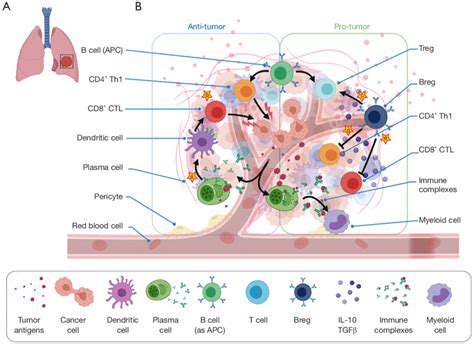
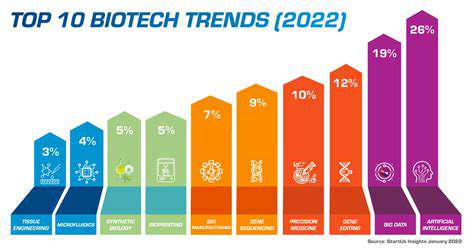
The field of healthcare is constantly evolving, and one of the most significant advancements is the rise of advanced diagnostic tools. These technologies are transforming the way diseases are detected, diagnosed, and treated, leading to earlier interventions and improved patient outcomes. Advanced imaging techniques, such as MRI and CT scans, provide detailed visualizations of internal structures, enabling doctors to pinpoint abnormalities with remarkable accuracy. This capability is crucial for early detection of cancers, neurological disorders, and other critical conditions.
These sophisticated tools are not just improving diagnostic accuracy; they are also enhancing the overall efficiency of healthcare systems. Automated analysis of medical images, powered by artificial intelligence, allows for faster interpretation of results, freeing up valuable time for clinicians to focus on patient care. This streamlined process can significantly reduce diagnostic turnaround times, leading to quicker treatment decisions and improved patient experience.
Precision Medicine and Personalized Care
The development of advanced diagnostic tools has paved the way for a new era in healthcare: precision medicine. By analyzing a patient's unique genetic makeup and other biological factors, doctors can tailor treatment plans to individual needs. This personalized approach has the potential to dramatically improve treatment effectiveness and minimize adverse side effects.
Genetic testing, for example, can identify specific genetic mutations that predispose individuals to certain diseases. This knowledge allows for preventative measures and early interventions, potentially saving lives. Moreover, personalized medicine extends beyond genetics to incorporate factors like lifestyle, environmental exposures, and other individual characteristics, providing a more comprehensive understanding of the patient's health profile.
Another crucial aspect of precision medicine is the ability to monitor treatment response in real-time. Advanced diagnostic tools provide continuous data on a patient's condition, enabling doctors to adjust treatment strategies as needed. This dynamic approach maximizes the effectiveness of therapies and minimizes the risk of complications.
Impact on Disease Prevention and Public Health
Advanced diagnostic tools are not just beneficial for individual patients; they also play a crucial role in disease prevention and public health initiatives. By identifying individuals at risk for specific conditions, healthcare professionals can implement targeted prevention strategies. Early detection of outbreaks, through sophisticated laboratory testing and surveillance systems, allows for swift containment and mitigation efforts, preventing widespread epidemics. Improved diagnostic capabilities also contribute to epidemiological research, providing valuable insights into disease patterns and transmission dynamics.
Furthermore, the ability to identify and track disease trends can help public health officials develop more effective preventative measures, improve healthcare infrastructure, and allocate resources more efficiently. This proactive approach to public health is crucial for a healthier and safer society.
The accessibility and affordability of these advanced diagnostic tools are also important factors to consider for widespread implementation. Efforts to bring these technologies to underserved communities are crucial to ensuring equitable access to quality healthcare for all.
