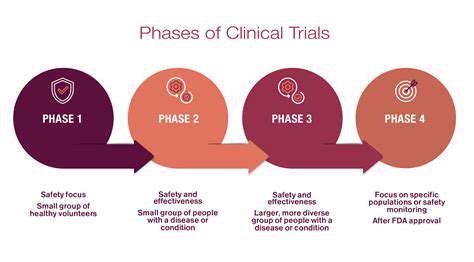
Introduction to Drug Manufacturing Optimization
Understanding the Importance of Optimization
Drug manufacturing optimization is crucial for ensuring the quality, safety, and efficacy of pharmaceutical products. By streamlining processes, minimizing errors, and maximizing yield, manufacturers can reduce costs, improve efficiency, and ultimately contribute to the timely availability of life-saving medications. This approach not only benefits the pharmaceutical industry but also patients who rely on these products for their health and well-being.
Optimizing drug manufacturing is a multifaceted endeavor that requires a comprehensive understanding of the entire production process, from raw material sourcing to final product packaging. It encompasses various strategies and techniques aimed at continuous improvement and enhanced performance.
Key Drivers for Optimization Initiatives
Several factors drive the need for optimization in drug manufacturing. Regulatory requirements, increasing competition, and the rising demand for complex and innovative therapies all contribute to the pressure to enhance efficiency and productivity. Furthermore, the need to reduce manufacturing costs while maintaining high quality standards necessitates a focus on optimization strategies.
The industry constantly seeks ways to improve the speed of development, production, and distribution of new and existing drugs, thus creating a strong incentive for optimization.
Process Analytical Technology (PAT) Integration
Process Analytical Technology (PAT) plays a pivotal role in drug manufacturing optimization. PAT enables real-time monitoring and control of critical process parameters, allowing manufacturers to make informed decisions and adjustments throughout the manufacturing process. This data-driven approach empowers manufacturers to detect potential deviations early, preventing costly errors and ensuring product quality.
PAT's use in drug manufacturing has led to significant improvements in the efficiency and consistency of the production process, resulting in a more robust and reliable output.
Improving Quality Control and Assurance
Robust quality control and assurance measures are essential components of any successful drug manufacturing optimization strategy. Implementing stringent quality control protocols at each stage of production ensures that the final product meets the required safety and efficacy standards. This includes thorough testing, validation, and documentation to maintain traceability and compliance with regulatory guidelines.
A strong emphasis on quality control minimizes the risk of defective products reaching the market, protecting patients and upholding the reputation of the pharmaceutical company.
Supply Chain Optimization
Optimizing the drug supply chain is another critical aspect of drug manufacturing optimization. This involves streamlining the procurement of raw materials, reducing transportation times, and enhancing inventory management. Efficient supply chain management ensures a consistent and reliable flow of materials throughout the production process, minimizing delays and maximizing output.
Statistical Process Control (SPC) and Data Analysis
Statistical Process Control (SPC) methodologies are valuable tools in optimizing drug manufacturing. By analyzing data from various stages of the production process, manufacturers can identify patterns, trends, and potential issues. This data-driven approach allows for proactive intervention, preventing deviations and ensuring process consistency.
Implementing SPC procedures results in a more predictable and controlled manufacturing environment, ultimately leading to higher quality products and reduced production costs.
Sustainability Considerations in Optimization
Modern drug manufacturing optimization must incorporate sustainability considerations. This involves minimizing environmental impact by reducing waste, conserving energy, and using eco-friendly materials. Sustainable practices not only benefit the environment but also contribute to the long-term viability and reputation of the pharmaceutical company.
Adopting sustainable practices is a crucial aspect of responsible drug manufacturing and aligns with the growing global emphasis on environmental protection and resource conservation.
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance and Patient Safety
Understanding the Importance of Regulatory Compliance
Maintaining meticulous adherence to regulatory frameworks is paramount in ensuring the safety and efficacy of pharmaceuticals. This encompasses a wide range of standards, from Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to specific guidelines set by national and international regulatory bodies. Failure to meet these standards can lead to significant repercussions, including product recalls, legal action, and a tarnished reputation, ultimately impacting patient safety and the long-term viability of the organization.
A robust compliance program, integrated into every aspect of drug manufacturing, safeguards against errors and deviations. This proactive approach fosters a culture of quality, ensuring consistent production of high-quality, safe medications that meet the highest standards of efficacy and safety.
Implementing Robust Quality Control Measures
Effective quality control (QC) measures are essential for maintaining consistent product quality throughout the entire drug manufacturing process. This includes rigorous testing at various stages, from raw material inspection to finished product analysis. Implementing sophisticated analytical techniques, coupled with meticulous documentation and record-keeping, helps identify and mitigate potential quality issues early in the process.
The use of advanced analytical instrumentation and trained personnel ensures that quality standards are upheld. This proactive approach not only enhances product safety but also safeguards the company's reputation and fosters patient confidence in the efficacy of the medications produced.
Maintaining Secure and Controlled Environments
Pharmaceutical manufacturing environments must be rigorously controlled to prevent contamination and maintain product integrity. This involves employing stringent environmental controls, such as maintaining appropriate temperature, humidity, and air quality, to avoid compromising the quality and safety of the manufactured drugs.
Implementing stringent procedures for handling materials and personnel, along with meticulous record-keeping, helps ensure that the manufacturing environment remains sterile and free from contaminants. This commitment to maintaining a secure environment helps to guarantee the quality and safety of the final product and protects against potential liabilities.
Ensuring Traceability and Documentation
Maintaining comprehensive traceability of materials and products throughout the manufacturing process is crucial for regulatory compliance and patient safety. This includes meticulously documenting every step, from raw material receipt to final product release. Detailed records provide critical information in case of any issues or recalls, enabling swift identification and resolution of problems.
Effective traceability systems and comprehensive documentation procedures support regulatory audits and facilitate rapid identification of potential deviations or quality issues. This meticulous documentation, combined with stringent quality control measures, ensures accountability, transparency, and a proactive approach to maintaining the highest standards of patient safety.
Training and Development of Personnel
A well-trained workforce is critical to upholding regulatory compliance and ensuring patient safety in the drug manufacturing process. Comprehensive training programs should cover GMP guidelines, quality control procedures, and safety protocols. Regular updates and refresher courses are essential to keep personnel abreast of evolving regulations and best practices.
Investing in employee training demonstrates a commitment to quality and safety, fostering a culture of compliance within the organization. This not only reduces the risk of errors and deviations but also enhances the overall efficiency and productivity of the manufacturing process, ultimately leading to a safer and more reliable product.
Continuous Improvement and Risk Management
A culture of continuous improvement is essential for optimizing drug manufacturing processes and maintaining regulatory compliance. This involves regularly evaluating existing procedures, identifying potential risks, and implementing corrective actions to mitigate these risks. A robust risk management framework ensures that potential hazards are identified and addressed proactively.
Implementing a comprehensive risk assessment protocol, combined with a commitment to continuous improvement, helps identify potential weaknesses in the manufacturing process and proactively address them. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of adverse events, ensures patient safety, and maintains compliance with evolving regulations.