Biomonitoring for Early Detection of Environmental Damage
Understanding the Concept of Biomonitoring
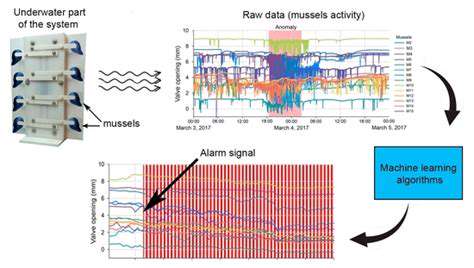
Biomonitoring, in its simplest form, is the process of assessing the health of living organisms to understand and quantify the impact of environmental factors. It's a crucial tool for environmental science and public health, offering a proactive approach to identifying potential threats before they manifest as widespread problems. This method relies on observing biological indicators, which can be a variety of organisms, from microorganisms to large mammals, to gauge the overall health of an ecosystem.
By monitoring these biological indicators, scientists can gain valuable insights into the subtle shifts in environmental conditions. These shifts, often imperceptible to human observation, can be early warning signs of pollution, climate change, or other environmental stressors. This early detection capability is vital for timely intervention and mitigation strategies.
Types of Biomonitoring Techniques
Various biomonitoring techniques exist, each with its specific strengths and limitations. Some methods focus on analyzing the tissues of organisms, while others concentrate on observing their behavior or physiology. For example, analyzing the concentration of pollutants in plant tissues can provide insight into the levels of contamination in the surrounding environment.
Another technique involves studying the genetic makeup of organisms to identify potential mutations or alterations linked to environmental stressors. This approach can provide a more detailed understanding of long-term effects and potential risks.
Biomonitoring for Environmental Pollution
Biomonitoring plays a vital role in detecting and assessing environmental pollution. By examining the health of organisms in a polluted area, scientists can determine the extent and nature of the pollution, enabling the development of targeted remediation strategies.
This approach is far more sensitive than traditional methods of chemical analysis and can identify subtle, but significant, changes in the environment. It can pinpoint the source of pollution and assess the long-term impacts on the ecosystem.
Biomonitoring and Public Health
Biomonitoring is not limited to environmental concerns; it also has significant implications for public health. By examining human populations and their exposure to environmental contaminants, scientists can identify potential health risks and develop preventive measures.
Monitoring the levels of pollutants in human blood or urine can provide valuable insights into individual exposure levels and potential health impacts. This information is crucial for developing public health guidelines and policies to mitigate risks.
Applications of Biomonitoring in Different Ecosystems
Biomonitoring techniques are applicable across a diverse range of ecosystems, from aquatic environments to terrestrial ecosystems. The specific organisms and methods used often vary depending on the ecosystem and the pollutants of concern.
For instance, in aquatic ecosystems, fish and invertebrates can act as excellent indicators of water quality. In terrestrial ecosystems, plants and birds can reveal the presence of pollutants and the impact of climate change.
Future Trends and Challenges in Biomonitoring
The field of biomonitoring is continuously evolving, with new technologies and approaches emerging to enhance its effectiveness and scope. Advances in molecular biology and genetic analysis are revolutionizing biomonitoring, enabling more detailed and sensitive assessments of environmental impacts.
However, challenges remain, including the need for standardized protocols, robust data analysis techniques, and the development of cost-effective methods for widespread implementation. Addressing these challenges is crucial for ensuring the continued success and relevance of biomonitoring in environmental protection and public health.