Molecular Diagnostics: Unveiling the Secrets of DNA and RNA
Decoding the Blueprint: Understanding DNA Sequencing
DNA sequencing, a cornerstone of molecular diagnostics, allows scientists to determine the precise order of nucleotides (adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine) within a DNA molecule. This information is crucial for identifying genetic variations that may be associated with diseases. Advanced sequencing technologies, such as next-generation sequencing (NGS), have dramatically increased the speed and reduced the cost of sequencing, enabling researchers to analyze entire genomes or specific genes with unprecedented efficiency. Understanding these sequences is fundamental to understanding the genetic basis of diseases and developing targeted therapies.
The ability to rapidly and accurately sequence DNA has revolutionized medical research, providing insights into the genetic underpinnings of various disorders. By comparing the DNA sequences of healthy individuals and those with a particular disease, researchers can pinpoint specific mutations or variations that may contribute to the condition. This knowledge is vital for developing diagnostic tools, personalized medicine approaches, and gene therapies.
RNA Analysis: Unraveling the Transcriptome
RNA, a crucial intermediary molecule in the central dogma of molecular biology, plays a vital role in protein synthesis. Analyzing RNA molecules, particularly messenger RNA (mRNA), provides valuable insights into gene expression levels and activity. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) and other non-coding RNAs also play important roles in regulating gene expression and are increasingly recognized as important biomarkers for disease. This transcriptomic analysis is instrumental in understanding how genes are turned on and off in response to various stimuli, including disease processes.
Genetic Variations and Disease Predisposition
Genetic variations, such as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and copy number variations (CNVs), can significantly influence an individual's susceptibility to certain diseases. Identifying these variations through molecular diagnostic techniques is crucial for predicting disease risk and tailoring preventative strategies. Understanding the interplay between genetic predisposition and environmental factors is essential for developing effective preventive measures and personalized treatment plans.
Cancer Diagnostics: Detecting and Characterizing Tumors
Molecular diagnostics are transforming cancer care by providing powerful tools for detecting, diagnosing, and characterizing tumors. Analyzing tumor DNA and RNA can reveal specific genetic mutations and alterations that drive tumor growth and metastasis. This information is vital for selecting the most effective treatment strategies, including targeted therapies and immunotherapies tailored to the unique genetic profile of each cancer.
Infectious Disease Diagnostics: Identifying Pathogens
Rapid and accurate identification of pathogens is critical for effective infectious disease management. Molecular diagnostics, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assays, allow for the detection of specific microbial DNA or RNA sequences, enabling rapid diagnosis and monitoring of infections. This timely information is essential for guiding treatment decisions and preventing outbreaks. The development of molecular diagnostic tools can help to improve public health outcomes in the fight against infectious diseases.
Prenatal Diagnostics: Assessing Fetal Health
Molecular diagnostics have revolutionized prenatal care, offering a non-invasive way to assess fetal health and detect genetic disorders. Techniques like non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) allow for the analysis of fetal DNA circulating in maternal blood, providing information about potential chromosomal abnormalities and genetic conditions. These advancements empower expectant parents to make informed decisions about their pregnancies and prepare for the needs of their children.
Personalized Medicine: Tailoring Treatments to Individuals
The ability to analyze an individual's unique genetic profile is ushering in a new era of personalized medicine. Molecular diagnostics play a pivotal role in tailoring treatments to the specific needs of each patient. By understanding the genetic basis of a disease, clinicians can select therapies that are more likely to be effective and minimize adverse effects. This approach promises to improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs by optimizing treatment strategies for individual patients.
