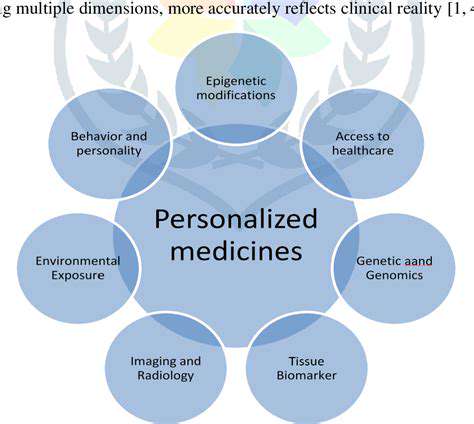
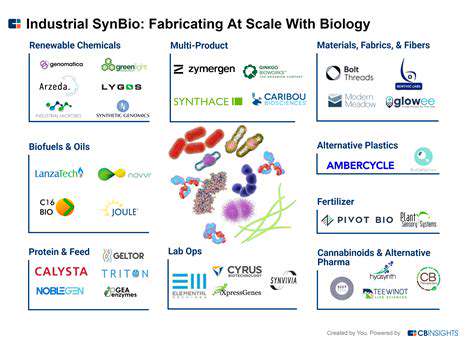
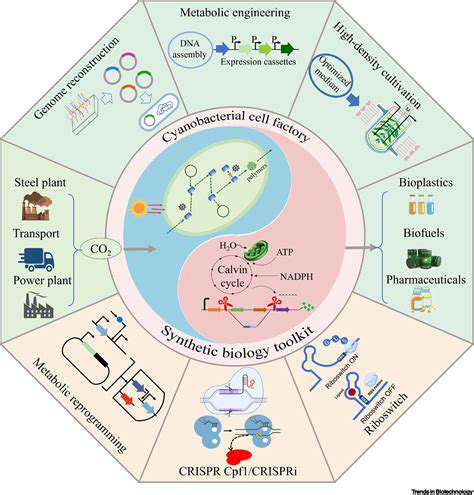
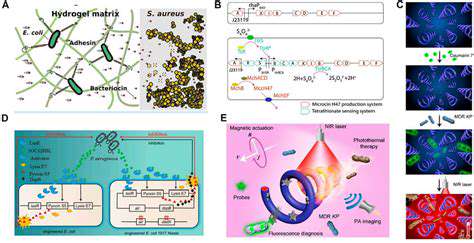
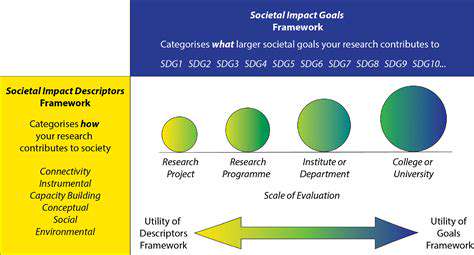
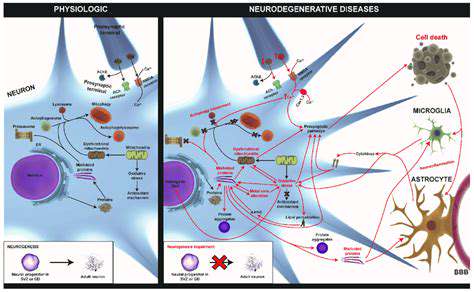
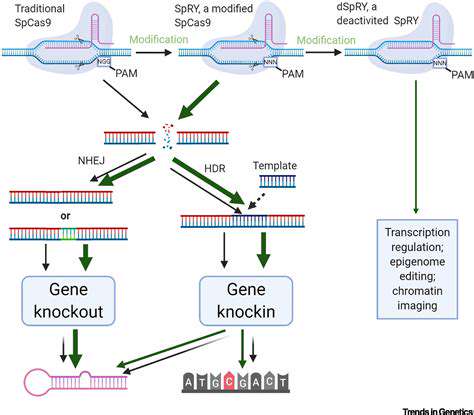
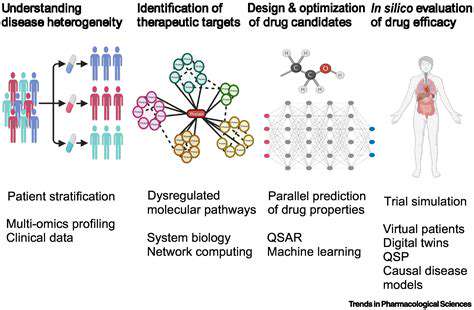
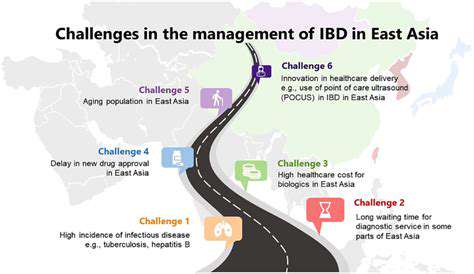
Addressing the Challenges of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD)
Understanding Inflationary Pressures
Inflation, a persistent rise in the general price level of goods and services in an economy, presents a complex set of challenges. Understanding these pressures is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate its negative impacts. Inflationary pressures can stem from a multitude of factors, including supply chain disruptions, increased demand, and monetary policy decisions. Analyzing these underlying causes is vital to crafting targeted solutions.
One significant aspect of inflationary pressures lies in the interplay between supply and demand. When demand outpaces supply, prices tend to rise. Conversely, disruptions in the supply chain, such as those experienced during global events, can also lead to price increases. Understanding the specific drivers of inflation in a given economy is critical to developing tailored solutions.
The Impact of Inflation on Consumers
Inflation has a direct and often profound impact on consumers. Rising prices erode purchasing power, making it more difficult for individuals to afford essential goods and services. This can lead to financial strain, affecting household budgets and overall economic well-being. The burden of inflation disproportionately affects low- and middle-income households, who often spend a larger portion of their income on necessities.
The impact of inflation on consumers extends beyond the immediate cost of goods and services. Increased uncertainty regarding future price levels can also lead to reduced consumer confidence and spending. This can create a negative feedback loop, further hindering economic growth.
Government Responses to Inflationary Pressures
