Introduction to the Growing Importance of Sustainable Practices
Sustainable practices are no longer a niche concept confined to environmental circles; they are rapidly becoming a critical component of successful businesses and impactful initiatives worldwide. The demand for environmentally conscious and socially responsible solutions is on the rise, driving a fundamental shift in how we approach production, consumption, and resource management. This shift is not just about protecting the planet; it's about building a more resilient and equitable future for all.
The growing awareness of environmental issues, coupled with increasing consumer pressure for ethical products and services, has placed sustainability at the forefront of many industries. Companies that embrace sustainable practices are often better positioned to attract and retain talent, as well as build stronger relationships with customers who value ethical and responsible business practices.
The Economic Benefits of Sustainable Practices
Beyond the obvious environmental advantages, embracing sustainable practices can yield substantial economic benefits. Implementing energy-efficient technologies, for example, can lead to significant cost savings in utility bills over time, while reducing reliance on finite resources can lower production costs and enhance resilience to fluctuating market prices. This is particularly significant for businesses operating in industries with high energy consumption.
Sustainable practices often involve innovative solutions that drive innovation and create new market opportunities. For example, the development of renewable energy technologies has spurred the growth of a significant sector and created numerous high-skilled jobs. Furthermore, companies that prioritize sustainability often find themselves with a distinct competitive advantage, attracting environmentally conscious consumers and investors who are increasingly seeking such companies.
The Social Impact of Sustainable Practices
Sustainable practices have a profound impact on social well-being. By prioritizing fair labor practices and ethical sourcing, companies can contribute to a more equitable distribution of resources and opportunities. This includes supporting local communities, promoting fair wages, and ensuring safe working conditions for all employees. A commitment to sustainable practices can create a more just and inclusive society, addressing some of the most critical social issues of our time.
Sustainable practices also play a vital role in addressing issues like poverty and inequality. By investing in communities and promoting sustainable livelihoods, businesses can help to empower people and create positive change on a local and global scale. This social impact goes hand-in-hand with environmental stewardship and creates a more positive and prosperous future for all.
The Future of Sustainability in Business
The future of business is inextricably linked to sustainability. As the global population continues to grow, and the pressure on resources intensifies, the need for sustainable solutions will only become more critical. Companies that fail to adapt to these evolving demands will likely face significant challenges in the long term. Embracing sustainability is no longer a choice but a necessity for long-term success in the modern business landscape.
Integrating sustainability into core business strategies is no longer a trend, but a fundamental requirement for companies seeking to thrive in the years ahead. Investing in sustainable solutions, from renewable energy to ethical sourcing, will not only benefit the environment and society but also drive innovation, create value, and enhance a company's reputation and bottom line.
Global Regulatory Approaches to Gene Editing
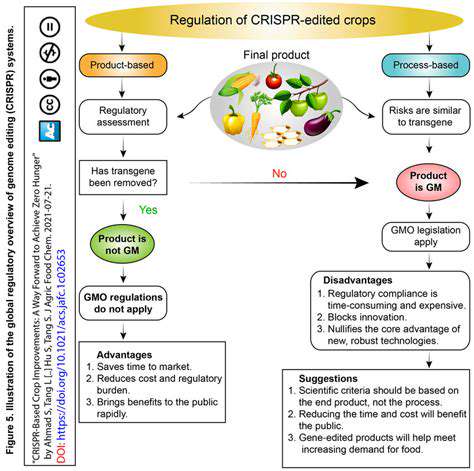
Harmonization of International Standards
One of the primary goals in global regulatory approaches is to establish harmonized standards that facilitate international cooperation. Harmonization reduces technical barriers to trade and ensures that safety and quality standards are consistent across borders. This involves collaboration among various regulatory agencies, industry stakeholders, and international organizations like the World Trade Organization (WTO) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). By aligning regulations, companies can streamline their processes and reduce compliance costs, ultimately benefiting consumers worldwide.
However, achieving complete harmonization is complex due to differing national priorities, economic considerations, and technological capabilities. Countries may adapt international standards to suit local contexts, which can sometimes lead to discrepancies. Nonetheless, ongoing dialogue and joint initiatives are crucial for narrowing these gaps and fostering a cohesive global regulatory environment.
