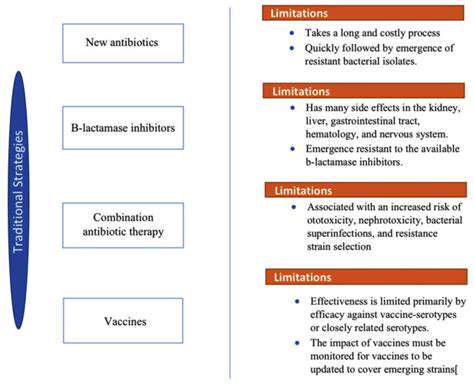
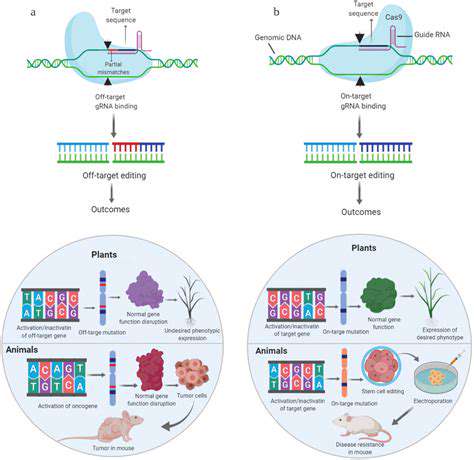
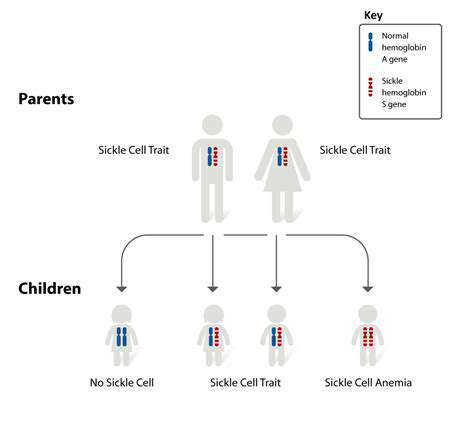
Modern medicine stands on the brink of a revolution with tools like CRISPR-Cas9 enabling precise alterations to our genetic blueprint. These advancements create possibilities for addressing genetic disorders once thought untreatable - conditions such as cystic fibrosis, Huntington's disease, and sickle cell anemia now face potential cures. The healthcare implications are staggering, offering hope where none existed before.
Direct genetic modification represents perhaps the most significant breakthrough in medical science this century. Beyond disease treatment, researchers are investigating agricultural applications, environmental solutions, and fundamental biological discoveries through these techniques.
Ethical Considerations and Public Perception
While the potential benefits are enormous, gene editing presents profound ethical dilemmas. Unintended consequences at both individual and societal levels demand rigorous oversight and thoughtful regulation. The controversial practice of germline editing, which affects future generations, remains particularly contentious due to its irreversible nature.
Public understanding and acceptance will largely determine how these technologies develop. Transparent discussions and comprehensive education initiatives are essential for building societal trust and ensuring responsible implementation that serves humanity's best interests.
Technical Advancements and Challenges
The field continues evolving rapidly, with newer methods offering enhanced precision while reducing unintended genetic modifications. Despite progress, significant obstacles remain regarding perfecting targeting accuracy and minimizing procedure-related risks.
Effective delivery of editing tools to specific cells presents another major challenge. Scientists are investigating various delivery mechanisms to improve safety and efficacy as these technologies advance toward clinical applications.
The Future of Gene Therapy
Gene therapy's trajectory depends on carefully balancing its extraordinary potential against legitimate concerns. With continued research and ethical guidance, genetic editing may transform medicine, potentially eliminating hereditary diseases altogether. Maintaining open dialogue among researchers, policymakers, and the public remains crucial as these technologies progress.
Clinical integration requires thorough testing, careful evaluation of outcomes, and comprehensive understanding of long-term effects. This measured approach ensures maximum benefit while minimizing potential drawbacks.
