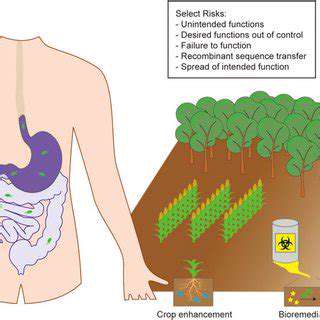
Introduction to Gene Editing and its Regulatory Challenges
Understanding Gene Editing Technologies
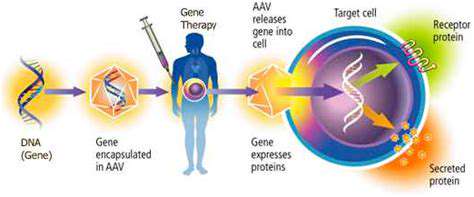
Gene editing technologies, like CRISPR-Cas9, offer unprecedented potential to treat genetic diseases and enhance human capabilities. These technologies allow scientists to precisely target and modify DNA sequences within a genome, potentially correcting faulty genes responsible for various disorders. This precise manipulation holds immense promise for developing cures for conditions currently considered intractable, offering hope for a future where genetic diseases are a thing of the past. However, this powerful tool also raises significant ethical and regulatory concerns, particularly regarding its potential misuse and off-target effects.
Different gene-editing tools, each with unique characteristics and mechanisms of action, are being developed and refined. Understanding these nuances is crucial for navigating the regulatory landscape surrounding their use. From Zinc Finger Nucleases (ZFNs) to Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nucleases (TALENs), the evolution of these technologies has brought forth progressively more precise and efficient methods for altering DNA. This evolution, while promising, demands a robust regulatory framework to ensure responsible development and application.
The Ethical Considerations of Gene Editing
Gene editing technologies raise profound ethical questions, particularly regarding germline editing, which alters the genetic makeup that can be passed on to future generations. This raises concerns about unintended consequences and the potential for creating unforeseen health problems. There is a need for societal dialogue and ethical frameworks to guide the responsible use of these powerful tools. The potential for genetic enhancement, while appealing, also raises concerns about exacerbating existing social inequalities and creating a two-tiered society, based on genetic access and capability.
The potential for misuse, such as creating designer babies or enhancing certain traits in a discriminatory manner, necessitates careful scrutiny and public discourse. The ethical implications extend beyond the immediate effects of the technology, encompassing considerations for future generations and the long-term impact on human diversity. These concerns underscore the necessity for robust ethical guidelines and public engagement in shaping the future of gene editing.
Regulatory Frameworks for Gene Editing
Establishing effective regulatory frameworks for gene editing is critical to ensuring both the safety and ethical application of these technologies. These frameworks need to be adaptable and responsive to the rapid advancements in the field, while simultaneously addressing the unique challenges posed by different gene editing tools and their potential applications. International collaboration and shared guidelines are essential to navigate the global implications of these technologies.
Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are grappling with the complex issue of balancing innovation with safety and ethical considerations. The development of clear guidelines for clinical trials, the oversight of research protocols, and the establishment of independent review boards are crucial components of these regulatory frameworks. Transparency and public engagement are essential to build trust and ensure that these technologies are developed and used in a responsible and equitable manner.
Challenges in Implementing Regulatory Pathways
Implementing effective regulatory pathways for gene editing faces numerous challenges, including the rapid pace of technological advancements, the complexity of the underlying scientific mechanisms, and the diverse applications across various fields. Defining clear lines of responsibility and accountability for different stakeholders, from researchers to clinicians, is a significant hurdle in ensuring safety and ethical standards.
Public Perception and Engagement in Gene Editing Regulation
Public perception plays a vital role in shaping the regulatory landscape for gene editing. Building public trust and fostering open dialogue are essential for ensuring that these technologies are developed and deployed responsibly. Education and outreach initiatives are crucial to address concerns and misconceptions about gene editing, promoting a comprehensive understanding of both the benefits and risks. Public engagement in policy discussions is key to establishing regulatory frameworks that reflect societal values and priorities.
Transparent communication about the risks and potential benefits of gene editing is critical for fostering informed public discourse and shaping public opinion. Engaging diverse stakeholders, including patients, researchers, ethicists, and policymakers, is essential for developing equitable and effective regulatory frameworks that balance innovation with public safety and ethical concerns.