National Regulatory Frameworks and Their Variability
Each country develops its own regulatory framework based on its unique economic, cultural, and political context. These frameworks often reflect local risk perceptions, legal systems, and public health priorities. For example, some nations may adopt strict safety standards, while others might lean toward more flexible regulations to promote innovation.
This variability can pose challenges for multinational companies aiming to comply with multiple jurisdictions simultaneously. They need to stay updated with diverse requirements, which may involve significant resources and expertise. Additionally, regulatory changes within countries can impact market access and delay product launches, emphasizing the importance of understanding local regulatory landscapes.
Role of International Organizations in Shaping Policies
International organizations play a vital role in guiding regulatory approaches by developing frameworks, providing technical assistance, and fostering dialogue among member states. The World Health Organization (WHO), for example, offers guidance on health-related standards, while the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) collaborates with counterparts worldwide to align safety protocols.
These organizations help promote best practices and facilitate mutual recognition agreements, which can expedite approval processes for new products. Their efforts support a more efficient global regulatory system that balances innovation, safety, and public health concerns. Active participation in such organizations is essential for countries seeking to enhance their regulatory capabilities and align with international norms.
Emerging Trends and Future Directions in Global Regulation
The landscape of global regulation is continuously evolving, driven by technological advancements, globalization, and increasing consumer awareness. Trends such as digital health, personalized medicine, and artificial intelligence are prompting regulators to adapt existing frameworks and develop new guidelines.
Future regulatory approaches are likely to emphasize flexibility, real-time monitoring, and adaptive standards that can keep pace with rapid innovation. Additionally, increased international cooperation and data sharing are expected to play a critical role in addressing cross-border challenges. Policymakers must stay proactive in shaping regulations that safeguard public interests while fostering technological progress.
Key Regulatory Challenges in Gene Editing Oversight
Complexity of Scientific Innovation and Regulatory Adaptation
The rapid advancement of gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR-Cas9, has outpaced the development of comprehensive regulatory frameworks. Regulators often struggle to keep pace with Scientific Innovations, which evolve faster than existing laws can adapt. This discrepancy creates a gap that could potentially allow for unregulated or poorly regulated applications, raising concerns about safety, ethics, and public trust. Ensuring that regulatory bodies have the capacity to understand and evaluate cutting-edge science is essential for effective oversight and responsible innovation.
Ethical Dilemmas and Public Engagement
Gene editing raises profound ethical questions, particularly regarding human germline modifications and potential unintended consequences. Regulators must balance scientific progress with societal values, which can vary significantly across cultures and jurisdictions. Engaging the public in meaningful discussions and establishing transparent decision-making processes are crucial steps toward building consensus and trust. Additionally, developing clear guidelines that address ethical considerations helps prevent misuse and ensures that gene editing applications align with societal norms.
International Coordination and Regulatory Harmonization
The global nature of gene editing research and applications presents significant challenges for regulatory oversight. Different countries have varying laws, standards, and enforcement mechanisms, which can lead to regulatory arbitrage or inconsistent safety protocols. Achieving international coordination and harmonization of regulations is vital for preventing unethical practices and ensuring a cohesive approach to oversight. Collaborative efforts among nations can facilitate information sharing, establish unified standards, and promote responsible development of gene editing technologies worldwide.
Adopting Zero Trust means embracing a holistic approach that emphasizes rigorous access controls, continuous monitoring, and precise data segmentation. These measures ensure data protection regardless of access origin, making security practices compatible with modern cloud infrastructures and remote work scenarios.
Best Practices for Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
Implementing a Robust Compliance Management System
A comprehensive compliance management system is essential for organizations to effectively monitor and adhere to applicable laws and regulations. Such a system should include clear policies, procedures, and controls that are regularly updated to reflect new regulatory requirements. By establishing a centralized platform for compliance documentation, organizations can streamline audits, track compliance activities, and promptly address any gaps or violations. Investing in compliance software tools can automate routine tasks, reduce human error, and provide real-time reporting, thereby enhancing overall compliance effectiveness.
