Gene editing technologies, like CRISPR-Cas9, offer unprecedented potential in combating pathogenic microorganisms. These tools allow scientists to precisely target and modify specific genes within an organism's DNA, paving the way for innovative therapies and preventive strategies. This precision is a significant advancement over traditional methods, offering the potential to eliminate disease-causing genes without unintended consequences. The ability to manipulate genetic material at such a fundamental level has the potential to revolutionize the fight against infectious diseases.
Targeting Pathogenic Genes for Elimination
A key application of gene editing is the direct targeting of genes responsible for the pathogenicity of various microorganisms. By disabling or modifying these essential genes, we can potentially render the pathogen harmless without harming the host organism. This approach holds promise for eradicating or significantly weakening the ability of disease-causing bacteria, viruses, and fungi to cause harm.
Scientists are exploring various strategies for disrupting genes critical to pathogen survival and replication. This includes targeting genes involved in virulence factors, metabolic pathways, and essential cellular functions. The success of these strategies hinges on the accurate identification and targeting of crucial genes within the pathogen genome.
Developing Novel Therapeutic Strategies
Gene editing technologies also offer the potential for developing novel therapeutic strategies to treat infectious diseases. These techniques could be used to enhance the immune system's response to pathogens, or to correct defects in host cells that make them susceptible to infection. This capability is particularly important for diseases that currently lack effective treatments or have limited treatment options.
For example, gene editing could potentially be used to modify immune cells to better recognize and destroy pathogens, or to modify host cells to resist infection. The possibilities are vast and exciting, representing a new frontier in medical treatment.
Ethical Considerations and Future Directions
Despite the immense promise of gene editing, it's crucial to address the ethical implications associated with its application. Careful consideration must be given to potential off-target effects, unintended consequences, and the equitable distribution of these powerful technologies. Addressing these concerns is vital to ensure responsible and beneficial application of gene editing in the fight against pathogens.
Future research in this field will focus on developing precise and safe gene editing tools, identifying new targets within pathogenic genomes, and assessing the long-term effects of these interventions. As technology advances, gene editing has the potential to play a significant role in preventing and treating a wide range of infectious diseases.
Ethical Considerations and Future Directions
Ethical Implications of Gene Editing in the Gut Microbiome
Gene editing technologies, particularly CRISPR-Cas9, offer unprecedented potential for manipulating the gut microbiome, potentially treating a range of diseases. However, the ethical implications of such interventions are complex and require careful consideration. The possibility of unintended consequences, both in the targeted gut microbiome and beyond, necessitates a thorough understanding of the long-term effects on human health. Furthermore, issues of equitable access to these potentially transformative therapies must be addressed, ensuring that the benefits are not limited to those who can afford them.
One key ethical concern centers on the potential for off-target effects. Modifying specific bacterial genes may have unforeseen consequences on other microbial populations within the gut, potentially disrupting the delicate balance of the ecosystem and leading to unforeseen health outcomes. Rigorous pre-clinical and clinical trials are crucial to identify and mitigate these risks, ensuring the safety and efficacy of these procedures. Transparency and open dialogue between researchers, policymakers, and the public are essential for navigating these complex ethical considerations.
Future Research Directions and Applications
Future research in gene editing and the gut microbiome should focus on developing precise and predictable methods for manipulating microbial communities. This includes exploring innovative strategies for targeting specific bacterial species or functions without disrupting the entire microbiome ecosystem. Developing more sophisticated models for predicting the long-term effects of gene editing interventions is vital for avoiding potential unintended consequences.
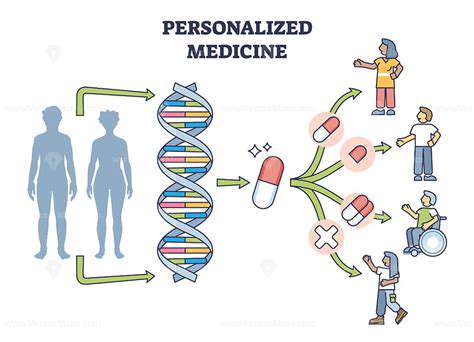
Beyond basic research, potential applications for gene editing in the gut microbiome extend to the development of personalized therapies for gut-related diseases. Tailoring treatments to an individual's specific microbiome composition could lead to more effective and targeted interventions. Furthermore, gene editing could potentially be used to engineer gut microbes for improved nutrient absorption, enhanced immune system function, or even the production of therapeutic compounds.
The development of robust, ethical guidelines and regulatory frameworks is critical for ensuring responsible and beneficial applications of gene editing technologies in the gut microbiome. International collaboration and consensus-building are essential to navigate the complex ethical and societal implications of these powerful new tools.
Further research is needed to understand the complex interactions within the gut microbiome and how gene editing can be used to address specific health needs. This includes investigation into the role of the gut microbiome in various diseases, the development of advanced diagnostic tools, and the creation of innovative therapeutic strategies.
The long-term effects on the broader ecosystem and the environment also warrant further investigation. A comprehensive understanding of the ecological impact of manipulating gut microbes is essential to ensure sustainable and responsible use of these technologies.
In conclusion, careful consideration of ethical implications alongside ongoing research is vital for harnessing the potential of gene editing in the gut microbiome for improved human health.