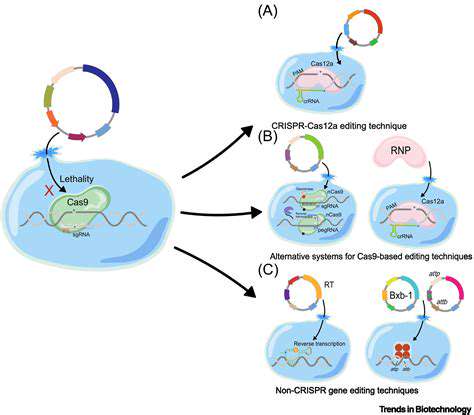
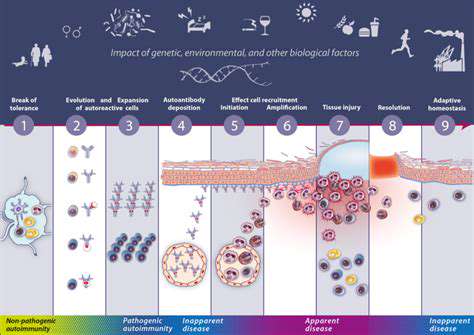
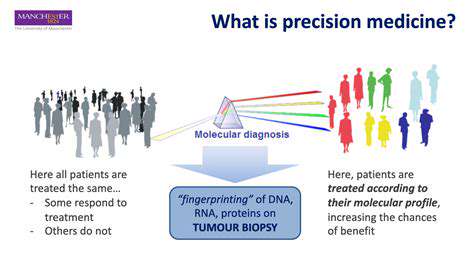
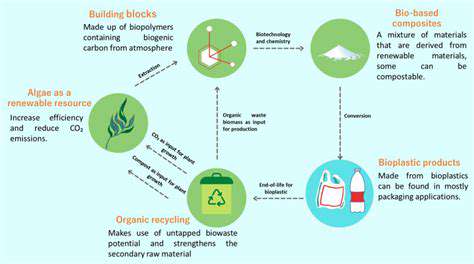
Targeted Nutritional Supplementation with Bioactive Compounds

Targeted Nutritional Supplementation: A Comprehensive Approach
Rather than applying generic solutions, targeted nutritional supplementation focuses on individual health requirements. Factors like metabolic rate, genetic predispositions, and lifestyle habits all influence how nutrients are processed. This method acknowledges that each person's biochemistry is as unique as their fingerprint. By analyzing these variables, practitioners can develop protocols that address specific health concerns while avoiding unnecessary supplementation.
The process involves continuous monitoring and adjustment, creating a dynamic approach to wellness. For instance, athletes might require different micronutrient ratios than sedentary individuals, while postmenopausal women often need specialized bone support. This level of personalization represents the future of preventative healthcare.
Identifying Specific Nutritional Gaps
Nutritional assessment has evolved far beyond simple dietary recalls. Modern practitioners now utilize comprehensive testing including:
- Advanced micronutrient panels
- Genetic SNP analysis
- Microbiome mapping
- Metabolic profiling
These tools reveal hidden imbalances that traditional methods might miss. For example, certain genetic variants can dramatically affect folate metabolism, requiring specific nutrient forms. Without proper testing, these subtle but critical deficiencies often go undetected for years.
Choosing the Right Supplements
The supplement industry suffers from significant quality control issues. Independent analyses reveal that many products contain contaminants or fail to deliver labeled potencies. When selecting supplements, consider:
- Third-party verification (e.g., NSF, USP)
- Bioavailable nutrient forms
- Manufacturing transparency
- Clinical research backing
Remember that more expensive doesn't always mean better quality. Some boutique brands charge premium prices while using inferior ingredients. Conversely, certain bulk manufacturers offer pharmaceutical-grade quality at reasonable costs.
Understanding the Importance of Dosage
Nutrient requirements follow a U-shaped curve - both deficiency and excess can cause problems. The optimal dose depends on multiple factors:
- Current nutritional status
- Medication interactions
- Genetic variations
- Life stage
Nutrient timing also plays a crucial role. Some compounds compete for absorption when taken together, while others demonstrate synergistic effects. Fat-soluble vitamins require dietary fats for proper uptake, and certain minerals are best absorbed with food.
Integrating Supplementation into a Healthy Lifestyle
Supplements should complement, not replace, foundational health practices. The most effective protocols combine:
- Nutrient-dense whole foods
- Regular physical activity
- Stress reduction techniques
- Quality sleep hygiene
Chronic stress and poor sleep can negate even the most carefully designed supplement regimen. The body's ability to utilize nutrients depends heavily on these lifestyle factors. For instance, magnesium requirements increase significantly during periods of high stress.
Monitoring Progress and Adjusting as Needed
Effective supplementation requires ongoing evaluation. Useful monitoring techniques include:
- Quarterly blood work
- Symptom tracking journals
- Functional medicine testing
- Body composition analysis
Nutrient needs change throughout life. Pregnancy, illness, athletic training, and aging all warrant protocol adjustments. Regular reassessment ensures the regimen remains aligned with current physiological demands.
