Gene Editing Techniques: A Revolution in Agriculture
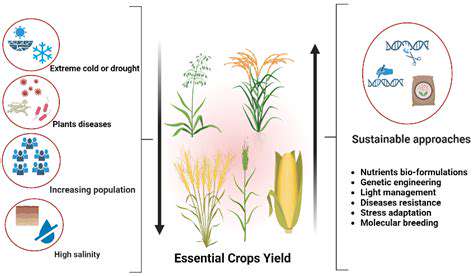
The development of gene-editing technologies, particularly CRISPR-Cas9, has opened up unprecedented possibilities for altering the genetic makeup of organisms, including crops. This revolutionary technology holds the potential to create crops with enhanced nutritional value, increased yields, and improved resistance to pests and diseases. This advancement promises to address global food security challenges by creating crops that thrive in challenging environments and are resilient to climate change.
Scientists are actively exploring various gene-editing strategies to improve crop traits. These techniques offer a precise and targeted approach compared to traditional breeding methods, significantly accelerating the development of desirable characteristics in plants.
Enhanced Nutritional Value: Feeding a Growing Population
Gene editing can be used to enhance the nutritional content of crops, making them more nutritious and fulfilling for consumers. This is a crucial step in addressing malnutrition and improving public health, particularly in regions where access to diverse and nutritious foods is limited. By introducing genes that increase the levels of essential vitamins and minerals, gene-edited crops can contribute significantly to a healthier population.
Furthermore, gene editing can also modify the composition of fatty acids and amino acids, potentially creating crops with a more balanced nutritional profile. This could lead to more efficient utilization of food resources and reduce reliance on supplemental nutrients.
Pest and Disease Resistance: Protecting Crops from Threats
Gene editing offers a powerful tool to engineer crops that are resistant to pests, diseases, and environmental stresses. This resistance can significantly reduce the need for chemical pesticides and herbicides, promoting more sustainable agricultural practices. By introducing genes that confer resistance to specific pathogens or pests, gene-edited crops can minimize crop losses and improve yield stability.
The development of crops resilient to extreme weather conditions, such as drought and salinity, is another significant application of gene editing. This resilience is crucial for maintaining food production in the face of climate change.
Increased Crop Yields: Meeting Global Food Demand
Gene editing can potentially boost crop yields by enhancing photosynthesis, nutrient uptake, and stress tolerance. By optimizing these key processes, gene-edited crops can produce more food per unit of land, which is vital for meeting the increasing global food demand. This increased productivity is crucial for feeding a growing population in a sustainable manner.
Moreover, gene editing can improve the efficiency of resource utilization, reducing the amount of water, fertilizer, and pesticides required to cultivate crops. This approach contributes to more sustainable agricultural practices and minimizes environmental impact.
Improved Crop Tolerance to Environmental Stresses
Gene editing can create crops that are more tolerant to various environmental stresses, such as drought, salinity, and extreme temperatures. This adaptability is essential for ensuring food security in regions facing climate change and environmental challenges. By engineering crops that can thrive in challenging conditions, gene editing can significantly enhance agricultural productivity in diverse climates.
These stress-tolerant crops are important in regions vulnerable to climate change. Gene editing provides a way to adapt crops to the changing environment and ensure reliable food production.
Economic Benefits and Societal Impacts
The economic benefits of gene-edited products are considerable, potentially leading to increased yields, reduced costs, and enhanced profitability for farmers. Gene-edited crops can enhance agricultural sustainability and reduce reliance on harmful pesticides and fertilizers. This can lead to significant cost savings and improved environmental outcomes.
Gene-edited crops can also have significant societal impacts by improving food security, reducing poverty, and enhancing access to nutritious food in vulnerable populations.
Ethical Considerations and Public Perception
Despite the numerous potential benefits, the development and deployment of gene-edited products raise important ethical considerations. Public perception and understanding of gene editing are crucial for responsible innovation and adoption. Addressing concerns regarding potential risks and benefits is essential to ensure a cautious and informed approach.
Open dialogue and transparent communication with the public and stakeholders are crucial for fostering trust and acceptance of gene-edited products.