Furthermore, a robust system fosters a culture of accountability within the organization. Training employees on compliance policies and emphasizing their importance helps embed compliance into daily operations. Regular internal audits and risk assessments are vital to identify potential areas of non-compliance before they escalate into legal issues. Ensuring that compliance management is integrated with corporate governance structures also promotes transparency and demonstrates a proactive approach to regulatory adherence, which can be advantageous during regulatory inspections or audits.
Continuous Employee Training and Awareness Programs
One of the most effective ways to maintain regulatory compliance is through ongoing employee training initiatives. These programs should be tailored to the specific regulatory landscape relevant to the organization's industry and geographic location. Regular training sessions ensure that staff stay informed about recent regulatory changes and understand their responsibilities in maintaining compliance. Engaging training methods, such as interactive workshops and e-learning modules, can improve knowledge retention and encourage active participation.
In addition to formal training, organizations should promote a culture of compliance by encouraging open communication about regulatory concerns and ethical practices. Creating easily accessible resources, such as compliance manuals and FAQs, helps employees quickly find answers to common questions. Recognizing and rewarding compliance adherence can also motivate staff to prioritize regulatory requirements, ultimately reducing the risk of violations and associated penalties.
Maintaining Transparent and Up-to-Date Documentation
Accurate and current documentation is a cornerstone of regulatory compliance. Organizations should maintain detailed records of all compliance-related activities, including policies, procedures, training records, audit reports, and incident reports. These documents serve as evidence during audits and inspections, demonstrating the organization's commitment to meeting legal obligations. Regular reviews and updates of documentation ensure that they reflect current regulations and organizational practices.
Transparency in record-keeping not only facilitates compliance audits but also builds trust with regulators, clients, and stakeholders. Implementing secure digital storage solutions can improve document management, allowing easy retrieval and sharing of information when needed. Additionally, establishing clear protocols for document control and versioning helps prevent outdated or incorrect information from being used, thereby minimizing compliance risks and supporting ongoing adherence to regulatory standards.
The Future of Gene Editing Regulation

Advancements in Gene Editing Technologies
Recent developments in gene editing, particularly with tools like CRISPR-Cas9, have revolutionized the field of genetics by enabling precise modifications to DNA sequences. These advancements have made it possible to target specific genetic mutations associated with various diseases, paving the way for personalized medicine. As technology continues to evolve, the accuracy and efficiency of gene editing are expected to improve significantly, reducing off-target effects and increasing safety.
Moreover, researchers are exploring novel gene editing techniques, such as base editing and prime editing, which allow for even more precise alterations without creating double-strand breaks in DNA. These innovations could open up new therapeutic possibilities that were previously unattainable, expanding the scope of what gene editing can achieve in both clinical and agricultural settings.
Ethical and Regulatory Challenges
The rapid progression of gene editing technologies raises critical ethical questions regarding their application, especially concerning human germline modifications. There is ongoing debate about the morality of editing embryos or reproductive cells, which could have lasting impacts on future generations. Regulatory Frameworks around the world are struggling to keep pace with technological advancements, creating a landscape of inconsistent policies and oversight. Establishing clear guidelines and international cooperation is essential to ensure responsible development and use of gene editing tools.
Balancing innovation with caution involves addressing concerns about consent, potential misuse, and ecological impacts. Public engagement and transparent dialogue between scientists, policymakers, and society are crucial in shaping regulations that protect ethical standards while fostering scientific progress.
The Impact on Healthcare and Agriculture
Gene editing holds enormous potential to transform healthcare by enabling the development of targeted therapies for genetic disorders, cancers, and infectious diseases. As regulatory landscapes mature, we can expect increased clinical trials and eventual approval of gene-based treatments that could dramatically improve patient outcomes. In agriculture, gene editing is being used to create crops that are more resistant to pests, diseases, and environmental stresses, which could contribute to global food security. The future of gene editing regulation will play a pivotal role in determining how quickly and safely these innovations reach the market.
However, widespread adoption depends on establishing robust safety standards and public trust. Effective regulation can help prevent misuse and ensure that benefits are accessible while minimizing risks associated with genetic modifications in both humans and the environment.