Understanding the Immune System's Role in Type 1 Diabetes
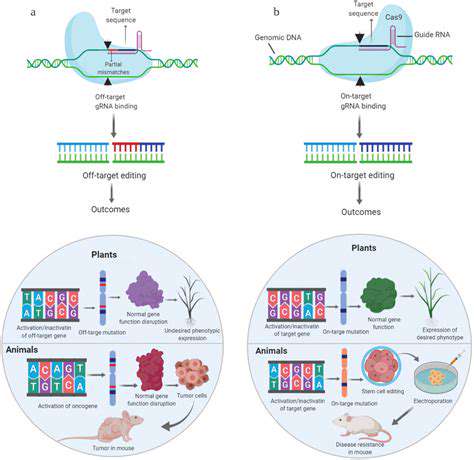
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease, meaning the body's immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This attack is a complex process involving a cascade of events where immune cells, primarily T cells, recognize and target these pancreatic beta cells as foreign invaders. Understanding the intricate mechanisms driving this autoimmune response is crucial for developing effective therapies, and gene editing holds promise for potentially disrupting these harmful processes.
The immune system's ability to distinguish between self and non-self is fundamental to its function. In Type 1 diabetes, this crucial distinction breaks down, leading to the devastating consequences of insulin deficiency. Researchers are actively investigating the specific triggers and pathways that initiate and perpetuate this self-destructive immune response. Pinpointing these vulnerabilities is essential for developing targeted interventions.
Gene Editing Strategies for Immune System Modulation
Gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR-Cas9, offer a powerful new tool for modulating the immune response in Type 1 diabetes. These technologies allow scientists to precisely target and modify specific genes within immune cells, potentially altering their ability to attack pancreatic beta cells. This approach could involve silencing genes involved in the immune response or introducing genes that dampen the inflammatory cascade.
The potential of gene editing extends beyond just targeting immune cells directly. Researchers are also exploring the possibility of modifying the genes within the pancreatic beta cells themselves, potentially making them less susceptible to attack. This dual-pronged strategy could offer a more comprehensive approach to managing the disease, reducing both the immune response and the susceptibility of the target cells.
Silencing Specific Immune Cells and Pathways
One key strategy involves targeting and silencing specific immune cells, such as T cells, that are crucial in the autoimmune attack. By using gene editing techniques to disable or modify the genes involved in T cell activation, researchers aim to reduce their ability to recognize and destroy pancreatic beta cells. This approach could potentially halt the progression of the disease or even reverse the autoimmune process in some cases.
Another avenue of research focuses on silencing specific signaling pathways within the immune system. These pathways often play a central role in the activation and proliferation of immune cells that attack pancreatic beta cells. Gene editing can be used to disrupt these pathways, thereby reducing the overall intensity of the immune response and protecting the insulin-producing cells.
Challenges and Future Directions in Immune System Targeting
While the potential of gene editing to target the immune system in Type 1 diabetes is significant, several challenges remain. One key challenge is the precise and efficient delivery of gene editing tools to the target cells within the complex environment of the immune system and the pancreas. Developing efficient delivery mechanisms is crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of these therapies.
Furthermore, ensuring the safety and long-term efficacy of these gene editing therapies is paramount. Extensive research and rigorous testing are needed to evaluate the potential off-target effects and long-term consequences of modifying the immune system in this way. These concerns need careful consideration as the field progresses.
Ethical Considerations and Public Health Implications
The development and implementation of gene editing therapies for Type 1 diabetes raise important ethical considerations. Ensuring equitable access to these potentially life-altering therapies across diverse populations is critical. Open dialogue and careful consideration of the societal and ethical implications are essential as these technologies continue to evolve.
The potential impact on public health is substantial. Preventing or effectively treating Type 1 diabetes could have significant implications for reducing the global burden of this chronic condition. However, responsible development and implementation of these technologies are crucial to ensure their benefits are maximized and risks are minimized.
Challenges and Future Directions
Overcoming Existing Barriers
One of the significant hurdles in the field of sustainable energy development is the high upfront cost of implementing renewable energy technologies. This often presents a significant barrier to adoption, especially for smaller businesses and developing nations. Overcoming this financial hurdle is crucial for widespread adoption and for achieving the global sustainability goals. Developing innovative financing models, such as government subsidies and tax incentives, is vital to make renewable energy more accessible and economically viable.
Furthermore, the intermittency of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, poses a challenge for grid stability. Ensuring a reliable and consistent energy supply is essential, requiring advancements in energy storage technologies and smart grid infrastructure. Efficient energy storage solutions are key to addressing this challenge and unlocking the full potential of renewable energy sources.
Technological Advancements
Continued research and development are crucial for improving the efficiency and reducing the cost of renewable energy technologies. For instance, advancements in solar panel technology are essential for increasing energy output per unit area and lowering the overall cost of solar power systems. This research must also focus on developing more efficient methods of extracting energy from renewable sources such as geothermal energy.
Another area of focus should be on developing more sustainable and environmentally friendly manufacturing processes for renewable energy technologies. Minimizing the environmental footprint of production is critical for achieving true sustainability. The focus should be on reducing material waste and incorporating recycled materials into the manufacturing process, thereby promoting a circular economy.
Policy and Regulatory Frameworks
Governments play a vital role in fostering the transition to sustainable energy by enacting supportive policies and regulations. Clear and consistent policies that incentivize renewable energy adoption are necessary to encourage investment and technological innovation. These policies must be well-structured and long-term oriented to ensure stability and predictability for investors. Establishing clear regulatory frameworks for energy storage and grid integration will facilitate the seamless integration of renewable energy sources into existing power grids.
International cooperation and knowledge sharing are essential for accelerating the global transition to sustainable energy. Collaboration between nations can facilitate the exchange of best practices and technologies, promoting a more equitable and rapid transition for all. Sharing best practices in policy development and regulatory frameworks is critical to fostering a global movement towards sustainable energy solutions.
Public Awareness and Engagement
Raising public awareness about the importance of sustainable energy is vital for driving support and engagement. Educating the public about the benefits of renewable energy, such as environmental protection and energy independence, is crucial for building public support for policy changes and technological advancements. Public understanding and acceptance are essential for successfully implementing sustainable energy solutions. Communicating the benefits and addressing concerns about the transition to a low-carbon economy through effective public outreach is paramount.
Investment and Financing Mechanisms
Attracting private investment is essential for scaling up renewable energy projects and infrastructure. Innovative financing mechanisms, such as green bonds and public-private partnerships, are necessary to mobilize capital for large-scale projects. Developing innovative investment strategies that prioritize long-term sustainability is critical to attracting and retaining capital. Supporting sustainable energy investments through policy incentives and streamlined regulatory processes is crucial for driving large-scale deployment.
Community Engagement and Equity
The transition to sustainable energy must be inclusive and equitable. Ensuring that the benefits of this transition are shared across communities and do not disproportionately affect marginalized groups is critical. Community involvement and engagement in decision-making processes are vital for ensuring that projects are tailored to the needs of the specific communities they will impact. Addressing the potential social impacts of renewable energy projects, such as job displacement or land use changes, is essential for achieving a just and equitable transition.