Potential Risks and Considerations
While generally safe when used appropriately, supplements can cause adverse effects in certain situations:
- Drug-nutrient interactions (e.g., vitamin K with blood thinners)
- Toxicity from fat-soluble vitamins
- Digestive upset from certain forms
- Allergic reactions to excipients
Always disclose all supplements to your healthcare providers. Many patients forget to mention their supplement use, potentially leading to dangerous interactions with prescribed medications.
Harnessing Microbial Resources for Enhanced Feed Efficiency
Microbial Diversity in the Digestive Tract
The digestive ecosystem represents one of nature's most complex symbiotic relationships. Ruminants like cattle host specialized microbial communities that convert indigestible plant matter into valuable nutrients. This microbial workforce includes:
- Cellulose-digesting bacteria
- Methanogenic archaea
- Protein-synthesizing microbes
- Vitamin-producing organisms
Recent metagenomic studies reveal surprising variations between individual animals, even within the same herd. This microbial fingerprint may explain why some animals thrive on identical feed rations while others struggle.
Enhancing Nutrient Release from Feed
Traditional feed processing often destroys valuable nutrients. Modern approaches focus on preserving bioactive compounds while improving digestibility:
- Controlled fermentation
- Enzyme pretreatment
- Precision milling
- Microbial inoculation
Feed efficiency improvements of 15-20% are achievable through optimized microbial management. This translates to significant reductions in feed costs and environmental impact across large operations.
Improving Protein and Energy Utilization
The gut microbiome actively participates in protein metabolism through:
- Non-protein nitrogen conversion
- Essential amino acid synthesis
- Anti-nutrient neutralization
- Digestive enzyme production
Energy extraction efficiency varies dramatically based on microbial composition. Some microbial strains can increase metabolizable energy by up to 12% compared to conventional digestion.
The Role of Prebiotics and Probiotics
Effective microbial management requires understanding prebiotic-probiotic synergies:
| Prebiotic Type | Target Microbes | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Fructooligosaccharides | Bifidobacteria | Improved calcium absorption |
| Mannan oligosaccharides | Lactobacilli | Pathogen inhibition |
| Beta-glucans | Multiple species | Immune modulation |
Genetic Selection for Host-Microbe Interactions
Emerging research identifies specific genetic markers associated with:
- Microbial colonization patterns
- Feed conversion efficiency
- Methane production
- Nutrient absorption capacity
Selective breeding based on these markers could revolutionize livestock production, potentially reducing methane emissions by 30% while improving growth rates.
Sustainable Feed Formulation Strategies
Modern feed formulation considers multiple sustainability metrics:
- Carbon footprint per kg of product
- Water usage efficiency
- Land use requirements
- Byproduct utilization
Algae-based feeds demonstrate particular promise, offering complete protein profiles while requiring minimal arable land and freshwater resources.
Economic and Environmental Benefits
The financial implications of improved feed efficiency are substantial:
- 5-7% reduction in feed costs
- 20-30% lower manure output
- Reduced veterinary expenses
- Higher product quality premiums
Environmental benefits extend beyond greenhouse gases, including reduced nitrogen runoff and lower antibiotic usage due to improved animal health.
The Future of Animal Nutrition: A Sustainable and Efficient Approach
Optimizing Nutrient Utilization
The next generation of feed additives will focus on:
- Nanoscale nutrient delivery
- pH-sensitive release systems
- Microbial consortia engineering
- Precision fermentation products
These technologies promise to double nutrient bioavailability while minimizing waste and environmental contamination.
Developing Novel Feed Ingredients
Alternative protein sources are undergoing rapid development:
- Single-cell proteins from industrial byproducts
- Insect larvae reared on food waste
- Lab-cultured microbial biomass
- Seaweed-based complete feeds
The economic viability of these alternatives improves annually as production scales and processing techniques advance.
Precision Nutrition for Enhanced Performance
Digital technologies enable real-time nutritional adjustments:
- Wearable biosensors
- Automated feeding systems
- AI-driven ration optimization
- Blockchain traceability
This approach reduces overfeeding by 10-15% while ensuring optimal nutrient delivery throughout the production cycle.
Improving Feed Efficiency
Cutting-edge research focuses on:
- Epigenetic modulators
- Metabolic pathway optimization
- Gut-brain axis manipulation
- Microbiome transplantation
Early trials show 18-22% improvements in feed conversion ratios through these advanced interventions.
Addressing Nutritional Deficiencies
Next-generation solutions include:
- CRISPR-enhanced crops with improved nutrient profiles
- Smart packaging that preserves nutrient integrity
- Nutrient recycling systems
- Personalized mineral supplements
These innovations could eliminate widespread deficiencies that currently cost the industry billions annually.
Enhancing Animal Health Through Nutrition
Nutritional immunology represents a growing field:
- Mucosal immunity boosters
- Pathogen-blocking feed additives
- Gut barrier strengtheners
- Anti-inflammatory nutrients
Proper nutritional support can reduce antibiotic use by 40-60% while improving overall flock/herd health.
Environmental Sustainability in Animal Feed Production
The circular economy model transforms waste streams:
- Food processing byproducts → high-value feed
- Agricultural residues → nutrient sources
- Municipal waste → insect feed
- CO2 emissions → algal biomass
This approach could reduce the feed industry's carbon footprint by 50% while creating new revenue streams from waste materials.