Governments play a crucial role in addressing inflationary pressures. Central banks often use monetary policy tools, such as interest rate adjustments, to manage inflation. Fiscal policy measures, such as government spending and taxation, can also influence aggregate demand and, consequently, price levels. Effective responses require careful consideration of the specific economic context and the potential impact of different policy choices.
Different countries and economies react differently to inflation. The effectiveness of government responses therefore depends on a variety of factors, including the specific economic structure and the prevailing political climate. Understanding these nuances is critical for crafting policies that are both effective and appropriate.
Mitigating the Effects of Inflationary Shocks
Companies and individuals can take steps to mitigate the effects of inflationary shocks. Diversifying investments, hedging against price fluctuations, and exploring alternative sources of income can help mitigate the impact of inflation. For businesses, adapting pricing strategies and improving supply chain resilience are crucial for navigating inflationary periods.
Long-term strategies are also important. Investing in education and skills development can equip individuals with the ability to adapt to changing economic conditions. Building financial resilience, including emergency funds and appropriate insurance, is essential for navigating periods of uncertainty and economic volatility.
Long-Term Strategies for Managing Inflation
Addressing the challenges of inflation requires a multifaceted approach that considers both short-term and long-term strategies. Sustainable economic growth, coupled with robust fiscal and monetary policies, is essential for maintaining price stability. Investing in infrastructure and promoting innovation can enhance productivity and long-term economic resilience.
Long-term strategies also include promoting competition, reducing barriers to entry in markets, and encouraging innovation. These efforts can foster greater efficiency, drive down costs, and ultimately contribute to long-term price stability. Furthermore, international cooperation and coordination on macroeconomic policies are crucial to navigating global inflationary pressures effectively.