Harnessing Nature's Power
The burgeoning field of bio-based beauty is revolutionizing personal care formulations, drawing inspiration from nature's vast repository of potent ingredients. Instead of relying solely on synthetic chemicals, innovators are exploring the use of plant extracts, natural oils, and other renewable resources. This approach promises not only gentler formulations but also a more sustainable and environmentally conscious path forward in the personal care industry. This shift reflects a growing consumer demand for products that align with ethical and ecological values.
This natural approach to personal care is not merely a trend; it's a response to mounting concerns about the environmental impact of synthetic chemicals and the potential health risks associated with some conventional ingredients. Consumers are increasingly seeking products that are both effective and environmentally responsible, driving demand for these innovative bio-based solutions.
Sustainable Sourcing and Manufacturing
A critical aspect of bio-based beauty lies in the sustainable sourcing of raw materials. Ethical sourcing practices are paramount, ensuring that these natural ingredients are harvested responsibly, minimizing environmental impact and supporting local communities. This extends beyond the ingredients themselves to encompass the entire manufacturing process, promoting eco-friendly practices throughout the supply chain.
Sustainable manufacturing practices are essential to maintaining the integrity of bio-based beauty products. This includes reducing water and energy consumption, minimizing waste generation, and employing closed-loop systems. These efforts to reduce the environmental footprint of production are crucial to the long-term viability and success of this innovative industry.
Bio-Based Alternatives to Synthetic Ingredients
Bio-based beauty products offer compelling alternatives to synthetic ingredients commonly found in conventional cosmetics. Natural emollients, humectants, and preservatives derived from plants and other renewable sources are replacing petroleum-derived counterparts. This shift is not just about sustainability; it's also about potentially improving product efficacy and safety profiles.
The development of bio-based alternatives is a dynamic process, driven by scientific research and technological advancements. Scientists are constantly exploring new sources and methods for producing natural substitutes, leading to a wider range of choices for consumers.
Improved Efficacy and Safety Profiles
Many bio-based ingredients demonstrate remarkable efficacy in skincare and hair care. Plant-derived extracts, for example, often exhibit potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, leading to improved skin health and reduced signs of aging. Bio-based preservatives are also showing great promise, offering natural alternatives to potentially harmful synthetic chemicals.
The safety profiles of bio-based ingredients are often better understood and more predictable compared to those of many synthetic chemicals. This contributes to a more secure and confident consumer experience, knowing that the products they use are less likely to trigger allergic reactions or other adverse effects.
The Role of Innovation in Formulation
Bio-based beauty necessitates innovative formulation strategies. Scientists and formulators need to understand the unique properties of natural ingredients and create effective and stable products. This means developing creative methods for extracting, purifying, and incorporating these ingredients into consistent and appealing formulations.
The ongoing research and development of novel bio-based ingredients and delivery systems are key to further expanding the horizons of this emerging industry.
Consumer Acceptance and Market Trends
The increasing consumer awareness of environmental and health concerns is driving the demand for bio-based beauty products. Consumers are actively seeking out products that minimize their environmental footprint and prioritize natural ingredients. This trend is also impacting the market, with numerous brands incorporating bio-based technologies into their product lines.
The Future of Bio-Based Beauty
The future of bio-based beauty is bright, with potential for significant growth and innovation. Further research and development will lead to even more effective and sustainable formulations. As technology advances and consumer demand grows, bio-based beauty is poised to become a dominant force in the personal care industry, offering a more ethical and environmentally friendly path forward.
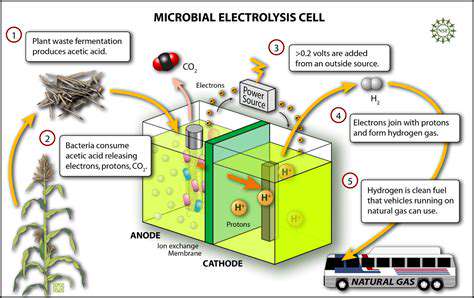
Harnessing Microbes for Novel Ingredients

Harnessing the Power of Microbes in Food Production
Microbes, those tiny organisms invisible to the naked eye, play a crucial role in numerous aspects of our lives, including food production. Their metabolic processes are often harnessed to create desirable qualities in foods, like texture, flavor, and preservation. From the fermentation of yogurt to the production of cheeses, microbes have been utilized for centuries to enhance the sensory experience and safety of food products.
