The field of personalized medicine, specifically in drug development, is experiencing a surge in innovation. This approach tailors treatments to individual patients based on their unique genetic makeup, environmental factors, and lifestyle. This personalized approach promises to dramatically improve treatment efficacy and minimize adverse effects, moving beyond a one-size-fits-all model. By understanding the intricate interplay of these factors, we can unlock targeted therapies that are more effective and safer for each individual.
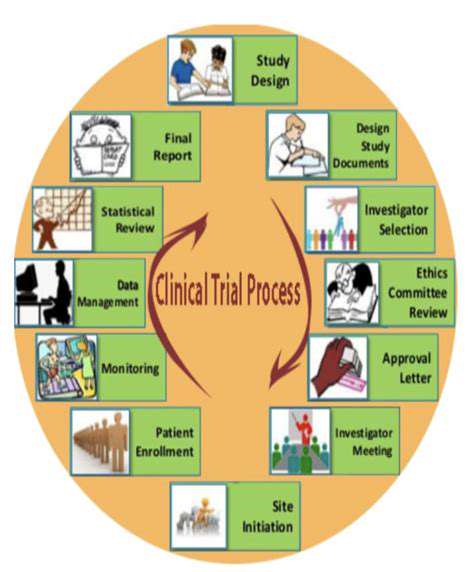
The traditional method of drug development often relies on large-scale clinical trials, which can be time-consuming and expensive. Personalized medicine, on the other hand, aims to accelerate the process by identifying specific genetic markers associated with disease progression and treatment response. This individualized approach allows for faster identification of effective therapies and reduced clinical trial durations.
Genetic Factors and Drug Response
Genetic variations play a pivotal role in how individuals respond to different medications. Certain genes influence the way drugs are metabolized, transported, and ultimately affect the body, leading to varying degrees of efficacy and side effects. Understanding these genetic variations is crucial in predicting individual drug responses and tailoring treatment regimens accordingly.
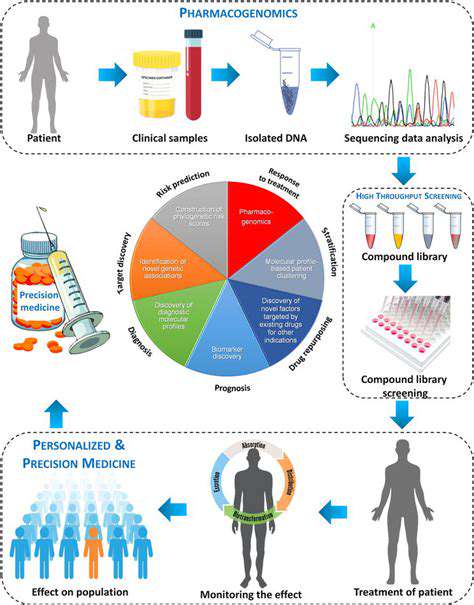
Pharmacogenomics, a branch of personalized medicine, studies the relationship between genes and drug response. By analyzing an individual's genetic profile, healthcare professionals can anticipate potential reactions to specific medications, enabling them to select the most appropriate treatment for that specific patient.
Environmental Influences on Drug Action
Beyond genetics, environmental factors, such as diet, lifestyle, and exposure to toxins, can also significantly influence how drugs interact with the body. These factors can modulate drug metabolism and absorption, potentially impacting the effectiveness and safety of a particular treatment.
A deeper understanding of the intricate interactions between environmental factors and drug action is crucial for developing personalized treatment strategies that account for these external influences. This information can be used to modify the dosage, timing, or even the type of medication to optimize its effectiveness and safety.
Developing Targeted Therapies
Personalized medicine enables the development of targeted therapies that precisely address the specific needs of each patient. This approach focuses on inhibiting or activating particular molecular pathways associated with disease progression, minimizing harm to healthy cells and maximizing treatment effectiveness.
Precision Diagnostics in Drug Selection
Advanced diagnostic tools, such as genomic sequencing and proteomic analysis, play a critical role in personalized drug development. These technologies provide detailed information about an individual's genetic makeup and protein expression, enabling the identification of specific biomarkers associated with disease and treatment response.
This information is critical for selecting the most appropriate drug and determining the optimal dosage. By analyzing these biomarkers, physicians can make informed decisions about treatment options, leading to more effective and targeted interventions.
