on genetic predispositions. The integration of technology is playing a crucial role, with advancements in gene editing technologies like CRISPR offering the potential for unprecedented precision in manipulating genetic material.
Beyond genetic engineering, non-invasive techniques are also gaining traction. These include cognitive training programs designed to improve memory and focus, and neurofeedback therapies that aim to regulate brainwave activity. The future of targeted trait enhancement likely involves a combination of these approaches, leveraging the strengths of each to achieve optimal results. A holistic understanding of the individual is essential, considering both genetic and environmental factors.
Ethical Considerations and Future Implications
The rapid advancement of targeted trait enhancement technologies raises significant ethical considerations. Questions surrounding equitable access, potential for misuse, and the impact on societal structures need careful consideration. Issues of fairness and social justice must be at the forefront of any discussion or implementation of these technologies. Ensuring that these advancements benefit all of humanity and do not exacerbate existing inequalities is paramount.
The future implications of targeted trait enhancement are far-reaching and complex. Will these technologies lead to a more homogenous population, or will they foster greater diversity in human capabilities? How will these advancements affect our understanding of what it means to be human? These questions demand thoughtful dialogue and collaboration among scientists, ethicists, policymakers, and the public to ensure responsible development and application.
Social commerce is rapidly transforming the way consumers interact with brands and make purchasing decisions. This shift is driven by the increasing integration of social media platforms into our daily lives. Consumers are now more likely to discover products and brands through social media channels rather than traditional search engines or online marketplaces. This evolution highlights a significant change in consumer behavior and presents new opportunities for businesses to engage with their target audience.
The Future of Sustainable Agriculture: Addressing Challenges and Ethical Considerations

Sustainable Practices for Enhanced Crop Yields
Adopting sustainable agricultural practices is crucial for boosting crop yields while minimizing environmental impact. These practices encompass a range of techniques, from precision irrigation methods to the strategic use of cover crops. Improved water management, for example, can significantly reduce water waste and enhance crop productivity, leading to higher yields in the long run. Precision agriculture, utilizing technology like GPS and sensors, allows farmers to target specific areas with the precise amount of fertilizer and water needed, minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency.
Integrated pest management (IPM) strategies, which combine various methods like biological controls and crop rotation, can dramatically reduce reliance on harmful pesticides. This approach not only protects the environment but also safeguards human health, ensuring the safety and quality of agricultural products. Furthermore, the adoption of drought-resistant crop varieties and climate-smart agriculture techniques can enhance resilience to the changing climatic conditions.
Technological Advancements in Farming
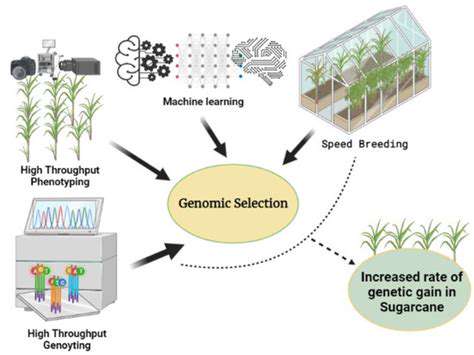
Technological advancements are revolutionizing the agricultural landscape, offering innovative solutions for boosting efficiency and sustainability. Automation, robotics, and data analytics are playing increasingly important roles in optimizing various aspects of farming operations. Precision agriculture, as mentioned earlier, utilizes technology to optimize resource use, leading to improved yields and reduced environmental impact. Moreover, advancements in sensor technology allow farmers to monitor soil conditions, crop health, and weather patterns in real-time, enabling proactive adjustments for optimal growth.
The integration of drones and remote sensing technology provides valuable insights into farm operations. This allows for detailed assessments of crop health and field conditions, enabling early detection of potential issues, such as disease outbreaks or nutrient deficiencies. These technological advancements are poised to transform farming practices, making them more efficient, sustainable, and productive.
The Role of Biodiversity in Sustainable Farming
Maintaining biodiversity is essential for a resilient and sustainable agricultural system. Diverse ecosystems support a wider range of beneficial insects, pollinators, and soil organisms, contributing to overall crop health and reducing the need for synthetic pesticides. Crop diversification, including the integration of cover crops and diverse plant species, enhances soil health, improves nutrient cycling, and promotes pest and disease resistance.
Promoting biodiversity within and around agricultural lands can create a more balanced and robust ecosystem. This approach not only enhances crop productivity but also contributes to the preservation of natural resources and the overall health of the environment. Integrating native plants and habitats into agricultural landscapes can provide crucial resources for pollinators and other beneficial organisms, ultimately supporting a more harmonious and sustainable agricultural system.
Enhancing Water Management in Agriculture
Efficient water management is crucial for sustainable agriculture, especially in regions facing water scarcity. Innovative irrigation techniques, such as drip irrigation and sprinkler systems, can significantly reduce water consumption compared to traditional methods. Implementing water-efficient irrigation strategies is essential for conserving water resources and ensuring long-term agricultural sustainability.
Water conservation is essential for the long-term viability of agriculture, particularly in regions experiencing water stress. Utilizing rainwater harvesting and water recycling technologies can further enhance water use efficiency in agriculture, reducing reliance on freshwater sources. By adopting these innovative water management practices, we can ensure the sustainable production of food for future generations.
Consumer Awareness and Demand for Sustainable Products
Consumer awareness and demand for sustainable agricultural products are driving significant changes in the food industry. Consumers are increasingly seeking out products that are produced using environmentally friendly methods and that prioritize animal welfare and worker rights. This growing demand is creating opportunities for farmers to adopt sustainable practices and market their products to a discerning customer base.
The increasing awareness of the environmental impact of food production is influencing consumer choices. Consumers are more actively seeking out products that align with their values, driving the market towards more sustainable agricultural practices. This shift in consumer behavior is encouraging farmers to prioritize sustainability, impacting the future of agriculture.