The use of microbes in food production offers significant advantages. For example, microbial fermentation can contribute to the development of unique flavors and textures that consumers crave. Furthermore, some microbial processes can enhance the nutritional value of foods by increasing the availability of certain vitamins or minerals.
Microbial Diversity in Food Applications
A vast array of microbes are employed in food production, each contributing unique characteristics to the final product. Yeast, for instance, is essential in baking, converting sugars into carbon dioxide, leading to the characteristic rise in bread. Bacteria, such as Lactobacillus species, are used to ferment dairy products, creating the tangy flavors and textures found in yogurt and sauerkraut.
Beyond these well-known examples, a growing number of microbes are being investigated for their potential applications in food production. Researchers are exploring the use of specific microbes to create novel food products with enhanced nutritional profiles and novel sensory experiences. This exploration opens exciting possibilities for tailored food production with potential health benefits.
The Role of Microbes in Food Preservation
Microbes are not only used to create desirable flavors and textures, but also to preserve foods. Fermentation processes, which involve the growth of specific microbes, can inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria, thereby extending the shelf life of food products. This is a critical aspect of food safety and security. By creating an environment unfavorable to harmful microorganisms, fermentation methods can significantly reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses.
Traditional methods of food preservation often rely on inhibiting the growth of microbes through techniques like salting or drying. However, microbial fermentation offers a more natural and sustainable approach. This natural preservation method is gaining increasing interest as consumers seek healthier and more environmentally friendly food production methods.
Future Applications and Innovations
The future of harnessing microbes in food production looks promising. Advancements in genetic engineering and metabolic engineering are paving the way for developing microbes with even more specific and tailored functionalities. This could lead to the creation of foods with improved nutritional content, enhanced flavor profiles, and reduced environmental impact. Precision fermentation, guided by scientific understanding, will likely play a crucial role in future food production.
As our understanding of microbial metabolism deepens, we can expect to see innovative applications of microbes in food production, leading to the development of novel food products and improved food preservation techniques. This will likely involve the use of genetically modified microbes for tailored production of specific metabolites.
A website is a crucial foundation for any modern business, but it's only one piece of the puzzle. To truly thrive in today's digital landscape, you need to expand your online presence beyond the confines of your website. This involves exploring diverse online platforms and engaging with your audience in various ways.
Sustainable Alternatives to Traditional Ingredients

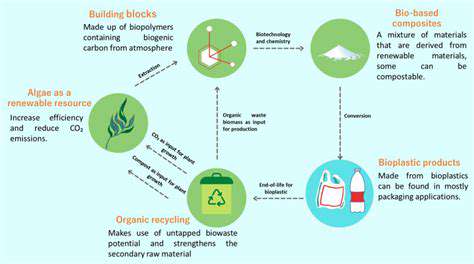
Sustainable Alternatives to Traditional Plastics
The pervasive use of plastics has created a significant environmental crisis, contributing to pollution of land and water. This widespread dependence on fossil fuel-derived plastics necessitates a transition to more sustainable alternatives. Finding replacements that maintain comparable functionality while minimizing environmental impact is a critical challenge. Many innovative solutions are emerging, promising a future with reduced plastic waste.
Bioplastics, derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane, offer a potential pathway to sustainability. However, the environmental impact of bioplastic production must be carefully assessed, including the land use required for cultivation and the energy consumption in processing. The scalability and cost-effectiveness of these alternatives are crucial factors in their widespread adoption.
Plant-Based Materials and Composites
Plant-based materials, such as bamboo, wood pulp, and various plant fibers, are gaining traction as sustainable alternatives. These materials often exhibit impressive strength and durability, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, including packaging, construction, and textiles. Their natural origin and inherent biodegradability make them a promising avenue for reducing reliance on traditional petroleum-based plastics.
Composites, which combine plant-based fibers with polymers or other reinforcing materials, offer enhanced properties. These materials can be tailored for specific applications, achieving desired levels of strength, flexibility, and other characteristics. The development of innovative composite materials represents a key area of research focused on creating sustainable alternatives with superior performance.
Furthermore, the development of bio-based adhesives and coatings using plant extracts can significantly reduce the use of petroleum-derived products in various industries. These sustainable alternatives aim to improve the overall environmental footprint of products while preserving their functionality.
The shift towards plant-based materials and composites is driven by a desire for materials with a reduced environmental impact. These materials often require less energy to produce and can be readily recycled or composted, minimizing waste generation.
