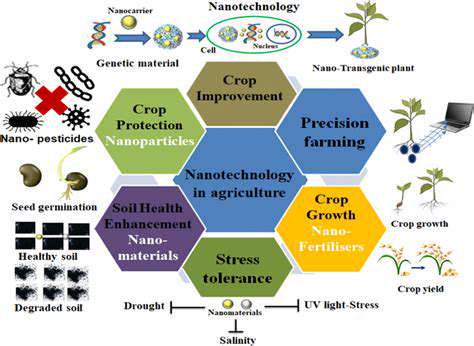
Strategies for Efficient Drug Approval Processes

Pre-clinical Testing and Validation
Thorough pre-clinical testing is crucial for identifying potential drug candidates and assessing their safety and efficacy before human trials. This phase involves rigorous laboratory experiments, animal studies, and computational modeling to evaluate the drug's mechanism of action, target engagement, and potential side effects. Careful attention to detail and adherence to strict protocols throughout this stage is paramount for minimizing risks associated with human clinical trials. The results of these studies inform the design of subsequent clinical trials and ultimately contribute to optimizing the drug development process.
A key aspect of pre-clinical testing is the selection of appropriate animal models. These models should closely mimic the human condition to accurately reflect the drug's potential therapeutic effects and side effects. This process requires careful consideration of the specific disease target and the potential mechanisms of action of the drug candidate.
Target Identification and Validation
Identifying the precise biological target for a drug is a critical first step in the drug development process. This involves understanding the disease mechanism and pinpointing the specific molecular pathways or proteins that are involved. Precise target identification is essential for developing effective and safe drugs that specifically interact with the desired target. This step requires an in-depth understanding of the biological pathways relevant to the disease and the use of advanced bioinformatics and biochemical techniques.
Validated targets provide a scientific basis for subsequent drug development efforts. Once a specific target is identified, it's essential to confirm that it plays a crucial role in the disease process, allowing for targeted drug development.
Drug Design and Optimization
Once the target is identified, the next phase involves designing and optimizing drug molecules that can effectively interact with the target. This often involves utilizing computer-aided drug design (CADD) methods to predict and evaluate potential drug candidates based on their binding affinities and other relevant properties. This step relies heavily on computational modeling and experimental validation to ensure that the proposed drug candidate possesses the desired properties.
This process often involves iterative modifications to the drug molecule, a process called drug optimization, to enhance its potency, selectivity, and pharmacokinetic properties.
Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Studies
Understanding how the drug interacts with the body is critical for optimizing its therapeutic effect and minimizing potential side effects. This involves pharmacokinetic (PK) studies, which examine how the body absorbs, distributes, metabolizes, and eliminates the drug. These studies are crucial for determining the appropriate dosage regimen and predicting the drug's behaviour in the body.
Pharmacodynamic (PD) studies, in contrast, investigate the drug's effects on the body and how its activity relates to its concentration. Both PK and PD studies are essential for determining the optimal dosing strategy and predicting the drug's effectiveness.
Clinical Trial Design and Execution
Clinical trials are crucial for assessing the safety and efficacy of a drug candidate in humans. The design of these trials needs to be carefully considered and rigorously executed to ensure the reliability and validity of the results. These studies typically involve different phases, each designed to evaluate specific aspects of the drug's performance.
Careful planning, ethical considerations, and rigorous data analysis are crucial for successful clinical trials, which ultimately guide the decision-making process for regulatory approval.
Regulatory Approvals and Submissions
Obtaining regulatory approval is a crucial step in the drug development process, ensuring that the drug meets safety and efficacy standards. The process involves a complex set of steps, including data submission and review by regulatory agencies like the FDA. Meeting these rigorous standards is essential for ensuring public safety and efficacy.
The regulatory approval process can be lengthy and complex, involving multiple rounds of review and revisions to ensure the safety and efficacy of the drug candidate.
Post-Market Surveillance and Monitoring
Even after a drug is approved, ongoing monitoring and surveillance are essential to detect and manage any potential adverse effects. Post-market surveillance involves tracking the long-term safety and effectiveness of the drug in the wider population. This surveillance is vital for identifying any previously unknown risks or benefits.
Continuous monitoring of a drug's performance in the real-world setting is vital for maintaining public safety and refining knowledge about its potential benefits and risks.