Introduction to Synthetic Biology in Biosensing
Defining Synthetic Biology in Biosensing
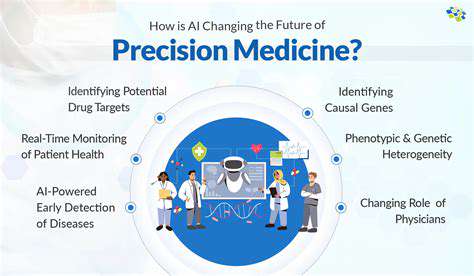
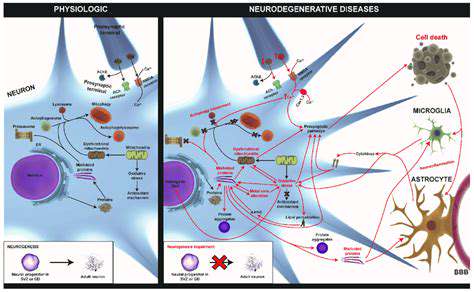
Synthetic biology, in the context of biosensing, is a rapidly evolving field focused on engineering biological systems to detect and quantify specific molecules or events. This involves designing and constructing novel biological components, such as genes, proteins, and metabolic pathways, to create sensing platforms. The goal is to develop highly sensitive, specific, and adaptable biosensors capable of detecting a wide range of analytes, from environmental pollutants to disease biomarkers.
Traditional biosensors often rely on natural biological systems, but synthetic biology offers the potential to optimize these systems, enhancing their performance and creating entirely new sensing mechanisms. This approach allows for greater control over the sensing process, enabling the development of tailored biosensors for specific applications.
Key Components of Synthetic Biosensors
A crucial aspect of synthetic biosensors lies in the carefully selected components. These include genetic circuits, which act as the brains of the sensor, dictating how the system responds to the target molecule. Genetically encoded reporters, which produce measurable signals in response to the target, are also essential. Finally, the choice of biological chassis, such as bacteria or yeast, determines the platform's robustness and suitability for different environments.
The interplay between these components creates a sophisticated system capable of converting a biological interaction into a measurable signal. Understanding and manipulating these interactions is key to maximizing the sensitivity and specificity of the biosensor.
Applications of Synthetic Biology in Biosensing
The applications of synthetic biology in biosensing are vast and span diverse fields. Environmental monitoring, for example, benefits from biosensors that can detect pollutants in water and soil, providing real-time data for environmental protection and remediation efforts. In healthcare, synthetic biosensors could revolutionize disease diagnostics, enabling early detection and personalized treatment strategies.
Beyond these applications, synthetic biology holds promise for food safety, agricultural monitoring, and industrial processes. The ability to tailor biosensors to specific needs allows for a wide range of potential applications.
Advantages of Synthetic Biosensors Over Traditional Methods
Synthetic biosensors offer significant advantages over traditional biosensing approaches. Enhanced sensitivity and specificity are hallmarks of this technology. The ability to engineer biosensors for specific targets, combined with their rapid response times, makes them highly desirable for various applications. This precision and speed are essential for real-time monitoring and decision-making, whether in environmental analysis, medical diagnostics, or industrial quality control.
Additionally, synthetic biosensors can be engineered to operate in diverse environments, broadening their applicability and robustness.
Challenges and Future Directions
While the potential of synthetic biology in biosensing is immense, several challenges remain. Cost-effectiveness and scalability are crucial for widespread adoption. Furthermore, ensuring the reliability and stability of these engineered systems over time is essential for practical applications. Addressing these challenges is critical for realizing the full potential of synthetic biosensors.
Future research will likely focus on improving the robustness and versatility of synthetic biosensors, exploring new chassis organisms, and developing novel sensing mechanisms. This will lead to even more sensitive, specific, and adaptable biosensors, paving the way for innovative applications across a multitude of fields.

Future Directions and Challenges
Expanding Research Horizons
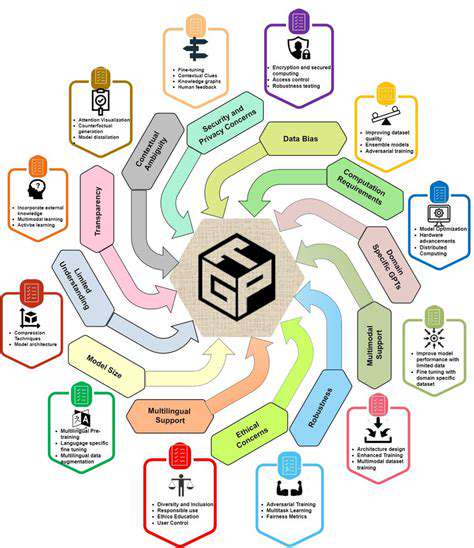
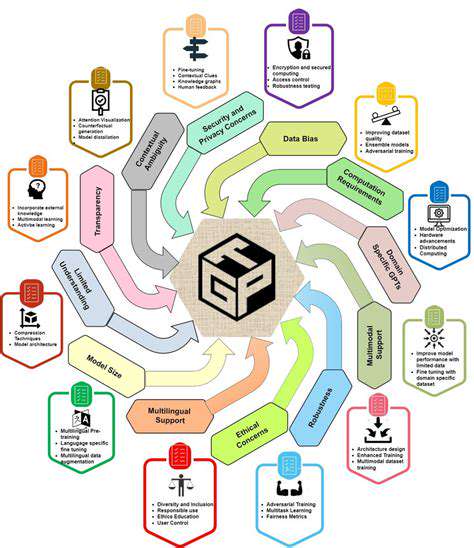
Future research in this area should explore the long-term impacts of emerging technologies on various societal sectors. Understanding how these technologies will reshape economies and influence social structures is crucial for proactive policymaking. This includes examining potential disruptions to existing industries, the creation of new job markets, and the ways in which these technologies might exacerbate existing inequalities.
Addressing Ethical Considerations
The ethical implications of these technologies must be thoroughly investigated. This involves considering issues such as data privacy, algorithmic bias, and the potential for misuse. Robust ethical frameworks and guidelines are essential to ensure responsible development and deployment, preventing unintended consequences.
Specific attention should be paid to the potential for these technologies to be used to manipulate individuals or to create social division. Safeguards and regulatory mechanisms are necessary to mitigate such risks and protect vulnerable populations.
Improving Accessibility and Inclusivity
Efforts should be made to ensure that the benefits of these technologies are accessible to everyone, regardless of socioeconomic status or geographic location. Bridging the digital divide and fostering equitable access are critical to avoiding further marginalization. This includes developing user-friendly interfaces, providing affordable access to technology, and offering relevant training and support.
Enhancing Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing
Interdisciplinary collaborations between researchers, policymakers, and industry professionals are essential to address the complex challenges associated with these technologies. Knowledge sharing and open dialogue are vital for developing innovative solutions and ensuring the responsible advancement of these technologies. This approach can foster a collective understanding that considers the multifaceted impacts of new technologies.
Fostering Public Engagement and Education
Engaging the public in discussions about these technologies is crucial for building trust and ensuring societal buy-in. Transparency and open communication are essential to fostering informed public discourse and addressing concerns about these technologies. Educational initiatives aimed at increasing public understanding of these technologies and their potential implications are also necessary.
Developing Robust Regulatory Frameworks
Developing robust regulatory frameworks is essential to manage the risks associated with these emerging technologies. Clear guidelines and regulations are needed to ensure safety, security, and ethical considerations are at the forefront of development and implementation. These frameworks must be adaptable and responsive to the rapid evolution of these technologies, and must be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changing societal needs and contexts.