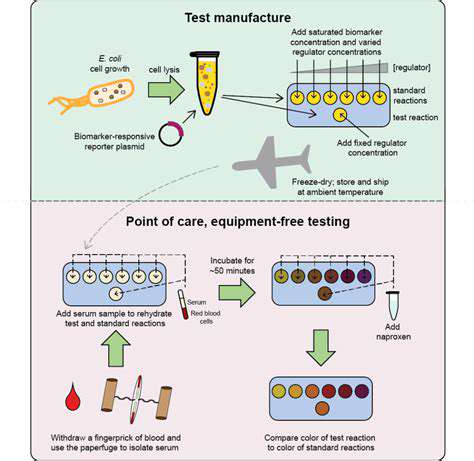
Rapid Point-of-Care Diagnostics: Bringing the Lab to the Patient
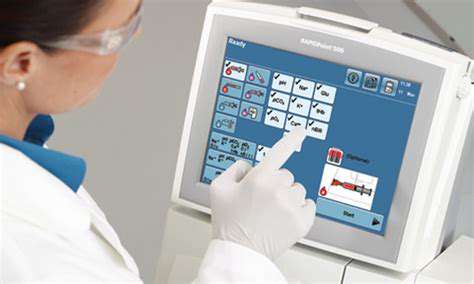
Rapid Point-of-Care Diagnostics: Benefits and Applications
Rapid point-of-care diagnostics (POCT) are revolutionizing healthcare by providing immediate results for various medical conditions. This technology allows for faster diagnosis and treatment, enabling clinicians to make informed decisions in real-time, leading to improved patient outcomes. The ability to obtain results quickly is crucial in emergency situations and for managing chronic conditions. This speed enables prompt interventions, avoiding potential delays in treatment.
POCT instruments are increasingly sophisticated, offering a wide range of capabilities beyond initial screening. These advanced devices often incorporate sophisticated algorithms and data analysis to provide more comprehensive diagnostic information. This translates to better diagnostic accuracy and a reduction in the need for more extensive, time-consuming laboratory testing.
Technological Advancements in POCT
Significant advancements in microfluidics, biosensors, and portable electronics have fueled the evolution of POCT. These advancements have led to smaller, more portable devices that require minimal training and resources to operate. These innovative technologies enable widespread use in diverse healthcare settings, from hospitals and clinics to remote areas and even in-home care settings.
The incorporation of sophisticated algorithms and data analysis further enhances the utility of POCT. These advancements contribute to improved diagnostic accuracy and reliability, making POCT a valuable tool for healthcare professionals.
Improved Patient Outcomes
Faster diagnosis translates directly to improved patient outcomes. Early detection and intervention can significantly reduce morbidity and mortality rates for various conditions. Prompt treatment based on immediate results helps prevent complications and allows for more effective management of acute illnesses. Moreover, POCT empowers patients to take an active role in their health management.
Cost-Effectiveness and Accessibility
POCT often proves to be more cost-effective than traditional laboratory testing, particularly when considering the reduced need for expensive equipment and personnel. These savings are significant, especially in resource-constrained settings, making POCT a valuable tool for improving healthcare access and affordability.
Furthermore, POCT empowers healthcare providers to provide care in more remote or underserved areas, thereby increasing accessibility and reducing disparities in healthcare access.
Integration with Electronic Health Records (EHR)
The seamless integration of POCT results with electronic health records (EHRs) is a crucial aspect of its impact. This integration streamlines patient care by providing clinicians with instant access to critical information, enabling better decision-making. The real-time data flow enhances communication and collaboration among healthcare providers, improving the overall quality of patient care.
Addressing Specific Healthcare Needs
POCT devices can be tailored to address specific healthcare needs, catering to various clinical areas. These personalized applications encompass a wide array of applications, from blood glucose monitoring to rapid infectious disease diagnosis. This adaptability makes POCT a versatile tool for improving diagnostic capabilities and treatment plans across a spectrum of medical conditions.
From emergency departments to outpatient clinics, POCT offers a flexible and adaptable solution for rapid diagnostics, improving patient care and healthcare efficiency.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the numerous benefits, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of POCT. These challenges encompass issues related to regulatory approvals, standardization, and the maintenance of quality control measures. Addressing these challenges is critical for ensuring the reliability and accuracy of POCT results.
Future research and development will focus on innovations in point-of-care diagnostics, creating more sophisticated, portable devices with enhanced capabilities and wider applications in healthcare. This will further improve diagnostic precision and expand accessibility, thus improving the quality of healthcare worldwide.