Regulatory Frameworks and Societal Impact
Developing comprehensive oversight systems is critical for responsible genetic editing advancement. These must address consent protocols, potential misuse, and equitable access to emerging therapies. International cooperation will prove vital given the global implications.
The ripple effects of genetic editing extend well beyond healthcare, influencing agriculture, conservation efforts, and our fundamental understanding of biology. Considering long-term consequences carefully will ensure these powerful tools are used responsibly for humanity's benefit.
Ethical Implications of Personalized Medicine
Personalized Medicine and Privacy
Tailoring treatments to individual genetic profiles represents a medical breakthrough, but raises complex privacy concerns. Handling sensitive genetic information necessitates robust safeguards against misuse and discrimination. Implementing stringent data protection protocols and clear usage guidelines is essential for maintaining patient trust in this rapidly advancing field.
Protecting genetic privacy requires comprehensive regulations preventing unauthorized data sharing. This includes securing healthcare systems and research databases while educating patients about their genetic rights and options.
Equity and Access to Personalized Treatments
While promising revolutionary healthcare improvements, personalized medicine risks exacerbating health disparities due to high costs. Creating affordable access models through innovative funding approaches and cost-effective diagnostic development is crucial for equitable implementation.
Educational initiatives targeting diverse populations must accompany technological advancements to ensure broad understanding and appropriate application of these personalized approaches.
The Role of Informed Consent and Patient Autonomy
Informed consent becomes particularly complex in personalized medicine, requiring clear communication about genetic testing implications. Providing accessible information empowers patients to make decisions aligned with their values and healthcare goals.
Healthcare providers must develop effective communication strategies to address patient concerns and facilitate truly informed choices regarding genetic testing and personalized treatment options.
The Role of Biotechnology in Agriculture and Food Production

Genetic Engineering for Enhanced Crop Traits
Agricultural biotechnology enables targeted crop improvements through precise genetic modifications. This scientific approach facilitates development of plants with superior yields, nutritional content, and environmental resilience. Such advancements help address food security challenges in adverse growing conditions.
Contemporary agricultural practices increasingly rely on these biotechnological tools to create hardier, more productive crops. From drought-resistant varieties to nutritionally-enhanced staples, the potential applications continue expanding.
Improving Pest and Disease Resistance
Biotechnology offers environmentally-friendly solutions for crop protection by developing naturally resistant plant varieties. This reduces reliance on chemical pesticides while maintaining crop health and yield potential.
Ongoing research enhances these genetic modifications' effectiveness, providing sustainable protection against evolving agricultural threats.
Enhanced Nutritional Value
Biofortified crops developed through biotechnology address global malnutrition by increasing essential nutrient content. These nutritionally-enhanced varieties can significantly improve public health outcomes, particularly in food-insecure regions.
Such innovations demonstrate biotechnology's potential to combat dietary deficiencies on a global scale through improved staple crops.
Sustainable Agricultural Practices
Biotechnology contributes to environmental sustainability by developing crops requiring fewer resources. These advancements reduce agriculture's ecological impact by decreasing chemical inputs while maintaining productivity.
Environmentally-adapted crops help farmers confront climate challenges while preserving ecosystems.
Herbicide Tolerance
Herbicide-resistant crops enable more efficient weed control, increasing yields while reducing labor requirements. This technology has transformed large-scale farming practices worldwide.
The economic and operational benefits make this application particularly valuable for commercial agriculture.
Improving Crop Yield and Quality
Genetic modifications enhance both crop productivity and qualitative characteristics like shelf life and processing qualities. These improvements help meet rising global food demands while enhancing nutritional value.
Such biotechnological applications demonstrate how science can address multiple agricultural challenges simultaneously.
When it comes to fueling your body, personalized nutrition plans account for individual factors including age, activity levels, and health goals. These customized approaches optimize macronutrient balance for specific objectives like weight management or athletic performance. Proper nutritional optimization functions like high-grade fuel for human physiology, supporting both immediate performance and long-term wellness.