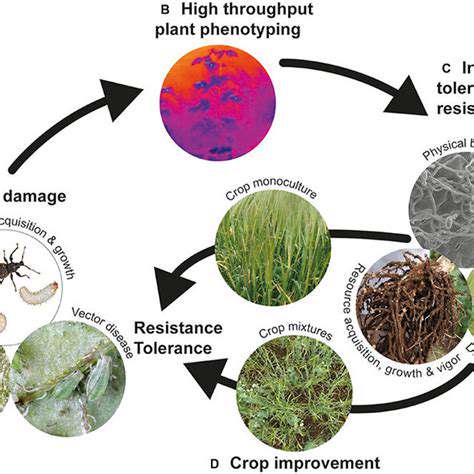
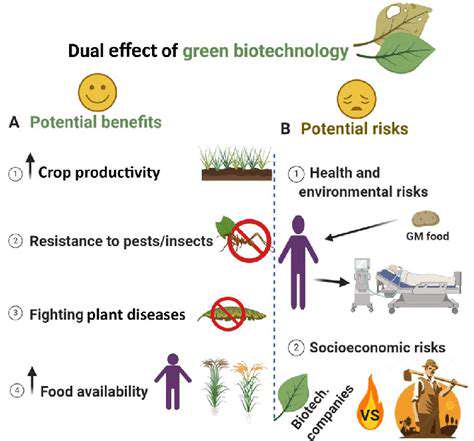
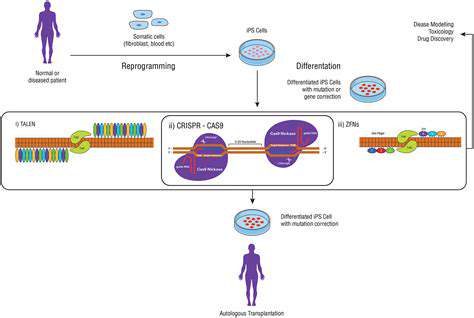
The High Costs of Research and Development

Research and Development Investment
Innovation thrives on research and development (R&D), yet this essential process demands substantial financial commitment. Organizations must allocate considerable resources to fund experimental projects, prototype development, and exhaustive testing procedures. These expenditures can rapidly escalate, potentially limiting a company's capacity to invest in other critical operational areas.
R&D investment varies dramatically across industries and project complexities. Pharmaceutical firms, for instance, encounter extraordinary expenses due to comprehensive clinical trials and regulatory processes. Meanwhile, emerging startups might dedicate a smaller portion of their budget to R&D, though the actual financial outlay remains significant for their scale.
Intellectual Property Protection
Safeguarding intellectual property (IP) is crucial for monetizing research outcomes and securing investment returns. This typically involves obtaining patents, trademarks, and copyrights to protect innovations from unauthorized use. The expense of acquiring and maintaining these protections can be substantial, particularly for intricate technologies or international markets.
Legal costs associated with IP protection often increase during patent filings and enforcement actions. Continuous monitoring and maintenance of these protections are necessary to preserve their validity, adding to the ongoing financial obligations.
Talent Acquisition and Retention
Securing and keeping exceptional research talent is fundamental for successful R&D operations. Highly qualified scientists, engineers, and researchers command premium compensation packages due to intense market demand. These employment costs, combined with the need for specialized equipment and facilities, create significant financial pressure for organizations.
The competitive landscape for research professionals often compels companies to offer attractive remuneration packages, including competitive salaries, comprehensive benefits, and potential signing incentives. Additionally, cultivating an engaging work environment is vital for talent retention and innovation cultivation, further contributing to overall expenses.
Infrastructure and Equipment
Contemporary research frequently requires advanced infrastructure and specialized equipment, including high-tech laboratories, sophisticated imaging systems, and specialized software solutions. Procuring and maintaining such equipment represents a major capital investment for research organizations.
Ongoing infrastructure maintenance is equally critical. The costs associated with equipment repairs, upgrades, and routine calibration can substantially impact an organization's financial resources.
Time and Risk Factors
R&D initiatives inherently involve extended timelines and substantial uncertainty. The unpredictable nature of research outcomes and potential for project failures can lead to prolonged durations and unanticipated costs. These factors complicate financial planning and resource allocation strategies.
The extended duration of research projects necessitates sustained financial commitment. Developing contingency plans for potential obstacles is crucial to completing projects within established budgets.

Maintaining Ethical Standards and Public Trust
Ensuring Transparency and Accountability in Research
Upholding ethical standards in biotechnology research demands unwavering commitment to transparency and accountability throughout all research phases. This includes clearly disclosing potential conflicts of interest, rigorously adhering to informed consent protocols, and maintaining uncompromising data integrity. Open communication with stakeholders fosters public trust and enables constructive feedback that can enhance research methodologies and mitigate potential risks. Transparent practices allow independent evaluation of research approaches, thereby strengthening scientific credibility.
Establishing clear, adaptable regulations is essential for conducting research responsibly. Developing robust oversight mechanisms, including ethical review boards and regulatory agencies, helps prevent potential misuse of biotechnological advancements while maximizing their benefits.
Addressing Societal Impacts and Equitable Access
Biotechnology innovations have far-reaching societal consequences that require consideration from diverse perspectives. Evaluating potential environmental effects, economic implications, and social equity issues is crucial for ensuring widespread benefit distribution. Preventing treatment disparities requires making life-saving therapies accessible across socioeconomic and geographic boundaries.
Ensuring equitable access to biotechnological advancements necessitates incorporating input from marginalized communities. Proactive measures must address potential exacerbation of existing inequalities. Comprehensive public education initiatives can empower individuals to understand and engage with biotechnological developments affecting their communities.
Attracting and Retaining Talent
Attracting Top Talent in a Competitive Market
The biotechnology sector faces intense competition for skilled professionals. Beyond competitive salaries, companies must cultivate stimulating work environments that promote innovation, collaboration, and career growth. Flexible work arrangements, mentorship programs, and employee resource groups contribute significantly to job satisfaction and retention.
Demonstrating commitment to ethical practices and social responsibility resonates strongly with potential employees, particularly younger professionals who value organizational purpose beyond financial metrics.
The Importance of Competitive Compensation and Benefits Packages
While workplace culture matters, competitive compensation remains essential for talent acquisition. Biotechnology specialists expect industry-standard salaries and comprehensive benefits. Regular market analysis ensures compensation packages remain attractive compared to industry peers.
Addressing the Challenges of Work-Life Balance
The demanding nature of biotech research necessitates addressing work-life balance concerns. Implementing flexible schedules and promoting employee wellness initiatives helps maintain long-term staff retention.
Cultivating a Culture of Innovation and Collaboration
Fostering creativity and knowledge-sharing is vital in this dynamic field. Creating platforms for idea exchange and interdisciplinary cooperation accelerates innovation while valuing diverse perspectives.
Investing in Employee Development and Training
Continuous learning opportunities demonstrate organizational commitment to professional growth. Supporting advanced education and skills development helps employees stay current with industry advancements.
Developing a Strong Employer Brand
Effectively communicating organizational values and culture attracts qualified candidates. Authentic representation of workplace environment and research achievements enhances recruitment efforts in this competitive sector.