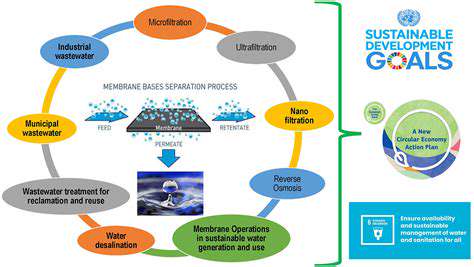
Innovations in Recycling and Upcycling
While developing new materials is essential, existing plastic waste presents a pressing challenge. Innovative recycling technologies are crucial for effectively managing the existing plastic infrastructure. Advanced recycling methods, such as chemical recycling, aim to break down plastics into their constituent components for reuse in new products.
Upcycling, which involves transforming waste materials into higher-value products, is another valuable approach. This process can extend the lifespan of plastics and reduce the demand for virgin materials. These efforts represent a vital step toward a circular economy for plastics.
Investing in infrastructure for effective plastic sorting and processing is critical to facilitating widespread recycling and upcycling initiatives. Efforts to educate consumers about responsible plastic disposal and promote reusable alternatives are also crucial components of a comprehensive sustainability strategy.
Ethical Considerations and Future Outlook
Ethical Implications of Synthetic Biology in Cosmetics
The integration of synthetic biology into cosmetics raises significant ethical concerns. One major point of contention revolves around the potential for unforeseen health consequences. While rigorous testing is crucial, the complexity of biological systems means that long-term effects might not be immediately apparent. Consumers need transparency and assurance that products are thoroughly evaluated for safety before entering the market. This necessitates robust regulatory frameworks that adapt to the rapid advancements in synthetic biology.
Another ethical dimension involves the potential for exacerbating existing inequalities. If synthetically produced ingredients become more expensive than naturally derived alternatives, access to effective and affordable cosmetics could be limited to wealthier demographics. Strategies to ensure equitable access and affordability must be considered alongside the development and implementation of these technologies.
Potential for Allergic Reactions and Immunological Responses
The introduction of novel synthetic biological components into cosmetic products raises concerns about potential allergic reactions and immunological responses in consumers. The body's immune system may react unexpectedly to these unfamiliar molecules, leading to skin irritation, rashes, or more severe allergic reactions. Rigorous testing protocols are essential to identify and mitigate these risks before products reach the market. This includes not only testing for immediate reactions but also evaluating long-term exposure effects.
Furthermore, the potential for cross-reactivity between synthetic components and existing allergens needs careful consideration. This is crucial to prevent unintended consequences and ensure consumer safety. Detailed and comprehensive studies are necessary to understand the intricacies of the human immune system's interaction with these novel elements.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
The environmental impact of synthetic biology in cosmetics is a critical area of concern. The production processes associated with certain synthetic components might involve high energy consumption or the use of hazardous chemicals. Careful consideration must be given to minimizing the environmental footprint of these products, from the raw materials to their disposal. Sustainable practices, including resource efficiency and eco-friendly manufacturing processes, are essential to mitigate the potential negative impact.
Intellectual Property Rights and Access to Technology
The development of synthetic biology-based cosmetics is likely to generate significant intellectual property rights issues. Defining clear ownership and licensing agreements for these technologies is essential to ensure fair compensation for innovators while fostering innovation and access to these advancements for all. Transparency in these agreements is paramount to avoid potential monopolies and ensure equitable access to the benefits of this technology.
Regulatory Challenges and Future Guidelines
The rapid pace of synthetic biology advancement poses significant challenges for regulatory bodies. Existing regulations may not adequately address the unique complexities of synthetic biology-derived ingredients in cosmetics. Developing clear, comprehensive, and adaptable regulatory guidelines is crucial to ensure consumer safety and prevent the misuse of this technology. International collaborations and open discussions between scientists, regulators, and industry stakeholders are vital for establishing robust ethical frameworks.
Consumer Education and Transparency
Ultimately, informed consumer choices are essential to the responsible use of synthetic biology in cosmetics. Clear and accessible information about the ingredients, manufacturing processes, and potential benefits and risks of these products is crucial. Education initiatives aimed at empowering consumers with the knowledge to make informed decisions about the products they use are vital. Transparency in product labeling and readily available scientific data will build consumer trust and confidence in the safety and efficacy of synthetic biology-based cosmetics.