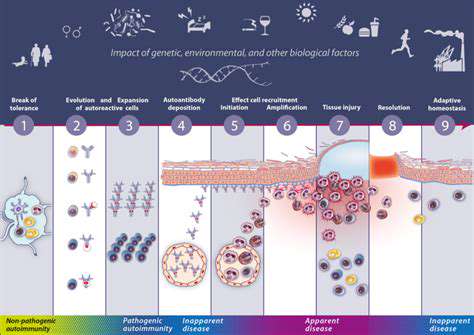
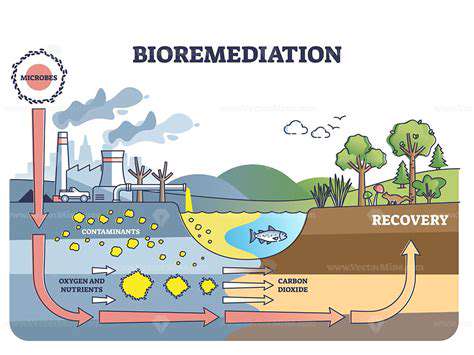
Immunomodulation introduces a groundbreaking strategy that recalibrates rather than suppresses immune function. This nuanced method offers superior precision compared to conventional immunosuppression, potentially yielding better clinical results with fewer complications. The approach focuses on restoring immune homeostasis while preserving protective responses.
Targeting Specific Immune Pathways
Modern immunomodulators zero in on precise immunological mechanisms driving lung inflammation. Potential strategies include restraining particular immune cell activation, intercepting cytokine production, or adjusting regulatory cell behavior. Investigators are working to map the most pertinent pathways and design interventions that selectively influence these routes.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite their potential, immunomodulators face substantial hurdles in development and implementation. Creating therapies that balance efficacy with safety demands rigorous evaluation of adverse effects and customization for individual patients. Future investigations should emphasize biomarker discovery for treatment prediction and the creation of increasingly targeted solutions tailored to patients' unique biological profiles.
Clinical Trials and Emerging Therapies
An expanding portfolio of clinical studies is assessing innovative immunomodulators for diverse pulmonary inflammations. Cutting-edge interventions like engineered monoclonal antibodies and specialized molecular inhibitors demonstrate encouraging preliminary data. These developments mark significant strides toward transforming treatment paradigms for these challenging conditions.
The Role of Gene Therapy and Cellular Therapies
Gene Therapy Approaches in Rare Respiratory Diseases
Gene-based interventions offer unprecedented opportunities to potentially cure rather than merely treat inherited respiratory disorders. By addressing genetic root causes, these therapies might provide lasting solutions. Scientists are evaluating multiple gene delivery methods, including engineered viral carriers, while navigating the respiratory system's unique challenges and immune considerations.
Translating these approaches from bench to bedside presents formidable obstacles, particularly for rare pulmonary conditions. Key challenges include achieving precise cellular targeting, sustaining therapeutic gene expression, and managing safety concerns. Despite these hurdles, the transformative potential for patients justifies continued intensive investigation.
Cellular Therapies for Lung Regeneration and Repair
Regenerative medicine utilizing cellular approaches opens new frontiers for respiratory disease treatment. Stem cell-based strategies aim to reconstruct damaged lung architecture by introducing healthy, functional cells. Critical to success is ensuring transplanted cells integrate properly without triggering harmful immune reactions or uncontrolled growth.
The ability to guide stem cell differentiation into specific lung lineages represents a pivotal research focus. Breakthroughs in this domain could fundamentally alter treatment paradigms for previously incurable respiratory conditions.
Personalized Gene Therapy Strategies
Customized genetic interventions are becoming essential to address the heterogeneity of respiratory disorders. Each patient's distinct genetic signature demands precisely tailored therapeutic vectors. Advanced genomic analysis techniques now enable researchers to design patient-specific treatment blueprints that account for individual mutation profiles and tissue characteristics.
This precision approach maximizes therapeutic impact while reducing adverse effects, potentially transforming outcomes for patients with rare genetic respiratory conditions.
Challenges in Drug Delivery for Gene and Cellular Therapies
The respiratory system's intricate architecture creates unique delivery obstacles for advanced therapies. Innovative solutions like smart nanoparticle systems and optimized aerosol formulations are under investigation to overcome these barriers. Simultaneously, researchers are developing strategies to prevent immune rejection of therapeutic payloads while ensuring sustained biological activity.
Success in these areas could dramatically enhance the clinical applicability of next-generation respiratory treatments.
Ethical Considerations in Gene and Cellular Therapies
Genetic and cellular interventions raise profound ethical questions regarding human genome modification and equitable access. Responsible development requires careful evaluation of long-term biological consequences and societal implications. Transparent public dialogue must accompany technological advancements to establish appropriate regulatory frameworks and ethical guidelines.
Addressing affordability and accessibility challenges remains paramount to ensure these potentially curative therapies benefit all eligible patients regardless of socioeconomic status.
Future Directions and Research Priorities
Advancing these innovative treatments requires concerted efforts across multiple fronts. Priority areas include refining delivery technologies, enhancing immune compatibility, and deepening understanding of disease mechanisms. Cross-disciplinary collaboration among researchers, clinicians, and patient advocates will be critical to translate scientific discoveries into meaningful clinical benefits.
Sustained investment in these cutting-edge approaches offers hope for dramatically improving quality of life for individuals battling rare respiratory conditions.