The Role of Risk Assessment in Regulatory Pathways
Understanding the Regulatory Landscape
Risk assessment plays a critical role in navigating the complex regulatory pathways for gene therapies. It's not just about identifying potential hazards; it's about proactively anticipating and mitigating risks throughout the entire development process, from initial research and preclinical trials to clinical trials and eventual market authorization. This comprehensive approach ensures that gene therapies are both safe and effective, ultimately benefiting patients while minimizing potential adverse events.
The regulatory landscape for gene therapies is constantly evolving, requiring a deep understanding of the specific guidelines and regulations in different jurisdictions. This understanding is paramount for researchers and developers to ensure compliance and maintain transparency throughout the process. Successful navigation hinges on a thorough knowledge of the interplay between scientific evidence, regulatory requirements, and ethical considerations.
Preclinical Risk Assessment
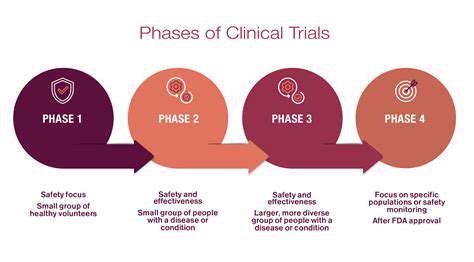
Preclinical risk assessment forms the bedrock of the entire regulatory pathway. This crucial phase involves evaluating the safety and efficacy of the gene therapy in laboratory settings, using animal models or in vitro systems. It's essential to identify potential risks related to the gene delivery method, the target gene, and the potential for off-target effects. Thorough preclinical studies are vital for informing the design of subsequent clinical trials and for demonstrating the safety profile of the therapy.
Clinical Trial Risk Assessment
Clinical trials are the cornerstone of evaluating gene therapies in humans. Rigorous risk assessment is essential throughout this phase, requiring close monitoring of patient outcomes, adverse events, and potential long-term effects. The assessment process includes careful evaluation of patient demographics, pre-existing conditions, and the specific gene therapy being tested. A proactive approach to identifying and mitigating risks is paramount for ensuring patient safety and the collection of robust clinical data.
Regulatory Submissions and Approvals
The regulatory submissions process requires a meticulous risk assessment to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of the gene therapy. This includes detailed analyses of preclinical and clinical trial data, addressing potential risks identified at each stage. The submission must clearly outline strategies for mitigating identified risks and demonstrate the overall benefit-risk profile of the therapy. A comprehensive risk assessment is crucial for gaining regulatory approval and ensuring public trust.
Post-Market Surveillance and Risk Management
Post-market surveillance is a critical component of the regulatory pathway, continuing the process of risk assessment beyond market authorization. This stage involves monitoring the long-term effects of the gene therapy in real-world use, identifying any unforeseen risks or adverse events. Continuous monitoring, data collection, and proactive risk management are crucial for adapting to new information and maintaining the safety and efficacy of the therapy over time.
Ethical Considerations in Risk Assessment
Ethical considerations are intertwined with every aspect of risk assessment in gene therapy development. This includes considerations of patient autonomy, informed consent, equitable access, and potential societal impacts. Ethical guidelines and oversight mechanisms are essential to ensure that the benefits of gene therapy are realized while mitigating potential harms. Open dialogue and transparency are crucial to address ethical concerns and build public trust.
Regulatory Frameworks and Standards Across Jurisdictions

Regulatory Frameworks and Their Impact
Regulatory frameworks play a crucial role in shaping the landscape of various industries. These frameworks establish guidelines, standards, and expectations for businesses and individuals, ensuring that operations are conducted ethically and responsibly, while also promoting consumer protection and market stability. Understanding the specific regulations and standards within a given industry is essential for successful navigation and compliance.
The complexity of regulatory frameworks can vary significantly depending on the industry and the specific jurisdiction. This complexity often necessitates dedicated resources and expertise for businesses to ensure they remain compliant with all applicable regulations. Furthermore, changes in regulatory frameworks can significantly impact business operations, requiring adaptation and adjustments to maintain compliance and profitability.
Standard Setting Organizations
Organizations like the ISO (International Organization for Standardization) and ANSI (American National Standards Institute) play a vital role in developing and maintaining industry standards. These standards provide a common language and set of expectations, facilitating interoperability and efficiency across different sectors. Clear standards contribute to the quality and reliability of products and services offered to consumers, while also promoting global trade and collaboration.
