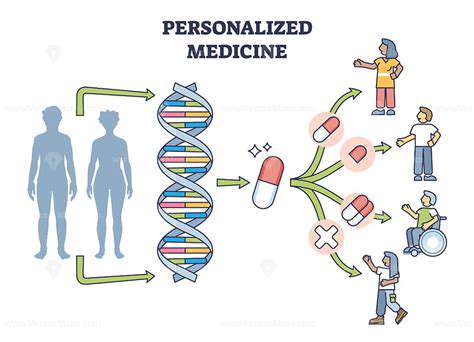
Understanding the Underlying Mechanisms
Neuropathic pain arises from damage or dysfunction of the nervous system, a complex network of billions of neurons. This damage can manifest in various ways, from nerve compression to autoimmune disorders, leading to a wide range of symptoms. It's important to understand the diverse pathways involved in the development and maintenance of this chronic pain condition.
The exact mechanisms behind neuropathic pain are still not fully understood, but it's clear that complex interactions between the nervous system and the body's inflammatory response play crucial roles. Researchers are actively investigating these interactions to develop more effective treatment strategies.
Types of Neuropathic Pain
Neuropathic pain isn't a single entity; it exists in many forms, each with its own set of symptoms and underlying causes. Peripheral neuropathies, for example, affect the nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord, often resulting from diabetes, infections, or injuries. Central neuropathies, on the other hand, stem from damage within the central nervous system, such as multiple sclerosis or stroke.
Diagnosis and Assessment
Diagnosing neuropathic pain can be challenging due to the variability in symptoms and the fact that the pain may not always correlate with visible nerve damage. Physicians rely on a combination of patient history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests to determine the cause and type of neuropathic pain.
A thorough evaluation is essential to rule out other potential causes of pain, such as arthritis or musculoskeletal issues. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan tailored to the individual's specific condition.
Impact on Daily Life
Neuropathic pain significantly impacts an individual's quality of life. The chronic and often debilitating nature of this pain can lead to difficulties in performing daily tasks, social withdrawal, and a decline in overall well-being. This can range from simple tasks like walking or dressing to more complex activities, impacting employment and relationships.
The emotional toll of chronic pain is often underestimated. Depression and anxiety are common comorbidities associated with neuropathic pain, further compounding the challenges faced by those affected.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for neuropathic pain is multifaceted and often involves a combination of approaches. Pharmacological interventions, including analgesics and anti-depressants, can help manage pain symptoms. Physical therapy and other non-pharmacological strategies can also be beneficial in improving function and reducing pain severity.
Emerging Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research into the mechanisms underlying neuropathic pain is paving the way for innovative treatment strategies. Scientists are exploring new avenues, such as targeting specific pain pathways and utilizing advanced imaging techniques, to gain a deeper understanding of this complex condition.
This ongoing research holds the promise of developing more effective and targeted therapies in the future, offering hope for better pain management and improved quality of life for those suffering from neuropathic pain.
Management Strategies and Support Systems
Effective management of neuropathic pain requires a holistic approach. This involves not only managing pain symptoms but also addressing the emotional and psychological well-being of the individual. Support groups and counseling can provide valuable emotional support and coping mechanisms for managing the challenges associated with chronic pain.
Implementing strategies such as relaxation techniques, mindfulness practices, and stress reduction techniques can significantly enhance the overall well-being of those experiencing neuropathic pain. This multifaceted approach to care is essential for long-term pain management and quality of life improvement.
Beyond the immediate payment of the ransom, organizations face significant financial repercussions. The costs extend far beyond the ransom amount itself, encompassing forensic analysis to identify the extent of the breach, data recovery efforts, and potential legal fees. These expenses can cripple a business, especially small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) lacking robust financial reserves.