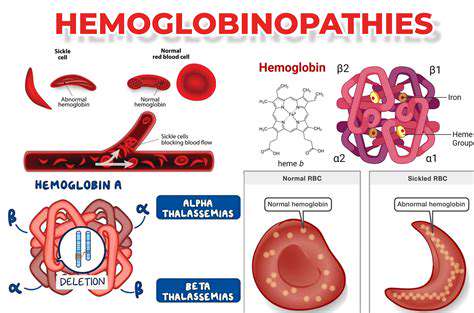
Clinical Trial Design Considerations for Rare Diseases

Participant Selection Criteria
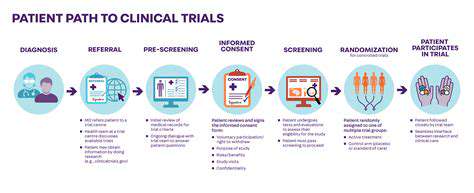
A crucial aspect of clinical trial design is the careful selection of participants. Defining clear and specific inclusion and exclusion criteria is essential to ensure that the study population is homogenous and relevant to the research question. These criteria should be precisely outlined in the study protocol, minimizing the risk of bias and ensuring that the results are generalizable to the target population. This rigorous approach guarantees that the study population accurately reflects the intended patient group, enabling the assessment of treatment efficacy and safety within a well-defined context.
Explicitly outlining criteria for participant recruitment, such as age, gender, medical history, and pre-existing conditions, is vital. This meticulous process helps ensure that the trial participants are representative of the population for whom the treatment or intervention is intended. Clear criteria also aid in minimizing confounding factors, improving the validity of the study results, and enhancing the generalizability of the findings.
Blinding and Randomization Strategies
Employing blinding strategies, whether single or double, is often a critical element of clinical trial design. Blinding helps to minimize bias, both from participants and researchers, ensuring a more objective assessment of treatment effects. This approach enhances the reliability and validity of the study findings. This practice is especially vital in evaluating subjective outcomes, like pain levels or quality of life.
Randomization is another critical component of clinical trial design. Random assignment of participants to treatment groups helps to balance baseline characteristics across groups, effectively minimizing confounding variables. This crucial process ensures that any observed differences between groups are attributable to the treatment or intervention and not to pre-existing differences in the participants. This unbiased approach promotes the validity and reliability of the study results.
Sample Size Calculation
Careful sample size calculation is essential for ensuring the study has sufficient power to detect a clinically meaningful difference between treatments, if one exists. Insufficient power can lead to a failure to detect a real effect, whereas an excessively large sample size can be wasteful and increase the cost and duration of the trial. Accurate calculation involves considering factors like the anticipated effect size, variability within the population, and the desired level of statistical significance.
Determining the appropriate sample size is crucial for the validity and reliability of the clinical trial outcomes. A sample size that is too small may result in a study that cannot detect a meaningful difference, while a sample size that is too large may be unnecessary and increase the study's cost and duration. Careful consideration of these factors is critical for the successful execution of any clinical trial.
Data Collection and Management
Robust data collection methods are paramount for the integrity of a clinical trial. Clearly defined data collection tools, such as questionnaires, standardized assessments, or laboratory tests, are necessary to ensure the consistency and accuracy of data gathered throughout the trial. Detailed protocols that specify the procedures for data entry and management are essential to minimize errors and ensure data integrity.
Thorough data management is crucial for the reliability and validity of the study results. The use of electronic data capture (EDC) systems can significantly enhance the quality, accuracy, and efficiency of data collection and management. This systematic approach to data handling helps to minimize data entry errors, facilitate data analysis, and ultimately improve the trustworthiness of the trial's conclusions.
Ethical Considerations and Regulatory Compliance
Adherence to stringent ethical guidelines and regulations is paramount in conducting clinical trials. These considerations encompass informed consent procedures, privacy protection, and the safety and well-being of all participants throughout the study. Ensuring participant safety and well-being are paramount during the entire trial process.
Adherence to ethical principles and regulatory guidelines is fundamental to the integrity and validity of clinical trials. Compliance with regulations, such as Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines, is essential for maintaining data integrity and ensuring participant safety. This commitment to ethical conduct safeguards the rights and well-being of participants and fosters public trust in the research process.
The Role of Patient Advocacy Groups in Drug Development
Patient Advocacy Groups: A Crucial Link in the Rare Disease Chain
Patient advocacy groups play a critical role in bridging the gap between patients with rare diseases and the pharmaceutical industry. Their intimate understanding of the daily struggles, specific symptoms, and unique needs of individuals affected by rare conditions allows them to provide invaluable insights throughout the drug development process. This direct connection to the lived experience of patients is crucial, as it ensures that research priorities align with the needs of the affected population, preventing the development of treatments that may not effectively address their specific challenges.
These groups often act as a powerful voice for patients who may otherwise be unheard or overlooked in the complex landscape of clinical research. Their advocacy extends beyond the initial research phases to encompass the ongoing monitoring and evaluation of treatments, ensuring that the patient perspective remains central to the development journey.
Identifying and Prioritizing Research Needs
Patient advocacy groups are uniquely positioned to identify unmet needs and research priorities within the rare disease community. Through surveys, focus groups, and direct engagement with patients, they can collect extensive data on symptoms, disease progression, and the impact of the disease on daily life. This data is invaluable in prioritizing research areas and guiding the development of targeted therapies.
Facilitating Patient Recruitment and Retention in Clinical Trials
Recruiting and retaining participants in clinical trials is a significant challenge, particularly for rare diseases where patient populations are often small and geographically dispersed. Patient advocacy groups possess extensive networks and relationships with patients, enabling them to effectively reach potential participants. Their expertise in communicating the importance of participating in clinical trials and navigating the complexities of the process significantly enhances recruitment and retention rates, ensuring a more representative sample for research studies.
Providing Valuable Feedback on Treatment Development
Patient advocacy groups provide invaluable feedback on the design and implementation of clinical trials. They offer insights into potential challenges related to treatment administration, potential side effects, and the overall patient experience. This feedback is crucial in refining the trial design to maximize efficiency and ensure that the treatment is well-suited for patients with rare conditions.
Championing Patient-Centric Drug Development Strategies
Advocacy groups are instrumental in promoting a patient-centric approach to drug development, ensuring that research is not only scientifically sound but also addresses the practical needs of patients. They advocate for the development of therapies that are easy to administer, safe, and effective in improving the quality of life for patients with rare diseases. They also advocate for access to these treatments, ensuring that advancements benefit the entire patient population.
Engaging with Regulatory Bodies and Research Institutions
Patient advocacy groups play a vital role in fostering communication and collaboration between patients, researchers, and regulatory bodies. They act as intermediaries, facilitating discussions and ensuring that patient perspectives are heard and considered throughout the entire drug development process. This engagement helps to streamline the regulatory process and ensures that research findings are effectively translated into accessible and beneficial treatments.
Building Awareness and Support Networks
Beyond the direct impact on drug development, patient advocacy groups build vital support networks within the rare disease community. By raising awareness about specific conditions and providing educational resources, they empower patients and families to navigate the complexities of living with a rare disease. These networks offer crucial emotional support and practical guidance, enhancing the overall well-being and resilience of individuals affected by these challenging conditions.