Ethical Considerations and Future Directions
The rise of personalized medicine raises important ethical considerations related to data privacy, access to advanced technologies, and equitable distribution of care. Striking a balance between innovation and responsible application is paramount for ensuring that personalized approaches benefit all members of society.
Future research in personalized drug development will likely focus on developing more sophisticated diagnostic tools, creating more personalized treatment regimens, and addressing the ethical and societal implications of this revolutionary approach. Continued advancements in this field will pave the way for a future where healthcare is truly tailored to the individual.
Applications in Clinical Practice
Personalized Medication Selection
Pharmacogenomics is transforming drug selection by identifying genetic variations that influence how individuals metabolize and respond to medications. This personalized approach allows clinicians to choose the most effective and safest drugs for each patient, minimizing adverse drug reactions and maximizing therapeutic outcomes. By understanding an individual's genetic makeup, doctors can predict potential drug interactions and tailor dosages to optimize efficacy while minimizing potential side effects. This precision medicine approach is particularly valuable for patients with complex medical histories or those who have not responded well to standard treatments.
This is a significant advancement over traditional trial-and-error approaches to medication selection, where the optimal treatment may not be determined until significant time and effort have been expended. By integrating genetic information into clinical practice, we can significantly improve patient care and reduce the risk of adverse events.
Predicting Drug Response
Pharmacogenomics offers the potential to predict how a patient will respond to a particular medication, going beyond simple trial and error. By analyzing a patient's genetic profile, clinicians can identify specific genetic markers that correlate with a drug's efficacy or toxicity. This information empowers doctors to select medications more likely to be effective and reduce the risk of adverse reactions, leading to improved treatment outcomes.
This proactive approach can significantly impact various therapeutic areas, from oncology to psychiatry, where patient responses to medications can vary widely. The ability to anticipate drug response allows for more informed treatment plans, saving valuable time and resources, while minimizing the potential for harmful side effects.
Optimizing Dosage Regimens
Pharmacogenomics allows for the optimization of dosage regimens based on individual genetic variations. Genetic factors influence how the body metabolizes drugs, impacting their concentration in the bloodstream. By understanding these variations, clinicians can tailor medication dosages to achieve the desired therapeutic effect while minimizing the risk of toxicity. This personalized approach to dosage can lead to improved treatment outcomes and reduced side effects.
Patients with certain genetic variants might require higher or lower dosages of a specific medication to achieve the same therapeutic effect. This personalized approach to dosage optimization can significantly improve treatment efficacy, reduce the frequency and severity of adverse effects, and enhance patient compliance.
Tailoring Treatment for Specific Conditions
Pharmacogenomics has profound implications for various medical conditions, offering tailored treatment strategies based on individual genetic predispositions. For instance, in oncology, understanding genetic variations can inform the selection of targeted therapies that are more effective for specific types of cancers. In psychiatry, genetic information can guide the selection of medications and dosages that are more likely to be effective in managing mood disorders.
By incorporating genetic information into treatment protocols, we can move beyond a one-size-fits-all approach to patient care and create personalized treatment plans that maximize efficacy and minimize potential harm. This approach is particularly impactful for conditions with significant inter-individual variability in response to treatment, such as cancer and mental health disorders.
Drug Metabolism and Toxicity Prediction
Pharmacogenomics provides valuable insights into how individuals metabolize drugs, which is crucial for predicting potential drug-related toxicity. By identifying genetic variations associated with drug metabolism, clinicians can anticipate the likelihood of adverse drug reactions and adjust treatment strategies accordingly. Understanding individual metabolic pathways allows for safer and more effective medication administration.
This knowledge allows for more informed decisions regarding drug selection, dosage, and duration of treatment, ultimately reducing the risk of harmful side effects. This is particularly important for patients with compromised liver or kidney function, who may be more susceptible to drug-related toxicity. The ability to predict potential toxicity enables proactive measures to mitigate risks, leading to enhanced patient safety.
Machine learning (ML) is a subset of AI that focuses on enabling computers to learn from data without explicit programming. Algorithms are trained on massive datasets, allowing them to identify patterns, make predictions, and improve their performance over time. This iterative learning process is crucial for developing sophisticated AI systems.