The establishment and maintenance of these standards are crucial for ensuring consistent quality and performance. They also foster trust and confidence among stakeholders, including consumers, manufacturers, and regulators. The ongoing review and refinement of standards are essential to address evolving technological advancements and industry practices.
Compliance and Enforcement
Maintaining compliance with regulatory frameworks is a critical aspect of any business operation. This involves a deep understanding of the specific regulations applicable to the business and the implementation of appropriate internal controls and procedures to ensure adherence. Failure to comply can lead to severe penalties, including financial fines, legal action, and reputational damage.
International Standards and Harmonization
International standards are increasingly important in a globalized world, facilitating trade and collaboration among countries. The harmonization of standards across different jurisdictions can reduce barriers to entry and promote fair competition. This is particularly important in industries with cross-border operations, ensuring consistency and clarity in regulations across different markets.
Impact on Businesses and Consumers
Regulatory frameworks have a multifaceted impact on both businesses and consumers. Businesses must adapt their operations to meet the requirements of these frameworks, which can involve significant investment in compliance resources and processes. Consumers benefit from the protections and standards established by these frameworks, ensuring a degree of product safety and reliability. However, regulatory burdens can sometimes increase costs, which can be passed on to consumers.
Challenges and Future Trends
The ever-evolving nature of technology and global markets presents ongoing challenges to regulatory frameworks. Staying abreast of these changes and adapting frameworks to meet emerging needs is crucial for maintaining their effectiveness and relevance. Future trends suggest a need for greater agility and flexibility in regulatory responses to address the complexities of a rapidly changing world, including emerging technologies and the need for sustainable practices.
Public Perception and Ethical Considerations in Gene Editing Regulations

Public Perception of Ethical Concerns
Public perception plays a crucial role in shaping the ethical landscape of many industries. Consumers are increasingly aware of ethical issues and are more likely to support companies that demonstrate a commitment to these values. This awareness often translates into increased scrutiny of businesses' practices and a willingness to boycott products or services perceived as unethical.
Understanding and responding to public perception of ethical concerns is essential for maintaining a positive brand image and building trust with stakeholders. A company's reputation can be severely damaged by negative perceptions, impacting sales, investor confidence, and employee morale.
Ethical Considerations in Business Operations
Businesses face a complex web of ethical considerations in their daily operations. From fair labor practices and environmental sustainability to transparency in supply chains and data privacy, maintaining ethical standards is critical for long-term success. Ethical dilemmas often arise when profit maximization conflicts with social responsibility.
Implementing robust ethical frameworks and codes of conduct can help businesses navigate these challenges and ensure that their actions align with societal values. This includes fostering a culture of ethical awareness and accountability within the organization.
Transparency and Accountability in Public Institutions
Maintaining transparency and accountability within public institutions is paramount for upholding public trust. Open communication and clear procedures are essential for demonstrating that decisions are made fairly and in the best interest of citizens. Public scrutiny is often high, and any perceived lack of transparency can lead to significant reputational damage and eroded public confidence.
Mechanisms for public feedback and oversight can play a vital role in ensuring ethical conduct and fostering a sense of shared responsibility.
Ethical Implications of Emerging Technologies
The rapid advancement of technology brings with it a host of new ethical considerations. Issues surrounding data privacy, algorithmic bias, and artificial intelligence applications necessitate careful consideration and proactive measures to mitigate potential harm. These emerging technologies often raise complex questions about human rights, societal impact, and the responsibility of developers and users alike.
Ethical Decision-Making in a Globalized World
Navigating ethical dilemmas in a globalized world requires a nuanced understanding of diverse cultural norms and values. Businesses and individuals operating internationally must be sensitive to varying ethical standards and strive to act responsibly and respectfully across different contexts. Global ethical standards and guidelines are often contested or poorly defined, making ethical decision-making particularly challenging.
The Role of Ethical Leadership
Ethical leadership is crucial for establishing a culture of integrity and accountability within organizations. Leaders who champion ethical values set a strong example for their teams and promote a positive work environment where ethical considerations are prioritized. Ethical leadership fosters trust, improves employee morale, and enhances the company's overall reputation. This includes promoting open communication, encouraging ethical dilemmas to be discussed, and holding individuals accountable for their actions.