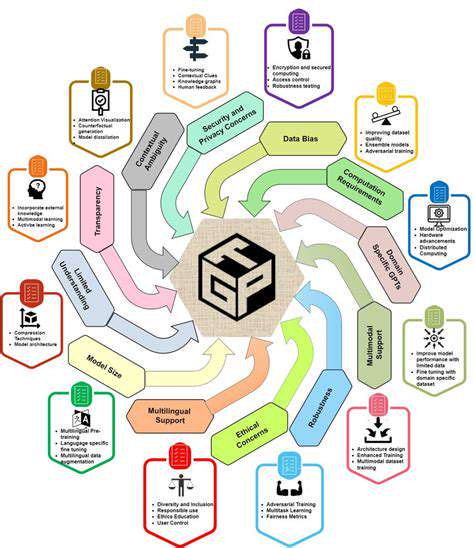
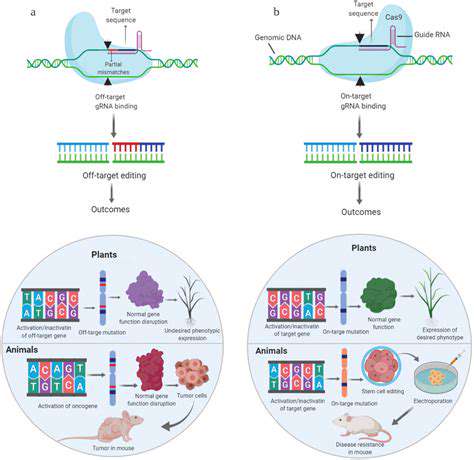
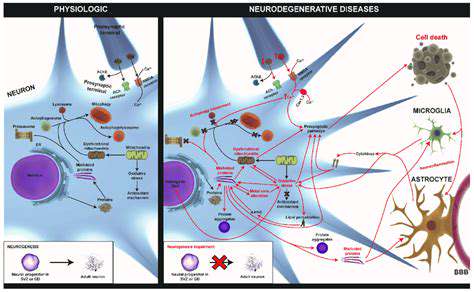
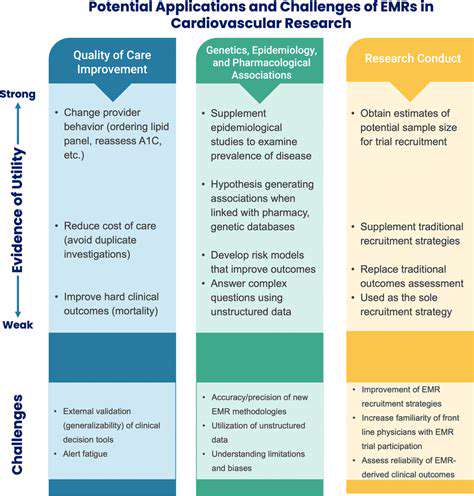
Potential Applications and Challenges
Potential Applications in Diverse Fields
The applications of this technology span a wide range of industries. From medical diagnostics to environmental monitoring, the potential impact is profound. Imagine a future where early disease detection is commonplace, or where pollution levels are automatically tracked and mitigated. This technology holds the key to unlocking significant advancements in numerous sectors.
Furthermore, its application in agriculture promises to revolutionize farming practices. Precision agriculture, utilizing real-time data, could optimize resource allocation and yield significantly. This could lead to more sustainable and efficient food production, crucial in addressing global food security challenges.
Challenges in Data Acquisition and Processing
One significant hurdle is the complexity of data acquisition. Collecting reliable and comprehensive data, especially from diverse and dynamic environments, presents a major challenge. This requires sophisticated sensor networks, robust communication protocols, and advanced data management systems.
Furthermore, processing the enormous volume of data generated by these systems is a significant computational task. Developing algorithms and infrastructure capable of handling and interpreting this data effectively is crucial for realizing the full potential of this technology. Effective data processing is essential to extract meaningful insights.
Ethical Considerations and Societal Impact
The widespread deployment of this technology raises crucial ethical questions. Privacy concerns, data security, and equitable access to the benefits of this technology must be carefully considered and addressed. A thoughtful approach to ethical implications is paramount to responsible development and implementation.
Moreover, the potential societal impact of this technology warrants careful consideration. How might it reshape industries, create new jobs, or exacerbate existing inequalities? Addressing these questions proactively is crucial for ensuring that this technology serves humanity's best interests.
Technological Advancements and Infrastructure Requirements
Continued advancements in sensor technology are essential for improving data quality and accuracy. Miniaturization, increased sensitivity, and enhanced robustness are key areas for development.
Moreover, reliable communication networks are vital for effectively transmitting data from remote locations. Developing robust and secure communication infrastructure is essential for the seamless operation of this technology.
Regulatory Frameworks and Standards
Establishing clear regulatory frameworks is essential to ensure the safe and responsible deployment of this technology. Standards for data security, privacy, and quality control are crucial for preventing misuse and ensuring public trust.
Moreover, international cooperation in developing and implementing these standards is necessary to address global implications and promote equitable access to the benefits of this technology. Harmonizing regulations across borders is a key component in the successful integration of this technology.
Economic Impacts and Market Potential
The economic potential of this technology is significant, opening new avenues for investment and job creation. The development and implementation of this technology could stimulate innovation across various sectors and lead to new market opportunities.
The potential for significant returns on investment, combined with the creation of new industries and jobs, makes this technology an attractive prospect for businesses and investors. This technology could create substantial economic benefits and opportunities.